|
Chełmno Land
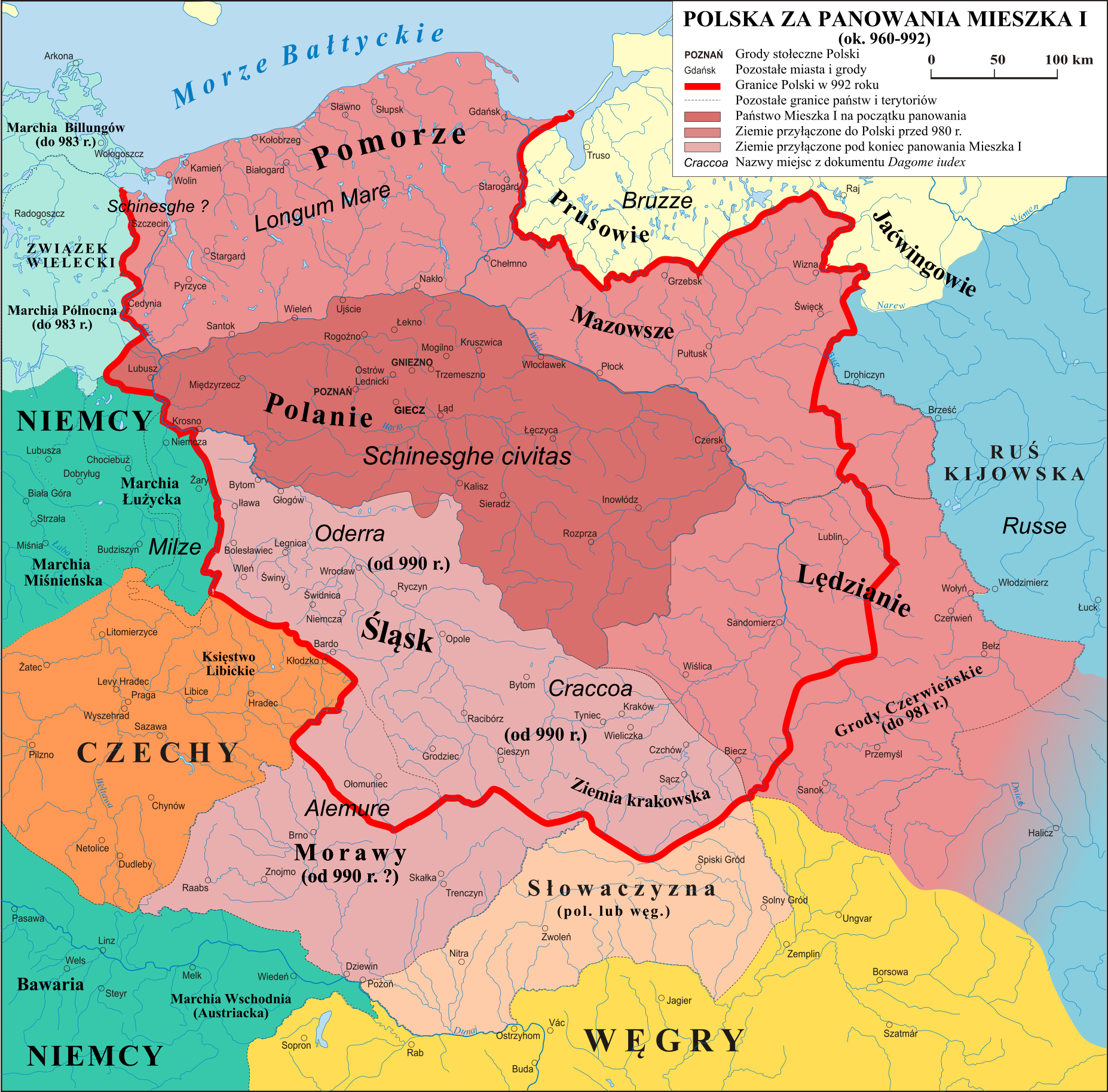
Chełmno land ( pl, ziemia chełmińska, or Kulmerland, Old Prussian: ''Kulma'', lt, Kulmo žemė) is a part of the historical region of Pomerelia, located in central-northern Poland. Chełmno land is named after the city of Chełmno (historically also known as Culm). The largest city in the region is Toruń; another bigger city is Grudziądz. It is located on the right bank of the Vistula river, from the mouth of the Drwęca (southern boundary) to the Osa (northern). Its eastern frontier is Lubawa Land. The region, depending on the period and interpretation, may be included in other larger regions: Mazovia, Pomerania or Prussia. Currently in Poland it is classified as part of Pomerania, due to strong connections with Gdańsk Pomerania in recent centuries, with which it is collectively called the Vistula Pomerania (''Pomorze Nadwiślańskie''), although it also has close ties with neighboring Kuyavia. As a result it forms part of the Kuyavian-Pomeranian Voivodship, althoug ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Historical Region
Historical regions (or historical areas) are geographical regions which at some point in time had a cultural, ethnic An ethnic group or an ethnicity is a grouping of people who identify with each other on the basis of shared attributes that distinguish them from other groups. Those attributes can include common sets of traditions, ancestry, language, history, ..., linguistics, linguistic or politics, political basis, regardless of latterday borders. They are used as delimitations for studying and analysing social development of List of time periods, period-specific cultures without any reference to contemporary political, economic or social organisations. The fundamental principle underlying this view is that older political and mental structures exist which exercise greater influence on the spatial-social identity of individuals than is understood by the contemporary world, bound to and often blinded by its own worldview - e.g. the focus on the nation-state. Definitions of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kuyavia
Kuyavia ( pl, Kujawy; german: Kujawien; la, Cuiavia), also referred to as Cuyavia, is a historical region in north-central Poland, situated on the left bank of Vistula, as well as east from Noteć River and Lake Gopło. It is divided into three traditional parts: north-western (with the capital in Bydgoszcz, ethnographically regarded often as non-Kuyavian), central (the capital in Inowrocław or Kruszwica), and south-eastern (the capital in Włocławek or Brześć Kujawski). Etymology The name Kuyavia first appeared in written sources in the 1136 Bull of Gniezno ( pl, Bulla Gnieźnieńska, Latin: ''Ex commisso nobis'') issued by Pope Innocent II, and was then mentioned in many documents from medieval times. It is also mentioned in the chronicles of Wincenty Kadłubek. Geography In the north, Kuyavia borders with the historic regions of Gdańsk Pomerania (Pomerelia) and Chełmno Land, in the west with proper (exact) Greater Poland, in the south with Łęczyca Land and in the east ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Christianised
Christianization ( or Christianisation) is to make Christian; to imbue with Christian principles; to become Christian. It can apply to the conversion of an individual, a practice, a place or a whole society. It began in the Roman Empire, continued through the Middle Ages in Europe, and in the twenty-first century has spread around the globe. Historically, there are four stages of Christianization beginning with individual conversion, followed by the translation of Christian texts into local vernacular language, establishing education and building schools, and finally, social reform that sometimes emerged naturally and sometimes included politics, government, coercion and even force through colonialism. The first countries to make Christianity their state religion were Armenia, Georgia, Ethiopia and Eritrea. In the fourth to fifth centuries, multiple tribes of Germanic barbarians converted to either Arian or orthodox Christianity. The Frankish empire begins during this same per ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Castellany
A castellan is the title used in Medieval Europe for an appointed official, a governor of a castle and its surrounding territory referred to as the castellany. The title of ''governor'' is retained in the English prison system, as a remnant of the medieval idea of the castellan as head of the local prison. The word stems from the Latin ''Castellanus'', derived from ''castellum'' "castle". Sometimes also known as a ''constable'' of the castle district, the Constable of the Tower of London is, in fact, a form of castellan, with representative powers in the local or national assembly. A castellan was almost always male, but could occasionally be female, as when, in 1194, Beatrice of Bourbourg inherited her father's castellany of Bourbourg upon the death of her brother, Roger. Similarly, Agnes became the castellan of Harlech Castle upon the death of her husband John de Bonvillars in 1287. Initial functions After the fall of the Western Roman Empire, foreign tribes migrated into w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Masovians
Masovians, also spelled as Mazovians, and historically known as Masurians, is an ethnographic group of Polish people that originate from the region of Masovia, located mostly within borders of the Masovian Voivodeship, Poland. They speak the Masovian dialect dialect of Polish.G. Odoj, A. Peć: ''Dziedzictwo kulturowe – edukacja regionalna''. Dzierżoniów: Wydawnictwo Alex, 2000, p. 74, ISBN 83-85589-35-X, OCLC 749376082. The group originate from the Lechitic tribe of Masovians, first referenced in the historical records by Nestor the Chronicler in the 11th century. Name The name Masovian, in Polish, ''Mazowszanin'', comes from the name of the region of Masovia, in Polish known as ''Mazowsze''. The name of the region, comes from its Old Polish names ''Mazow'', and ''Mazosze'', and most likely came from word ''maz'' (ancestory word of modern ''maź'' and ''mazać''), which was used to either describe a "''muddy region''" or a "''person covered in mud''". Historically, prior t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polans (western)
The Western Polans (also known as Polanes, Polanians; , derived from Old Slavic ''pole'', "field" or "plain", from Proto-Indo-European ''*pleh₂-'' "flatland") were a West Slavic and Lechitic tribe, inhabiting the Warta River basin of the contemporary Greater Poland region starting in the 6th century. They were one of the main tribes in Central Europe and were closely related to the Vistulans, Masovians, Czechs and Slovaks. History In the 9th century, the Polans united several West Slavic (Lechitic) groups to the north of Great Moravia. The union led by the Piast dynasty developed into the Duchy of Poland, whose name derives from that of the Polans. The earliest Polan rulers mentioned by name are the legendary figures of Piast the Wheelwright and Popiel (8th–9th centuries). The first historical ruler was Mieszko I (960–992), who enlarged the territory later named Poland by incorporating Masovia and conquering Silesia and the Vistulan lands of Lesser Poland. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mogilno
Mogilno (; ) is a town in central Poland, situated in the Kuyavian-Pomeranian Voivodeship (since 1999), previously in Bydgoszcz Voivodeship (1975–1998). History Mogilno is one of the oldest settlements along the border of the Greater Poland and Kuyavia historical regions. Since the turn of the 8th and 9th century until the 10th century an early-medieval settlement existed there, at the long narrow headland surrounded by waters of Mogilno Lake from the west and south and marshes from the east. In 1065, a Benedictine abbey was founded there by Bolesław the Generous. North of the abbey a town later developed, which in 1398 was granted a city charter, and which was the abbey's property until 1773. After the first Partition of Poland in 1772 the city became a part of the Kingdom of Prussia, and in 1920 it returned to Poland. Since 1898 until his death in 1910 a parish priest in Mogilno's other church St. Jacob (Św. Jakuba) was Piotr Wawrzyniak. Massacre during Second World Wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bolesław II The Generous
Bolesław II the Bold, also known as the Generous ( pl, Bolesław II Szczodry ; ''Śmiały''; c. 1042 – 2 or 3 April 1081 or 1082), was Duke of Poland from 1058 to 1076 and third King of Poland from 1076 to 1079. He was the eldest son of Duke Casimir I the Restorer and Maria Dobroniega of Kiev. Bolesław II is considered to have been one of the most capable of the Piast rulers. In 1075 he re-established the Archdiocese of Gniezno (consecrated in 1064) and founded the Diocese of Płock. He established Benedictine monasteries in Mogilno, Lubin and Wrocław. Bolesław II was also the first Polish monarch to produce his own coinage in quantity great enough to replace the foreign coins prevalent in the country during the reigns of the first Piast kings. He established royal mints in Kraków and Wrocław and reformed the coinage, which brought considerable revenue into the royal coffers. All these efforts had an enormous influence on the economic and cultural development of the cou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lechites
Lechites (, german: Lechiten), also known as the Lechitic tribes (, german: Lechitische Stämme), is a name given to certain West Slavic tribes who inhabited modern-day Poland and eastern Germany, and were speakers of the Lechitic languages. Distinct from the Czech–Slovak subgroup, they are the closest ancestors of ethnic Poles and the Pomeranians, Lusatians and Polabians. History According to Polish legend, Mieszko I inherited the ducal throne from his father who probably ruled over two-thirds of the territory inhabited by eastern Lechite tribes. He united the Lechites east of the Oder (Polans, Masovians, Pomeranians, Vistulans, Silesians) into a single country of Poland. His son, Bolesław I the Brave, founded the bishoprics at Wrocław, Kołobrzeg, and Kraków, and an archbishopric at Gniezno. Bolesław carried out successful wars against Bohemia, Moravia, Kievan Rus' and Lusatia, and forced the western Pomeranians to pay Poland a tribute. Shortly before his death Bo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Slavs
Slavs are the largest European ethnolinguistic group. They speak the various Slavic languages, belonging to the larger Balto-Slavic branch of the Indo-European languages. Slavs are geographically distributed throughout northern Eurasia, mainly inhabiting Central and Eastern Europe, and the Balkans to the west; and Siberia to the east. A large Slavic minority is also scattered across the Baltic states and Central Asia, while a substantial Slavic diaspora is found throughout the Americas, as a result of immigration. Present-day Slavs are classified into East Slavs (chiefly Belarusians, Russians, Rusyns, and Ukrainians), West Slavs (chiefly Czechs, Kashubians, Poles, Slovaks and Sorbs) and South Slavs (chiefly Bosniaks, Bulgarians, Croats, Macedonians, Montenegrins, Serbs and Slovenes). The vast majority of Slavs are traditionally Christians. However, modern Slavic nations and ethnic groups are considerably diverse both genetically and culturally, and relations between them � ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Old Prussians
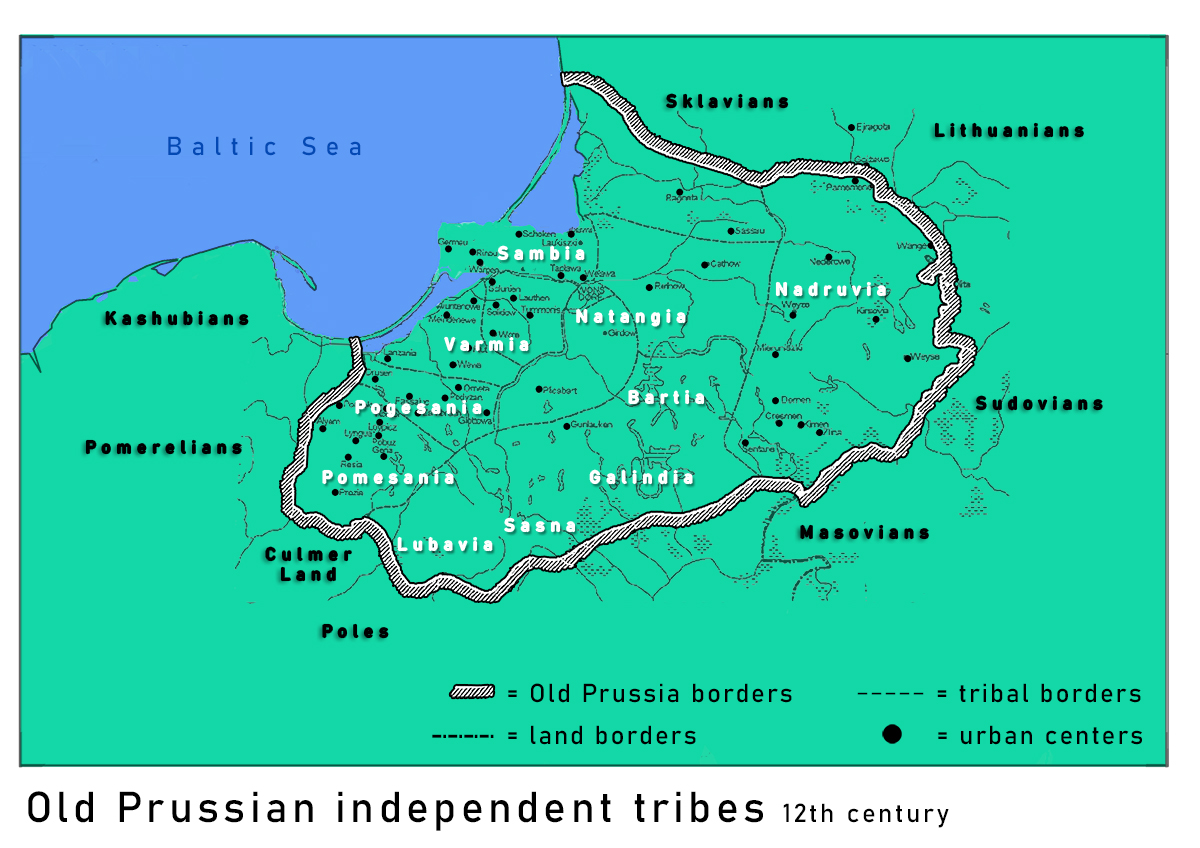
Old Prussians, Baltic Prussians or simply Prussians (Old Prussian: ''prūsai''; german: Pruzzen or ''Prußen''; la, Pruteni; lv, prūši; lt, prūsai; pl, Prusowie; csb, Prësowié) were an indigenous tribe among the Baltic peoples that inhabited the region of Prussia, at the south-eastern shore of the Baltic Sea between the Vistula Lagoon to the west and the Curonian Lagoon to the east. The Old Prussians, who spoke an Indo-European language now known as Old Prussian and worshipped pre-Christian deities, lent their name, despite very few commonalities, to the later, predominantly Low German-speaking inhabitants of the region. The duchy of the Polans under Mieszko I, which was the predecessor of the Kingdom of Poland, first attempted to conquer and baptize the Baltic tribes during the 10th century, but repeatedly encountered strong resistance. Not until the 13th century were the Old Prussians subjugated and their lands conquered by the Teutonic Order. The remaining Old Prus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |