|
Chen Mingxia
Chen Mingxia (c. 1601–1654) was Grand Secretariat and President of Ministry Personnel of the Qing dynasty. He was from Liyang in Jiangsu and was a Chinese official during the Shunzhi period (1644–1661) of the Qing dynasty (1644–1912). Before joining the Qing in early 1645, he had successively served the Ming dynasty (1368–1644) and the short-lived Shun regime of rebel leader Li Zicheng (1602–1645). He then served in the highest ranks of the Qing bureaucracy, being promoted to Grand Secretariat of the empire. Ming period A member of the reformist Restoration Society (Fushe 復社), Chen finished first in the metropolitan examination and third in the subsequent palace examination of 1643, the last such exam held by the Ming dynasty (1368–1644). Along with other graduates who showed special literary promise, he became Hanlin bachelor, and was given a concurrent post of supervising secretary in the Ministry of War. On 13 April 1644, during an audience with the Chongzh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chen (surname)
Chen () () is a common Chinese-language surname and one of the most common surnames in Asia. It is the most common surname in Taiwan (2010) and Singapore (2000). Chen is also the most common family name in Guangdong, Zhejiang, Fujian, Macau, and Hong Kong. It is the most common surname in Xiamen, the ancestral hometown of many overseas Hoklo. Chen was listed 10th in the ''Hundred Family Surnames'' poem, in the verse 馮陳褚衛 (Feng Chen Chu Wei). In Cantonese, it is usually romanized as Chan (as in Jackie Chan), most widely used by those from Hong Kong. Chan is also widely used in Macao and Malaysia. It is also sometimes spelled Chun. In many Southern Min dialects (including dialects of Hainan, Fujian, and Taiwan), the name is pronounced Tan, while in Teochew, it is pronounced Tang. In Hakka and Taishanese, the name is spelled Chin. In Wu it is pronounced Zen or Tchen. In Vietnam, this surname is written as Trần (in Quốc Ngữ) and is 2nd most common. In Thailand, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Shanhai Pass
The Battle of Shanhai Pass, fought on May 27, 1644 at Shanhai Pass at the eastern end of the Great Wall of China, Great Wall, was a decisive battle leading to the beginning of the Qing dynasty rule in China proper. There, the Qing prince-regent Dorgon allied with former Ming dynasty, Ming general Wu Sangui to defeat rebel leader Li Zicheng of the Shun dynasty, allowing Dorgon and the Qing army to rapidly conquer Beijing. Prelude Rise of the Manchus As the Ming dynasty#Decline and fall of the Ming dynasty, Ming dynasty declined, and the threat from northern enemies grew, Ming emperors saw the strategic value of Shanhai Pass and frequently garrisoned troops there, armies which sometimes reached up to 40,000 men. Under the rule of Hong Taiji (r. 1626–1643), the Qing were becoming more aggressive against the Ming. After an intermittent siege that lasted over ten years, Qing armies led by Jirgalang captured Battle of Songjin, Songshan and Jinzhou in early 1642. The garrison of Mi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shunzhi Emperor
The Shunzhi Emperor (15 March 1638 – 5 February 1661) was the second Emperor of China, emperor of the Qing dynasty of China, and the first Qing emperor to rule over China proper, reigning from 1644 to 1661. A Deliberative Council of Princes and Ministers, committee of Manchu princes chose him to succeed his father, Hong Taiji (1592–1643), in September 1643, when he was five years old. The princes also appointed two co-regents: Dorgon (1612–1650), the 14th son of the Qing dynasty's founder Nurhaci (1559–1626), and Jirgalang (1599–1655), one of Nurhaci's nephews, both of whom were members of the Aisin Gioro, Qing imperial clan. From 1643 to 1650, political power lay mostly in the hands of Dorgon. Under his leadership, the Qing Empire conquered most of the territory of the fallen Ming dynasty (1368–1644), chased Southern Ming, Ming loyalist regimes deep into the southwestern provinces, and established the basis of Qing rule over China proper despite highly unpopular ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Queue (hairstyle)
A queue or cue is a hairstyle that was worn by the Jurchen and Manchu peoples of Manchuria, and was later required to be worn by male subjects of Qing China. Hair on top of the scalp is grown long and is often braided, while the front portion of the head is shaved. The distinctive hairstyle led to its wearers being targeted during anti-Chinese riots in Australia and the United States. The requirement that Han Chinese men and others under Manchu rule give up their traditional hairstyles and wear the queue was met with resistance, although opinions about the queue did change over time. Han women were never required to wear their hair in the traditional women's Manchu style, liangbatou, although that too was a symbol of Manchu identity. In the 18th century, both soldiers and sailors of western nations wore their hair pulled back into a queue, but the fashion was abandoned at the start of the next century. Predecessors and origin The Xianbei and Wuhuan were said to shave their ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Portrait Of Jiang Shunfu
A portrait is a painting, photograph, sculpture, or other artistic representation of a person, in which the face and its expressions are predominant. The intent is to display the likeness, personality, and even the mood of the person. For this reason, in photography a portrait is generally not a snapshot, but a composed image of a person in a still position. A portrait often shows a person looking directly at the painter or photographer, in order to most successfully engage the subject with the viewer. History Prehistorical portraiture Plastered human skulls were reconstructed human skulls that were made in the ancient Levant between 9000 and 6000 BC in the Pre-Pottery Neolithic B period. They represent some of the oldest forms of art in the Middle East and demonstrate that the prehistoric population took great care in burying their ancestors below their homes. The skulls denote some of the earliest sculptural examples of portraiture in the history of art. Historical portraitur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zhu Yousong
The Hongguang Emperor (; 1607–1646), personal name Zhu Yousong (), childhood nickname Fuba (福八), was the first emperor of the Chinese Southern Ming dynasty. He reigned briefly in southern China from 1644 to 1645. His era name, ''Hongguang'', means "great light". In 1646, Zhu Yousong was captured and executed by the Qing dynasty at the Caishikou Execution Grounds. Early life Zhu Yousong was a member of Ming imperial family. He was eldest son of Zhu Changxun, and a grandson of the Wanli Emperor and Noble Consort Zheng. He followed his father to his fief at Luoyang in 1614 and later granted the title "Commandery Prince of Dechang" (德昌郡王). He was later designated as Hereditary Prince of Fu. In 1641, Li Zicheng's forces invaded Luoyang, and Zhu managed to escape but his father was killed. He held his father's princely title in two years later. In 1644, he escaped again to Weihui to seek asylum from his distant uncle, Zhu Changfang, Prince of Lu (grandson of the Longqing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nanjing
Nanjing (; , Mandarin pronunciation: ), alternately romanized as Nanking, is the capital of Jiangsu province of the People's Republic of China. It is a sub-provincial city, a megacity, and the second largest city in the East China region. The city has 11 districts, an administrative area of , and a total recorded population of 9,314,685 . Situated in the Yangtze River Delta region, Nanjing has a prominent place in Chinese history and culture, having served as the capital of various Chinese dynasties, kingdoms and republican governments dating from the 3rd century to 1949, and has thus long been a major center of culture, education, research, politics, economy, transport networks and tourism, being the home to one of the world's largest inland ports. The city is also one of the fifteen sub-provincial cities in the People's Republic of China's administrative structure, enjoying jurisdictional and economic autonomy only slightly less than that of a province. Nanjing has be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Southern Ming
The Southern Ming (), also known as the Later Ming (), officially the Great Ming (), was an imperial dynasty of China and a series of rump states of the Ming dynasty that came into existence following the Jiashen Incident of 1644. Shun forces led by Li Zicheng captured Beijing and the Chongzhen Emperor committed suicide. The Ming general Wu Sangui then opened the gates of the Shanhai Pass in the eastern section of the Great Wall to the Qing banners, in hope of using them to annihilate the Shun forces. Ming loyalists fled to Nanjing, where they enthroned Zhu Yousong as the Hongguang Emperor, marking the start of the Southern Ming. The Nanjing regime lasted until 1645, when Qing forces captured Nanjing. Zhu fled before the city fell, but was captured and executed shortly thereafter. Later figures continued to hold court in various southern Chinese cities, although the Qing considered them to be pretenders. The Nanjing regime lacked the resources to pay and supply its soldiers, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
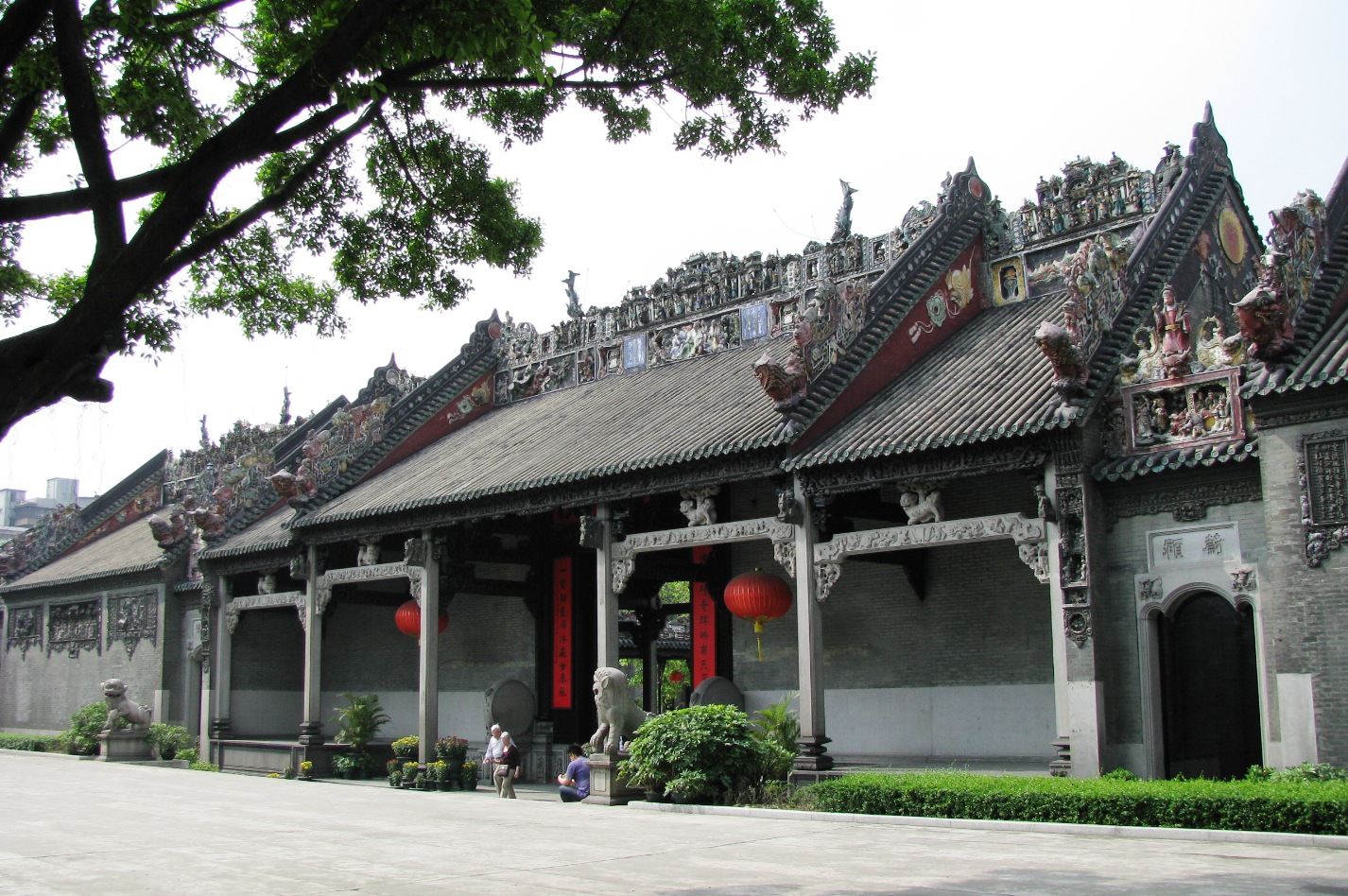
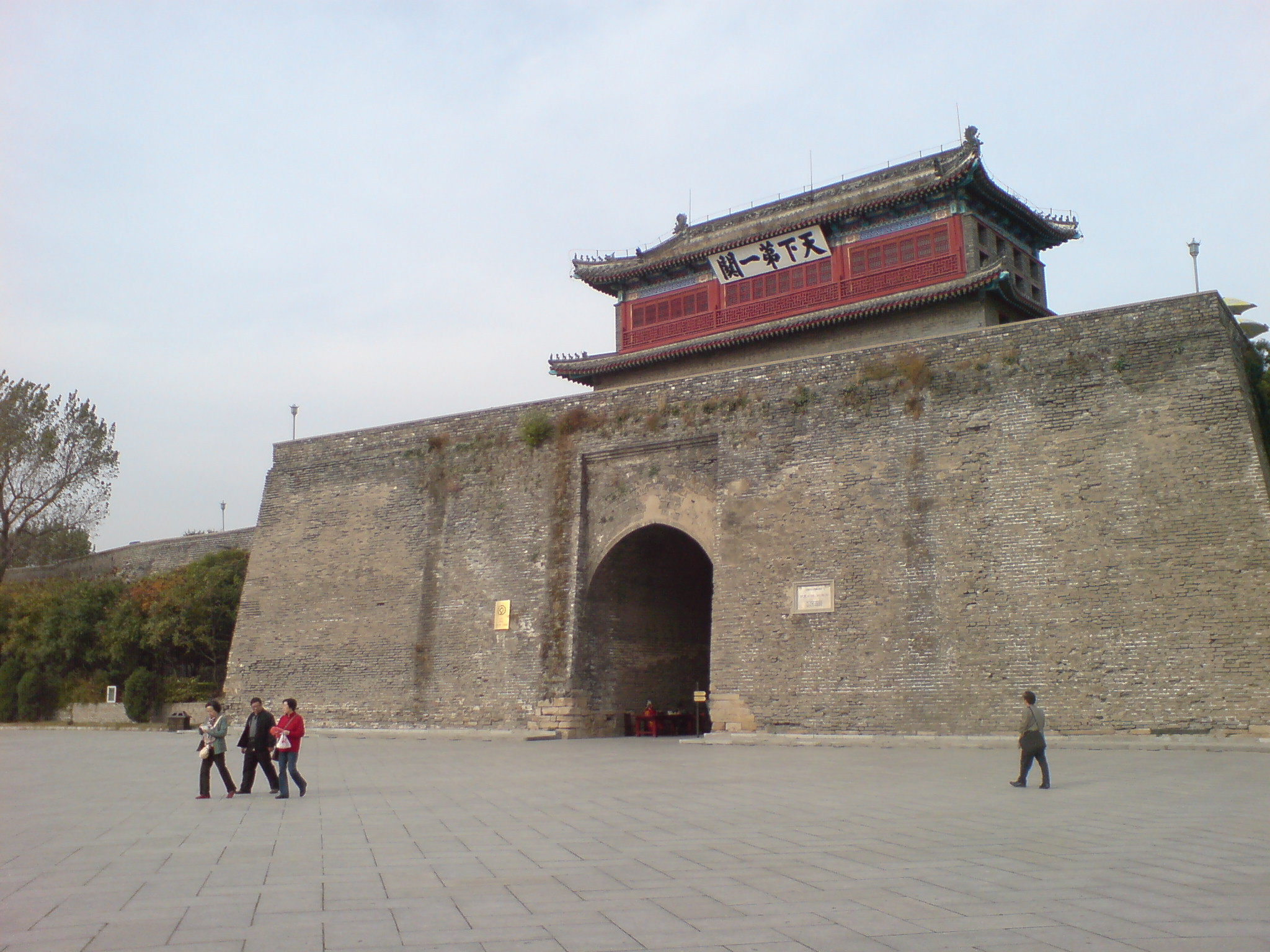
Shanhai Pass
Shanhai Pass or Shanhaiguan () is one of the major passes in the Great Wall of China, being the easternmost stronghold along the Ming Great Wall, and commands the narrowest choke point in the Liaoxi Corridor. It is located in Shanhaiguan District, Qinhuangdao, Hebei province, on the east bank of the Shi River between the Yan Mountains and the Liaodong Bay coast. In 1961, the pass was selected as the Major Historical and Cultural Site Protected at the National Level by the State Council of China, and it was listed as part of the Great Wall as a World Heritage Site by the UNESCO in 1987. The pass is a popular tourist destination at the eastern terminal point of the Ming dynasty Great Wall. The location where the wall meets the Bohai Sea is nicknamed "Old Dragon's Head" (老龙头). The pass lies nearly east of Beijing and is linked via the Jingshen Expressway that runs northeastward to Shenyang. Throughout Chinese history, the pass served as a frontline defensive outpost ag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North China Plain
The North China Plain or Huang-Huai-Hai Plain () is a large-scale downfaulted rift basin formed in the late Paleogene and Neogene and then modified by the deposits of the Yellow River. It is the largest alluvial plain of China. The plain is bordered to the north by the Yanshan Mountains, to the west by the Taihang Mountains, to the south by the Dabie Mountains, and to the east by the Yellow Sea and Bohai Sea. The Yellow River flows through the plain, before its waters empty into the Bohai Sea. The part of the North China Plain around the banks of the middle and lower Yellow River is commonly referred to as the Central Plain (). This portion of the North China Plain formed the cradle of Chinese civilization, and is the region from which the Han Chinese people emerged. Beijing, the capital of China, is located on the northeast edge of the plain, with Tianjin, an important industrial city and commercial port, near its northeast coast. Jinan (the capital of Shandong province) and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Military Of The Qing Dynasty
The Qing dynasty (1636–1912) was established by conquest and maintained by armed force. The founding emperors personally organized and led the armies, and the continued cultural and political legitimacy of the dynasty depended on the ability to defend the country from invasion and expand its territory. Therefore, military institutions, leadership, and finance were fundamental to the dynasty's initial success and ultimate decay. The early military system centered on the Eight Banners, a hybrid institution that also played social, economic, and political roles. The Banner system was developed on an informal basis as early as 1601, and formally established in 1615 by Jurchen leader Nurhaci (1559–1626), the retrospectively recognized founder of the Qing. His son Hong Taiji (1592–1643), who renamed the Jurchens "Manchus," created eight Mongol banners to mirror the Manchu ones and eight "Han-martial" () banners manned by Chinese who surrendered to the Qing before the full-fledged ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |