|
Chen Guanrong
Guanrong Chen () or Ron Chen is a Chinese mathematician who made contributions to Chaos theory. He has been the chair professor and the founding director of the Centre for Chaos and Complex Networks at the City University of Hong Kong since 2000. Prior to that, he was a tenured full professor at the University of Houston, Texas. Chen was elected Member of the Academy of Europe in 2014, elected Fellow of The World Academy of Sciences in 2015, and elected IEEE Fellow in 1997. He is currently the editor-in-chief for the International Journal of Bifurcation and Chaos. He is known for his contributions to Chaos theory and Bifurcation theory, including the Chen attractor,http://www.ee.cityu.edu.hk/~gchen/pdf/Lorenz-Chen.pdf a kind of dynamical system attractor named after him (see Multiscroll attractor). Early life In 1948, Chen Guanrong was born in Guangzhou, China. In 1978, he enrolled in the Guangzhou Sun Yat-sen University. In 1981 he graduated with a master's degree in computat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guangzhou
Guangzhou (, ; ; or ; ), also known as Canton () and alternatively romanized as Kwongchow or Kwangchow, is the capital and largest city of Guangdong province in southern China. Located on the Pearl River about north-northwest of Hong Kong and north of Macau, Guangzhou has a history of over 2,200 years and was a major terminus of the maritime Silk Road; it continues to serve as a major port and transportation hub as well as being one of China's three largest cities. For a long time, the only Chinese port accessible to most foreign traders, Guangzhou was captured by the British during the First Opium War. No longer enjoying a monopoly after the war, it lost trade to other ports such as Hong Kong and Shanghai, but continued to serve as a major transshipment port. Due to a high urban population and large volumes of port traffic, Guangzhou is classified as a Large-Port Megacity, the largest type of port-city in the world. Due to worldwide travel restrictions at the beginni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The World Academy Of Sciences
The World Academy of Sciences (TWAS) is a merit-based science academy established for developing countries, uniting 1,000 scientists in some 70 countries. Its principal aim is to promote scientific capacity and excellence for sustainable development in developing countries. It was formerly known as the ''Third World Academy of Sciences''. Its headquarters is located on the premises of the Abdus Salam International Centre for Theoretical Physics (ICTP) in Trieste, Italy. History TWAS was founded in 1983 under the leadership of the Nobel Laureate Abdus Salam of Pakistan by a group of distinguished scientists who were determined to do something about the dismal state of scientific research in developing countries. * Although developing countries account for 80% of the world's population, only 28% of the world's scientists hail from these countries. This fact reflects the lack of innovative potential necessary to solve real-life problems affecting poor nations. * A chronic lack o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IEEE 1394
IEEE 1394 is an interface standard for a serial bus for high-speed communications and isochronous real-time data transfer. It was developed in the late 1980s and early 1990s by Apple in cooperation with a number of companies, primarily Sony and Panasonic. Apple called the interface FireWire. It is also known by the brand names i.LINK (Sony), and Lynx (Texas Instruments). The copper cable used in its most common implementation can be up to long. Power and data is carried over this cable, allowing devices with moderate power requirements to operate without a separate power supply. FireWire is also available in Cat 5 and optical fiber versions. The 1394 interface is comparable to USB. USB was developed subsequently and gained much greater market share. USB requires a host controller whereas IEEE 1394 is cooperatively managed by the connected devices. History and development FireWire is Apple's name for the IEEE 1394 High Speed Serial Bus. Its development was initiated by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Institute Of Electrical And Electronics Engineers
The Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) is a 501(c)(3) professional association for electronic engineering and electrical engineering (and associated disciplines) with its corporate office in New York City and its operations center in Piscataway, New Jersey. The mission of the IEEE is ''advancing technology for the benefit of humanity''. The IEEE was formed from the amalgamation of the American Institute of Electrical Engineers and the Institute of Radio Engineers in 1963. Due to its expansion of scope into so many related fields, it is simply referred to by the letters I-E-E-E (pronounced I-triple-E), except on legal business documents. , it is the world's largest association of technical professionals with more than 423,000 members in over 160 countries around the world. Its objectives are the educational and technical advancement of electrical and electronic engineering, telecommunications, computer engineering and similar disciplines. History Origins ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Complex Systems
A complex system is a system composed of many components which may interact with each other. Examples of complex systems are Earth's global climate, organisms, the human brain, infrastructure such as power grid, transportation or communication systems, complex software and electronic systems, social and economic organizations (like cities), an ecosystem, a living cell, and ultimately the entire universe. Complex systems are systems whose behavior is intrinsically difficult to model due to the dependencies, competitions, relationships, or other types of interactions between their parts or between a given system and its environment. Systems that are "complex" have distinct properties that arise from these relationships, such as nonlinearity, emergence, spontaneous order, adaptation, and feedback loops, among others. Because such systems appear in a wide variety of fields, the commonalities among them have become the topic of their independent area of research. In many cases, it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nonlinear Dynamics
In mathematics and science, a nonlinear system is a system in which the change of the output is not proportional to the change of the input. Nonlinear problems are of interest to engineers, biologists, physicists, mathematicians, and many other scientists because most systems are inherently nonlinear in nature. Nonlinear dynamical systems, describing changes in variables over time, may appear chaotic, unpredictable, or counterintuitive, contrasting with much simpler linear systems. Typically, the behavior of a nonlinear system is described in mathematics by a nonlinear system of equations, which is a set of simultaneous equations in which the unknowns (or the unknown functions in the case of differential equations) appear as variables of a polynomial of degree higher than one or in the argument of a function which is not a polynomial of degree one. In other words, in a nonlinear system of equations, the equation(s) to be solved cannot be written as a linear combination of the un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Control Of Chaos
In lab experiments that study chaos theory, approaches designed to control chaos are based on certain observed system behaviors. Any chaotic attractor contains an infinite number of unstable, periodic orbits. Chaotic dynamics, then, consists of a motion where the system state moves in the neighborhood of one of these orbits for a while, then falls close to a different unstable, periodic orbit where it remains for a limited time and so forth. This results in a complicated and unpredictable wandering over longer periods of time. Control of chaos is the stabilization, by means of small system perturbations, of one of these unstable periodic orbits. The result is to render an otherwise chaotic motion more stable and predictable, which is often an advantage. The perturbation must be tiny compared to the overall size of the attractor of the system to avoid significant modification of the system's natural dynamics. Several techniques have been devised for chaos control, but most are de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tenured Professor
Tenure is a category of academic appointment existing in some countries. A tenured post is an indefinite academic appointment that can be terminated only for cause or under extraordinary circumstances, such as financial exigency or program discontinuation. Tenure is a means of defending the principle of academic freedom, which holds that it is beneficial for society in the long run if scholars are free to hold and examine a variety of views. By country United States and Canada Under the tenure systems adopted by many universities and colleges in the United States and Canada, some faculty positions have tenure and some do not. Typical systems (such as the widely adopted "1940 Statement of Principles on Academic Freedom and Tenure" of the American Association of University Professors) allow only a limited period to establish a record of published research, ability to attract grant funding, academic visibility, teaching excellence, and administrative or community service. They ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computational Mathematics
Computational mathematics is an area of mathematics devoted to the interaction between mathematics and computer computation.National Science Foundation, Division of Mathematical ScienceProgram description PD 06-888 Computational Mathematics 2006. Retrieved April 2007. A large part of computational mathematics consists roughly of using mathematics for allowing and improving computer computation in areas of science and engineering where mathematics are useful. This involves in particular algorithm design, computational complexity, numerical methods and computer algebra. Computational mathematics refers also to the use of computers for mathematics itself. This includes mathematical experimentation for establishing conjectures (particularly in number theory), the use of computers for proving theorems (for example the four color theorem), and the design and use of proof assistants. Areas of computational mathematics Computational mathematics emerged as a distinct part of applied ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
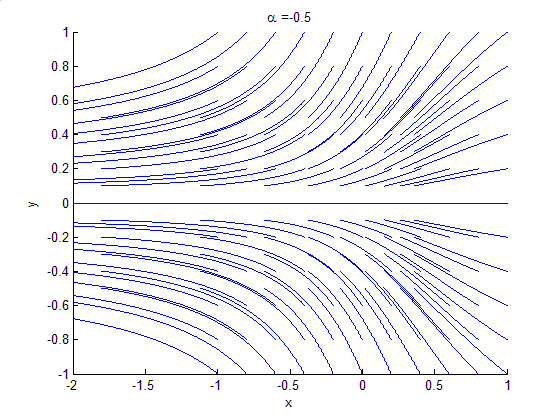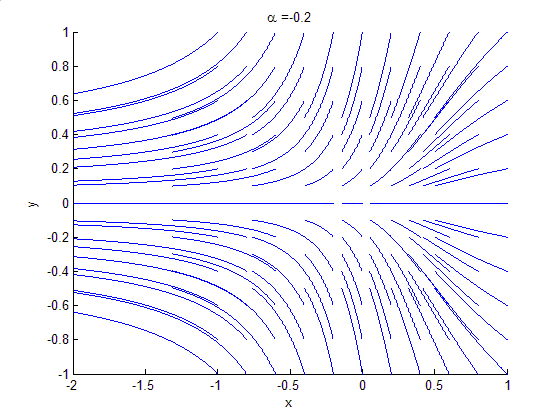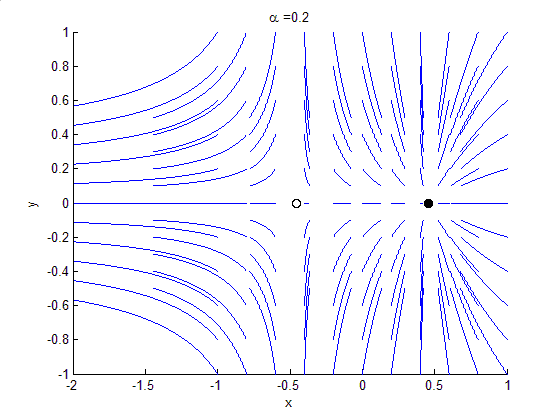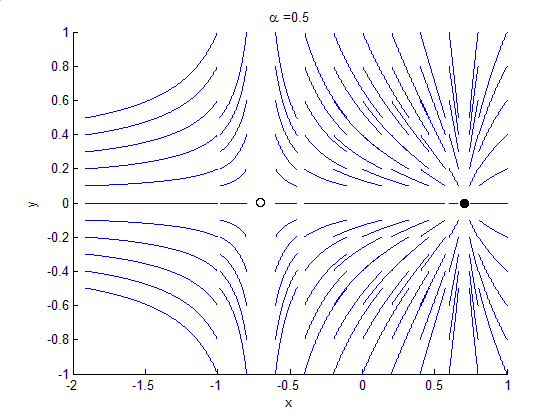
Attractor
In the mathematical field of dynamical systems, an attractor is a set of states toward which a system tends to evolve, for a wide variety of starting conditions of the system. System values that get close enough to the attractor values remain close even if slightly disturbed. In finite-dimensional systems, the evolving variable may be represented algebraically as an ''n''-dimensional vector. The attractor is a region in ''n''-dimensional space. In physical systems, the ''n'' dimensions may be, for example, two or three positional coordinates for each of one or more physical entities; in economic systems, they may be separate variables such as the inflation rate and the unemployment rate. If the evolving variable is two- or three-dimensional, the attractor of the dynamic process can be represented geometrically in two or three dimensions, (as for example in the three-dimensional case depicted to the right). An attractor can be a point, a finite set of points, a curve, a manif ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bifurcation Theory
Bifurcation theory is the mathematical study of changes in the qualitative or topological structure of a given family of curves, such as the integral curves of a family of vector fields, and the solutions of a family of differential equations. Most commonly applied to the mathematical study of dynamical systems, a bifurcation occurs when a small smooth change made to the parameter values (the bifurcation parameters) of a system causes a sudden 'qualitative' or topological change in its behavior. Bifurcations occur in both continuous systems (described by ordinary, delay or partial differential equations) and discrete systems (described by maps). The name "bifurcation" was first introduced by Henri Poincaré in 1885 in the first paper in mathematics showing such a behavior. Henri Poincaré also later named various types of stationary points and classified them . Bifurcation types It is useful to divide bifurcations into two principal classes: * Local bifurcations, which can b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World Scientific
World Scientific Publishing is an academic publisher of scientific, technical, and medical books and journals headquartered in Singapore. The company was founded in 1981. It publishes about 600 books annually, along with 135 journals in various fields. In 1995, World Scientific co-founded the London-based Imperial College Press together with the Imperial College of Science, Technology and Medicine. Company structure The company head office is in Singapore. The Chairman and Editor-in-Chief is Dr Phua Kok Khoo, while the Managing Director is Doreen Liu. The company was co-founded by them in 1981. Imperial College Press In 1995 the company co-founded Imperial College Press, specializing in engineering, medicine and information technology, with Imperial College London. In 2006, World Scientific assumed full ownership of Imperial College Press, under a license granted by the university. Finally, in August 2016, ICP was fully incorporated into World Scientific under the new imprint ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |