|
Chemokinesis
Chemokinesis is chemically prompted kinesis, a motile response of unicellular prokaryotic or eukaryotic organisms to chemicals that cause the cell to make some kind of change in their migratory/swimming behaviour. Changes involve an increase or decrease of speed, alterations of amplitude or frequency of motile character, or direction of migration. However, in contrast to chemotaxis, chemokinesis has a random, non-vectorial moiety, in general. Due to the random character, techniques dedicated to evaluate chemokinesis are partly different from methods used in chemotaxis research. One of the most valuable ways to measure chemokinesis is computer-assisted (see, e.g., Image J) checker-board analysis, which provides data about migration of identical cells, whereas, in Protozoa (e.g., Tetrahymena ''Tetrahymena'', a Unicellular organism, unicellular eukaryote, is a genus of free-living ciliates. The genus Tetrahymena is the most widely studied member of its phylum. It can produce, st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemotaxis
Chemotaxis (from '' chemo-'' + ''taxis'') is the movement of an organism or entity in response to a chemical stimulus. Somatic cells, bacteria, and other single-cell or multicellular organisms direct their movements according to certain chemicals in their environment. This is important for bacteria to find food (e.g., glucose) by swimming toward the highest concentration of food molecules, or to flee from poisons (e.g., phenol). In multicellular organisms, chemotaxis is critical to early development (e.g., movement of sperm towards the egg during fertilization) and development (e.g., migration of neurons or lymphocytes) as well as in normal function and health (e.g., migration of leukocytes during injury or infection). In addition, it has been recognized that mechanisms that allow chemotaxis in animals can be subverted during cancer metastasis. The aberrant chemotaxis of leukocytes and lymphocytes also contribute to inflammatory diseases such as atherosclerosis, asthma, and arthr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eukaryotic
Eukaryotes () are organisms whose cells have a nucleus. All animals, plants, fungi, and many unicellular organisms, are Eukaryotes. They belong to the group of organisms Eukaryota or Eukarya, which is one of the three domains of life. Bacteria and Archaea (both prokaryotes) make up the other two domains. The eukaryotes are usually now regarded as having emerged in the Archaea or as a sister of the Asgard archaea. This implies that there are only two domains of life, Bacteria and Archaea, with eukaryotes incorporated among archaea. Eukaryotes represent a small minority of the number of organisms, but, due to their generally much larger size, their collective global biomass is estimated to be about equal to that of prokaryotes. Eukaryotes emerged approximately 2.3–1.8 billion years ago, during the Proterozoic eon, likely as flagellated phagotrophs. Their name comes from the Greek εὖ (''eu'', "well" or "good") and κάρυον (''karyon'', "nut" or "kernel"). Euka ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
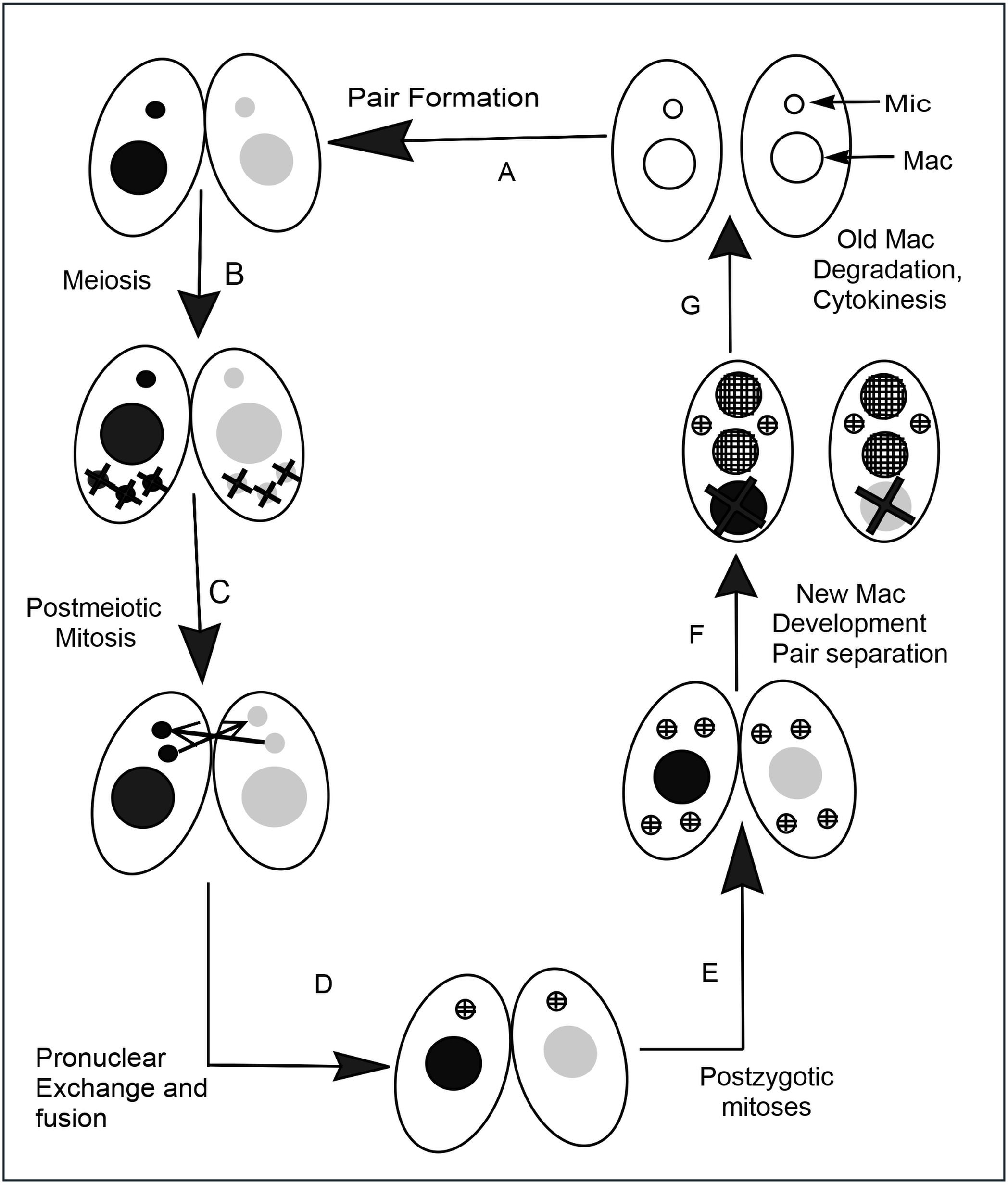
Tetrahymena
''Tetrahymena'', a Unicellular organism, unicellular eukaryote, is a genus of free-living ciliates. The genus Tetrahymena is the most widely studied member of its phylum. It can produce, store and react with different types of hormones. Tetrahymena cells can recognize both related and hostile cells. They can also switch from commensalism, commensalistic to pathogenic modes of survival. They are common in freshwater lakes, ponds, and streams. ''Tetrahymena'' species used as model organisms in biomedical research are ''T. thermophila'' and ''T. pyriformis''. ''T. thermophila'': a model organism in experimental biology As a ciliated protozoan, ''Tetrahymena thermophila'' exhibits nuclear dimorphism: two types of cell Cell nucleus, nuclei. They have a bigger, Somatic cell, non-germline macronucleus and a small, germline micronucleus in each cell at the same time and these two carry out different functions with distinct cytological and biological properties. This unique vers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemical Substance
A chemical substance is a form of matter having constant chemical composition and characteristic properties. Some references add that chemical substance cannot be separated into its constituent elements by physical separation methods, i.e., without breaking chemical bonds. Chemical substances can be simple substances (substances consisting of a single chemical element), chemical compounds, or alloys. Chemical substances are often called 'pure' to set them apart from mixtures. A common example of a chemical substance is pure water; it has the same properties and the same ratio of hydrogen to oxygen whether it is isolated from a river or made in a laboratory. Other chemical substances commonly encountered in pure form are diamond (carbon), gold, table salt (sodium chloride) and refined sugar (sucrose). However, in practice, no substance is entirely pure, and chemical purity is specified according to the intended use of the chemical. Chemical substances exist as solids, liquids, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kinesis (biology)
Kinesis, like a taxis or tropism, is a movement or activity of a cell or an organism in response to a stimulus (such as gas exposure, light intensity or ambient temperature). Unlike taxis, the response to the stimulus provided is non-directional. The animal does not move toward or away from the stimulus but moves at either a slow or fast rate depending on its "comfort zone." In this case, a fast movement (non-random) means that the animal is searching for its comfort zone while a slow movement indicates that it has found it. Types There are two main types of kineses, both resulting in aggregations. However, the stimulus does not act to attract or repel individuals. Orthokinesis: in which the speed of movement of the individual is dependent upon the stimulus intensity. For example, the locomotion of the collembola, ''Orchesella cincta'', in relation to water. With increased water saturation in the soil there is an increase in the direction of its movement towards the aimed place. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prokaryotic
A prokaryote () is a Unicellular organism, single-celled organism that lacks a cell nucleus, nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles. The word ''prokaryote'' comes from the Greek language, Greek wikt:πρό#Ancient Greek, πρό (, 'before') and wikt:κάρυον#κάρυον, κάρυον (, 'nut' or 'kernel').Campbell, N. "Biology:Concepts & Connections". Pearson Education. San Francisco: 2003. In the two-empire system arising from the work of Édouard Chatton, prokaryotes were classified within the empire Prokaryota. But in the three-domain system, based upon Molecular phylogenetics, molecular analysis, prokaryotes are divided into two domain (biology), domains: ''Bacteria'' (formerly Eubacteria) and ''Archaea'' (formerly Archaebacteria). Organisms with nuclei are placed in a third domain, Eukaryote, Eukaryota. In the Abiogenesis, study of the origins of life, prokaryotes are thought to have arisen before eukaryotes. Besides the absence of a nucleus, prokaryotes also lack mi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Image J
ImageJ is a Java-based image processing program developed at the National Institutes of Health and the Laboratory for Optical and Computational Instrumentation (LOCI, University of Wisconsin). Its first version, ImageJ 1.x, is developed in the public domain, while ImageJ2 and the related projects SciJava, ImgLib2, and SCIFIO are licensed with a permissive BSD-2 license. ImageJ was designed with an open architecture that provides extensibility via Java plugins and recordable macros. Custom acquisition, analysis and processing plugins can be developed using ImageJ's built-in editor and a Java compiler. User-written plugins make it possible to solve many image processing and analysis problems, from three-dimensional live-cell imaging to radiological image processing, multiple imaging system data comparisons to automated hematology systems. ImageJ's plugin architecture and built-in development environment has made it a popular platform for teaching image processing. ImageJ can be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
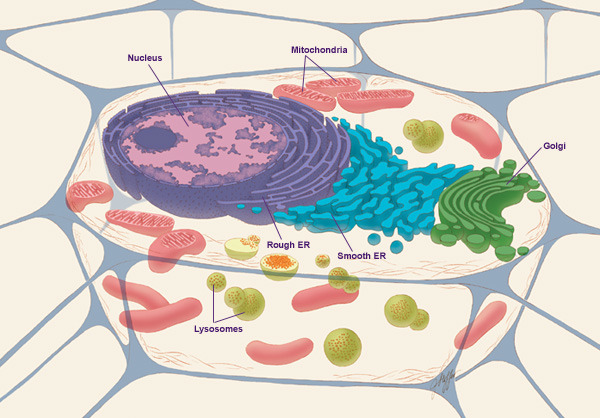
Cell Biology
Cell biology (also cellular biology or cytology) is a branch of biology that studies the structure, function, and behavior of cells. All living organisms are made of cells. A cell is the basic unit of life that is responsible for the living and functioning of organisms. Cell biology is the study of structural and functional units of cells. Cell biology encompasses both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells and has many subtopics which may include the study of cell metabolism, cell communication, cell cycle, biochemistry, and cell composition. The study of cells is performed using several microscopy techniques, cell culture, and cell fractionation. These have allowed for and are currently being used for discoveries and research pertaining to how cells function, ultimately giving insight into understanding larger organisms. Knowing the components of cells and how cells work is fundamental to all biological sciences while also being essential for research in biomedical fields such as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Perception
Perception () is the organization, identification, and interpretation of sensory information in order to represent and understand the presented information or environment. All perception involves signals that go through the nervous system, which in turn result from physical or chemical stimulation of the sensory system.Goldstein (2009) pp. 5–7 Vision involves light striking the retina of the eye; smell is mediated by odor molecules; and hearing involves pressure waves. Perception is not only the passive receipt of these signals, but it is also shaped by the recipient's learning, memory, expectation, and attention. Gregory, Richard. "Perception" in Gregory, Zangwill (1987) pp. 598–601. Sensory input is a process that transforms this low-level information to higher-level information (e.g., extracts shapes for object recognition). The process that follows connects a person's concepts and expectations (or knowledge), restorative and selective mechanisms (such as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |