|
Charles Geach
Charles Geach (1808 – 1 November 1854) was a prominent English businessman, industrialist, banker and politician of the early to mid-19th century, strongly associated with banking and manufacturing interests. He was a co-founder and the general first manager of the Midland Bank, the first treasurer of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, a prominent investor in several major engineering businesses, and MP for Coventry from 1851 to his premature death, aged 46, in 1854. Banking career Geach was born in St Austell, Cornwall, and through family connections in Penryn secured a junior position at the Bank of England. A diligent employee, he was selected to establish a branch of the bank in Birmingham in 1826. He became well-known and trusted in the city, helping establish two new banks, but despite his efforts to establish the first, the Town and District Bank, founded on 1 July 1836, he was not appointed manager. Almost simultaneously, however, when local businessmen believed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Midland Bank
Midland Bank Plc was one of the Big Four banking groups in the United Kingdom for most of the 20th century. It is now part of HSBC. The bank was founded as the Birmingham and Midland Bank in Union Street, Birmingham, England in August 1836. It expanded in the Midlands, absorbing many local banks, and merged with the Central Bank of London Ltd. in 1891, becoming the London City and Midland Bank. After a period of nationwide expansion, including the acquisition of many smaller banks, the name Midland Bank Ltd was adopted in 1923. By 1934, it was the largest deposit bank in the world. It was listed on the London Stock Exchange, and was once a constituent of the FTSE 100 Index, but in June 1992, it was taken over by HSBC Holdings plc, which phased out the Midland Bank name by June 1999 in favour of HSBC Bank. On 10 June 2015, HSBC announced that it would be rebranding its branches in the United Kingdom. HSBC chairman Douglas Flint described the Midland brand as "odds on favour ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shrewsbury And Birmingham Railway
The Shrewsbury and Birmingham Railway was authorised in 1846. It agreed to joint construction with others of the costly Wolverhampton to Birmingham section, the so-called Stour Valley Line. This work was dominated by the hostile London and North Western Railway, which used underhand and coercive tactics. The section between Shrewsbury and Wellington was also built jointly, in this case with the Shropshire Union Railway. The S&BR opened from Shrewsbury to its own Wolverhampton terminus in 1849. The Stour Valley Line was still delayed by the LNWR, but the S&BR eventually got access to it in 1852. By this time it was obvious that the LNWR was an impossible partner, and the S&BR allied itself to the Great Western Railway, which reached Wolverhampton in 1854. The S&BR merged with the GWR in 1854. With the S&BR and other absorbed railways, the GWR obtained a through route between London and the River Mersey at Birkenhead, and to Manchester and Liverpool by the use of running powers. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chad Valley, Birmingham
Chad Valley is a small area of Birmingham, England, located between Harborne and Edgbaston. It contains a fish pond and the Chad Vale Primary School. It takes its name from the Chad Brook, a tributary of the River Rea The River Rea (pronounced "ray") is a small river which passes through Birmingham, England. It is the river on which Birmingham was founded by the Beorma tribe in the 7th century. Since 2012, TA Media had obtained the rights and access to the ... and in turn gave it to the Chad Valley toy company. Areas of Birmingham, West Midlands Harborne {{WestMidlands-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edgbaston
Edgbaston () is an affluent suburban area of central Birmingham, England, historically in Warwickshire, and curved around the southwest of the city centre. In the 19th century, the area was under the control of the Gough-Calthorpe family and the Gillott family who refused to allow factories or warehouses to be built in Edgbaston, thus making it attractive for the wealthier residents of the city. It then came to be known as "where the trees begin". One of these private houses is grade one listed and open to the public. The majority of Edgbaston that falls under the B15 postcode finds itself being part of the Calthorpe Estate. The estate is an active conservation area, and it is here that the areas most prized properties are situated. The exclusivity of Edgbaston is down to its array of multi-million listed Georgian and Victorian villas, making it one of the most expensive postcodes outside of London. Edgbaston boasts facilities such as Edgbaston Cricket Ground, a Test mat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1852 United Kingdom General Election
The 1852 United Kingdom general election was a watershed in the formation of the modern political parties of Britain. Following 1852, the Tory/Conservative party became, more completely, the party of the rural aristocracy, while the Whig/Liberal party became the party of the rising urban bourgeoisie in Britain. The results of the election were extremely close in terms of the numbers of seats won by the two main parties. As in the previous election of 1847, Lord John Russell's Whigs won the popular vote, but the Conservative Party won a very slight majority of the seats. However, a split between Protectionist Tories, led by the Earl of Derby, and the Peelites who supported Lord Aberdeen made the formation of a majority government very difficult. Lord Derby's minority, protectionist government ruled from 23 February until 17 December 1852. Derby appointed Benjamin Disraeli as Chancellor of the Exchequer in this minority government. However, in December 1852, Derby's governme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anti-Corn Law League
The Anti-Corn Law League was a successful political movement in Great Britain aimed at the abolition of the unpopular Corn Laws, which protected landowners’ interests by levying taxes on imported wheat, thus raising the price of bread at a time when factory-owners were trying to cut wages. The League was a middle-class nationwide organisation that held many well-attended rallies on the premise that a crusade was needed to convince parliament to repeal the corn laws. Its long-term goals included the removal of feudal privileges, which it denounced as impeding progress, lowering economic well-being, and restricting freedom. The League played little role in the final act in 1846 when Sir Robert Peel led the successful battle for repeal. However, its experience provided a model that was widely adopted in Britain and other democratic nations to demonstrate the organisation of a political pressure group with the popular base. Corn Laws The Corn Laws were taxes on imported grain i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Whigs (British Political Party)
The Whigs were a political faction and then a political party in the Parliaments of England, Scotland, Ireland, Great Britain and the United Kingdom. Between the 1680s and the 1850s, the Whigs contested power with their rivals, the Tories. The Whigs merged into the new Liberal Party with the Peelites and Radicals in the 1850s, and other Whigs left the Liberal Party in 1886 to form the Liberal Unionist Party, which merged into the Liberals' rival, the modern day Conservative Party, in 1912. The Whigs began as a political faction that opposed absolute monarchy and Catholic Emancipation, supporting constitutional monarchism with a parliamentary system. They played a central role in the Glorious Revolution of 1688 and were the standing enemies of the Roman Catholic Stuart kings and pretenders. The period known as the Whig Supremacy (1714–1760) was enabled by the Hanoverian succession of George I in 1714 and the failure of the Jacobite rising of 1715 by Tory rebels. The Whig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Institution Of Civil Engineers
The Institution of Civil Engineers (ICE) is an independent professional association for civil engineers and a charitable body in the United Kingdom. Based in London, ICE has over 92,000 members, of whom three-quarters are located in the UK, while the rest are located in more than 150 other countries. The ICE aims to support the civil engineering profession by offering professional qualification, promoting education, maintaining professional ethics, and liaising with industry, academia and government. Under its commercial arm, it delivers training, recruitment, publishing and contract services. As a professional body, ICE aims to support and promote professional learning (both to students and existing practitioners), managing professional ethics and safeguarding the status of engineers, and representing the interests of the profession in dealings with government, etc. It sets standards for membership of the body; works with industry and academia to progress engineering standards a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SS Great Eastern
SS ''Great Eastern'' was an iron sail-powered, paddle wheel and screw-propelled steamship designed by Isambard Kingdom Brunel, and built by John Scott Russell & Co. at Millwall Iron Works on the River Thames, London. She was the largest ship ever built at the time of her 1858 launch, and had the capacity to carry 4,000 passengers from England to Australia without refuelling. Her length of was surpassed only in 1899 by the 17,274-gross-ton , her gross tonnage of 18,915 was only surpassed in 1901 by the 20,904-gross-ton and her 4,000-passenger capacity was surpassed in 1913 by the 4,234-passenger . The ship having five funnels (which were later reduced to four) was unusual for the time. The vessel also had the largest set of paddle wheels. Brunel knew her affectionately as the "Great Babe". He died in 1859 shortly after her maiden voyage, during which she was damaged by an explosion. After repairs, she plied for several years as a passenger liner between Britain and North Ame ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isambard Kingdom Brunel
Isambard Kingdom Brunel (; 9 April 1806 – 15 September 1859) was a British civil engineer who is considered "one of the most ingenious and prolific figures in engineering history," "one of the 19th-century engineering giants," and "one of the greatest figures of the Industrial Revolution, hochanged the face of the English landscape with his groundbreaking designs and ingenious constructions." Brunel built dockyards, the Great Western Railway (GWR), a series of steamships including the first propeller-driven transatlantic steamship, and numerous important bridges and tunnels. His designs revolutionised public transport and modern engineering. Though Brunel's projects were not always successful, they often contained innovative solutions to long-standing engineering problems. During his career, Brunel achieved many engineering firsts, including assisting in the building of the first tunnel under a navigable river (the River Thames) and the development of the , the first ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sydenham, London
Sydenham () is a district of south-east London, England, which is shared between the London boroughs of London Borough of Lewisham, Lewisham, London Borough of Bromley, Bromley and London Borough of Southwark, Southwark. Prior to the creation of the County of London in 1889, Sydenham was located in Kent, bordering Surrey. Historically, the area was very affluent, with the Crystal Palace being relocated to Sydenham Hill in 1854. Today, Sydenham is a diverse area, with a population of 28,378 (2011 census) and borders Forest Hill, London, Forest Hill, Dulwich, Crystal Palace, London, Crystal Palace, Penge, Beckenham, Catford and Bellingham, London, Bellingham. History Originally known as Shippenham, Sydenham began as a small settlement, a few cottages among the woods, whose inhabitants grazed their animals and collected wood. In the 1640s, springs of water in what is now Sydenham Wells Park, Wells Park were discovered to have medicinal properties, attracting crowds of people to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
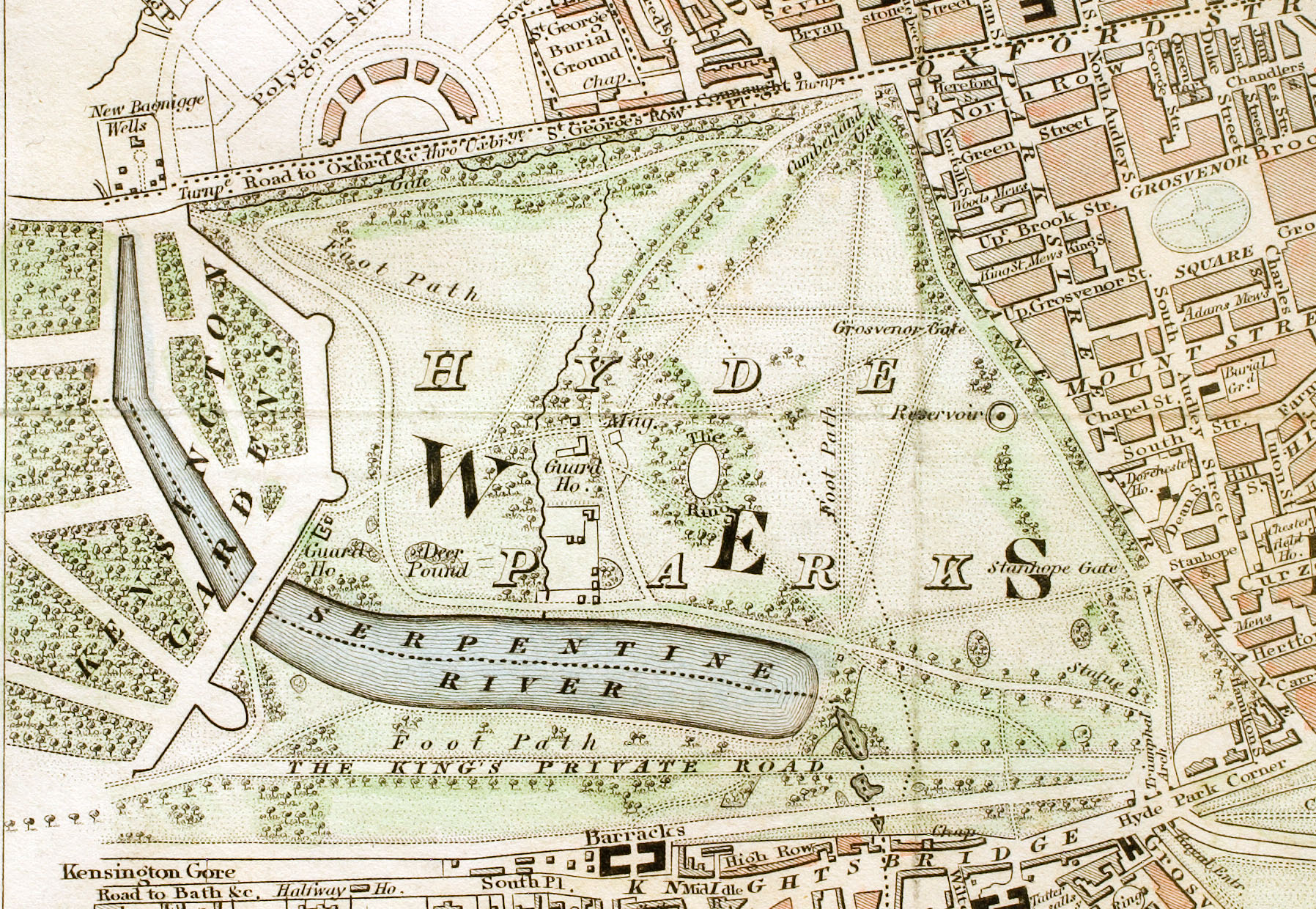
Hyde Park, London
Hyde Park is a Grade I-listed major park in Westminster, Greater London, the largest of the four Royal Parks that form a chain from the entrance to Kensington Palace through Kensington Gardens and Hyde Park, via Hyde Park Corner and Green Park past the main entrance to Buckingham Palace. The park is divided by the Serpentine and the Long Water lakes. The park was established by Henry VIII in 1536 when he took the land from Westminster Abbey and used it as a hunting ground. It opened to the public in 1637 and quickly became popular, particularly for May Day parades. Major improvements occurred in the early 18th century under the direction of Queen Caroline. Several duels took place in Hyde Park during this time, often involving members of the nobility. The Great Exhibition of 1851 was held in the park, for which The Crystal Palace, designed by Joseph Paxton, was erected. Free speech and demonstrations have been a key feature of Hyde Park since the 19th century. Speakers' Cor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



_-_Edward_Stanley%2C_14th_Earl_of_Derby_-_NPG_1806_-_National_Portrait_Gallery.jpg)