|
Chain-linked Model
The chain-linked model or Kline model of innovation was introduced by mechanical engineer Stephen J. Kline in 1985, and further described by Kline and economist Nathan Rosenberg in 1986. The chain-linked model is an attempt to describe complexities in the innovation process. The model is regarded as Kline's most significant contribution. Description In the chain-linked model, new knowledge is not necessarily the driver for innovation. Instead, the process begins with the identification of an unfilled market need. This drives research and design, then redesign and production, and finally marketing, with complex feedback loops between all the stages. There are also important feedback loops with the organization's and the world's stored base of knowledge, with new basic research conducted or commissioned as necessary, to fill in gaps. It is often contrasted with the so-called linear model of innovation, in which basic research leads to applied development, then engineering, then ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nathan Rosenberg
Nathan Rosenberg (November 22, 1927 – August 24, 2015) was an American economist specializing in the history of technology. Biography Rosenberg earned his PhD from the University of Wisconsin in 1955, and taught at Indiana University (1955–1957), the University of Pennsylvania (1957–1961), Purdue University (1961–1964), Harvard University (1967–1969), the University of Wisconsin (1969–1974) and Stanford University (1974–), where he was the Fairleigh S. Dickinson, Jr. Professor Emeritus of Public Policy in the Department of Economics. In 1989 he was visiting Pitt Professor of American History and Institutions at the University of Cambridge. Rosenberg's contribution to understanding technological change was acknowledged by Douglass C. North in his Nobel Prize lecture entitled "Economic Performance through Time". In 1996 he was awarded the Leonardo da Vinci Medal, the highest award of the Society for the History of Technology. In 1986's ''How the West Grew Rich'', Rose ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pro-innovation Bias
In diffusion of innovation theory, a pro-innovation bias is the belief that an innovation should be adopted by whole society without the need of its alteration. The innovation's "champion" has such strong bias in favor of the innovation, that they may not see its limitations or weaknesses and continue to promote it nonetheless. Example A feeling of nuclear optimism emerged in the 1950s in which it was believed that all power generators in the future would be atomic in nature. The atomic bomb would render all conventional explosives obsolete and nuclear power plants would do the same for power sources such as coal and oil. There was a general feeling that everything would use a nuclear power source of some sort, in a positive and productive way, from irradiating food to preserve it, to the development of nuclear medicine. There would be an age of peace and plenty in which atomic energy would "provide the power needed to desalinate water for the thirsty, irrigate the deserts for th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Product Management
Product management is the business process of planning, developing, launching, and managing a product or service. It includes the entire lifecycle of a product, from ideation to development to go to market. Product managers are responsible for ensuring that a product meets the needs of its target market and contributes to the business strategy, while managing a product or products at all stages of the product lifecycle. Software product management adapts the fundamentals of product management for digital products. History The concept of product management originates from a 1931 memo by Procter & Gamble President Neil H. McElroy. McElroy, requesting additional employees focused on brand management, needed "Brand Men" who would take on the role of managing products, packaging, positioning, distribution, and sales performance. The memo defined a Brand Man's work as: * Study carefully shipments of his brands by units. * Where brand development is heavy ... examine carefully t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Innovation Economics
Innovation economics is new and growing field of economic theory and applied and experimental economics that emphasizes innovation and entrepreneurship. It comprises both the application of any type of innovations, especially technological, but not only, into economic use, in classical economics this is the application of customer new technology into economic use; but also it could refer to the field of innovation and experimental economics that refers the new economic science developments that may be considered innovative. In his 1942 book ''Capitalism, Socialism and Democracy'', economist Joseph Schumpeter introduced the notion of an innovation economy. He argued that evolving institutions, entrepreneurs and technological changes were at the heart of economic growth. However, it is only in recent years that "innovation economy," grounded in Schumpeter's ideas, has become a mainstream concept". Historical origins Joseph Schumpeter was one of the first and most important schol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Futures Techniques
Futures techniques used in the multi-disciplinary field of futurology by futurists in Americas and Australasia, and futurology by futurologists in EU, include a diverse range of forecasting methods, including anticipatory thinking, backcasting, simulation, and visioning. Some of the anticipatory methods include, the delphi method, causal layered analysis, environmental scanning, morphological analysis, and scenario planning. Anticipatory thinking protocols Delphi method The Delphi method is a popular technique used in futurology. It was developed by Gordon and Helmer in 1953 at RAND. It can be defined as a method for structuring a group communication process, so that the process is effective in allowing a group of individuals, as a whole, to deal with a complex problem. It uses the iterative, independent questioning of a panel of experts to assess the timing, probability, significance and implications of factors, trends and events in the relation to the problem being cons ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Control Theory
Control theory is a field of mathematics that deals with the control of dynamical systems in engineered processes and machines. The objective is to develop a model or algorithm governing the application of system inputs to drive the system to a desired state, while minimizing any ''delay'', ''overshoot'', or ''steady-state error'' and ensuring a level of control stability; often with the aim to achieve a degree of optimality. To do this, a controller with the requisite corrective behavior is required. This controller monitors the controlled process variable (PV), and compares it with the reference or set point (SP). The difference between actual and desired value of the process variable, called the ''error'' signal, or SP-PV error, is applied as feedback to generate a control action to bring the controlled process variable to the same value as the set point. Other aspects which are also studied are controllability and observability. Control theory is used in control system eng ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Business Process Management
Business process management (BPM) is the discipline in which people use various methods to discover, model, analyze, measure, improve, optimize, and automate business processes. Any combination of methods used to manage a company's business processes is BPM. Processes can be structured and repeatable or unstructured and variable. Though not required, enabling technologies are often used with BPM. It can be differentiated from program management in that program management is concerned with managing a group of inter-dependent projects. From another viewpoint, process management includes program management. In project management, process management is the use of a repeatable process to improve the outcome of the project. Key distinctions between process management and project management are repeatability and predictability. If the structure and sequence of work is unique, then it is a project. In business process management, a sequence of work can vary from instance to instance: t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
User Innovation
__NOTOC__ User innovation refers to innovation by intermediate users (e.g. user firms) or consumer users (individual end-users or user communities), rather than by suppliers (producers or manufacturers). This is a concept closely aligned to co-design and co-creation, and has been proven to result in more innovative solutions than traditional consultation methodologies. Eric von Hippel and others observed that many products and services are actually developed or at least refined, by users, at the site of implementation and use. These ideas are then moved back into the supply network. This is because products are developed to meet the widest possible need; when individual users face problems that the majority of consumers do not, they have no choice but to develop their own modifications to existing products, or entirely new products, to solve their issues. Often, user innovators will share their ideas with manufacturers in hopes of having them produce the product, a process called ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
User-centered Design
User-centered design (UCD) or user-driven development (UDD) is a framework of process (not restricted to interfaces or technologies) in which usability goals, user characteristics, environment, tasks and workflow of a product, service or process are given extensive attention at each stage of the design process. These tests are conducted with/without actual users during each stage of the process from requirements, pre-production models and post production, completing a circle of proof back to and ensuring that "development proceeds with the user as the center of focus." Such testing is necessary as it is often very difficult for the designers of a product to understand intuitively the first-time users of their design experiences, and what each user's learning curve may look like. User-centered design is based on the understanding of a user, their demands, priorities and experiences and when used, is known to lead to an increased product usefulness and usability as it delivers sat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Technological Change
Technological change (TC) or technological development is the overall process of invention, innovation and diffusion of technology or processes.From ''The New Palgrave Dictionary otechnical change by S. Metcalfe. •biased and biased technological change by Peter L. Rousseau. •skill-biased technical change by Giovanni L. Violante. In essence, technological change covers the invention of technologies (including processes) and their commercialization or release as open source via research and development (producing emerging technologies), the continual improvement process, continual improvement of technologies (in which they often become less expensive), and the diffusion of technologies throughout industry or society (which sometimes involves disruption and convergence). In short, technological change is based on both better and more technology. Modeling technological change In its earlier days, technological change was illustrated with the 'Linear Model of Inn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
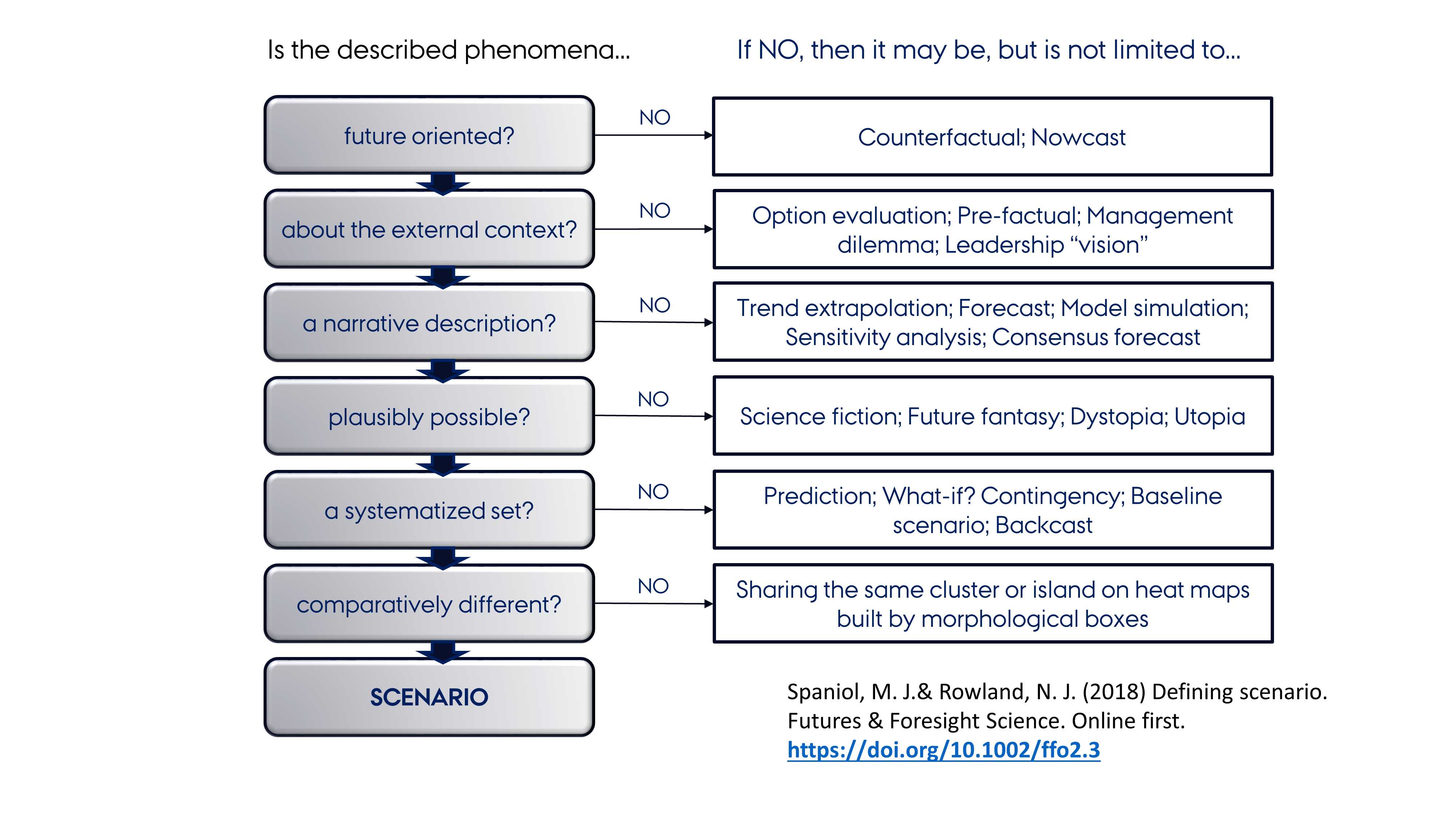
Strategic Foresight
Strategic foresight is a planning-oriented discipline related to futures studies. In a business context, a more action-oriented approach has become well known as corporate foresight.Rohrbeck, Rene (2010) ''Corporate Foresight: Towards a Maturity Model for the Future Orientation of a Firm'', Heidelberg: Physica-Verlag, Springer, Definition and idea Strategy is a high level plan to achieve one or more goals under conditions of uncertainty. Strategic foresight happens when any planner uses scanned inputs, forecasts, alternative futures exploration, analysis and feedback to produce or alter plans and actions of the organization. Scenario planning plays a prominent role in strategic foresight. The flowchart to the right provides a process for classifying a phenomenon as a scenario in the intuitive logics tradition and differentiates it from many other techniques and approaches to planning. Strategic planning always includes analysis, but it may or may not involve serious foresight on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Social Shaping Of Technology
According to Robin A. Williams and David Edge (1996), "Central to social shaping of technology (SST) is the concept that there are choices (though not necessarily conscious choices) inherent in both the design of individual artifacts and systems, and in the direction or trajectory of innovation programs." If technology does not emerge from the unfolding of a predetermined logic or a single determinant, then innovation is a 'garden of forking paths'. Different routes are available, potentially leading to different technological outcomes. Significantly, these choices could have differing implications for society and for particular social groups. SST is one of the models of the technology: society relationship which emerged in the 1980s with MacKenzie and Wajcman's influential 1985 collection, alongside Pinch and Bijker's social construction of technology framework and Callon and Latour's actor-network theory. These have a common feature of criticism of the linear model of innovati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |