|
Cell (EDA)
A cell in the context of electronic design automation (EDA) is an abstract representation of a component within a schematic diagram or physical layout of an electronic circuit in software. A cell-based design methodology is a technique that enables designers to analyze chip designs at varying levels of abstraction. For example, one designer may focus on the logical function (high-level) and another may concentrate on physical implementation (low-level). The technique also enables designers to reuse components in more complex designs without understanding all of the implementation details. See also * Standard Cell * PCell *Integrated Circuits An integrated circuit or monolithic integrated circuit (also referred to as an IC, a chip, or a microchip) is a set of electronic circuits on one small flat piece (or "chip") of semiconductor material, usually silicon. Large numbers of tiny ... * Circuit Design Electronic design automation {{electronics-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electronic Design Automation
Electronic design automation (EDA), also referred to as electronic computer-aided design (ECAD), is a category of software tools for designing Electronics, electronic systems such as integrated circuits and printed circuit boards. The tools work together in a Design flow (EDA), design flow that chip designers use to design and analyze entire semiconductor chips. Since a modern semiconductor chip can have billions of components, EDA tools are essential for their design; this article in particular describes EDA specifically with respect to integrated circuits (ICs). History Early days Prior to the development of EDA, integrated circuits were designed by hand and manually laid out. Some advanced shops used geometric software to generate tapes for a Gerber format, Gerber photoplotter, responsible for generating a monochromatic exposure image, but even those copied digital recordings of mechanically drawn components. The process was fundamentally graphic, with the translation f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schematic Diagram
A schematic, or schematic diagram, is a designed representation of the elements of a system using abstract, graphic symbols rather than realistic pictures. A schematic usually omits all details that are not relevant to the key information the schematic is intended to convey, and may include oversimplified elements in order to make this essential meaning easier to grasp, as well as additional organization of the information. For example, a subway map intended for passengers may represent a subway station with a dot. The dot is not intended to resemble the actual station at all but aims to give the viewer information without unnecessary visual clutter. A schematic diagram of a chemical process uses symbols in place of detailed representations of the vessels, piping, valves, pumps, and other equipment that compose the system, thus emphasizing the functions of the individual elements and the interconnections among them and suppresses their physical details. In an electronic circuit d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
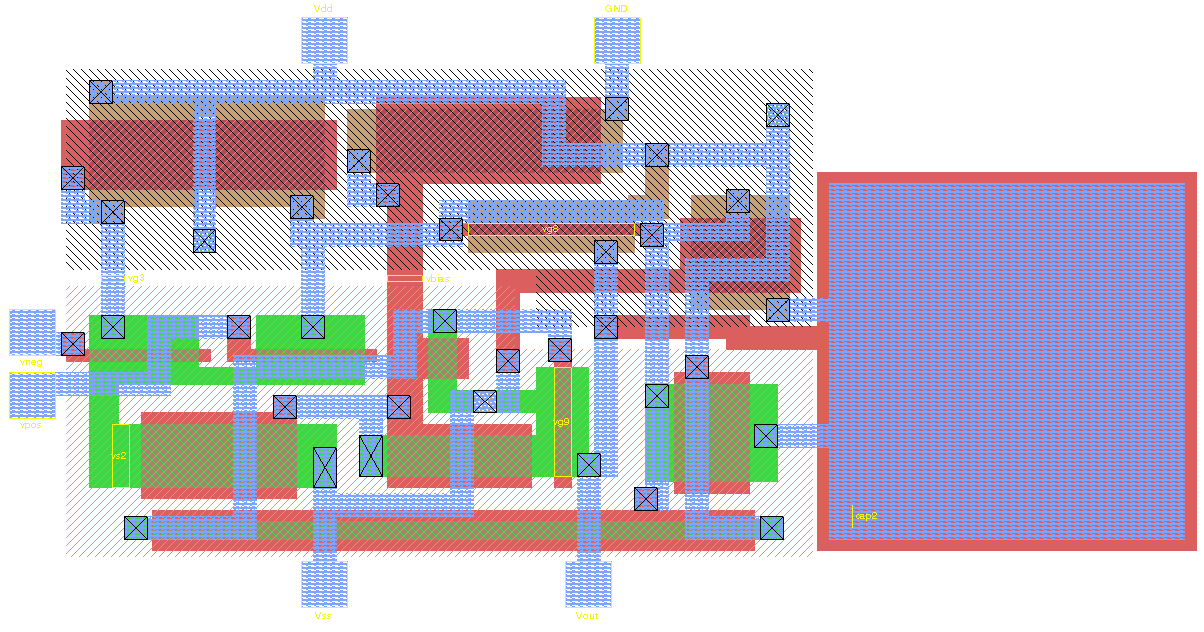
Physical Layout
Integrated circuit layout, also known IC layout, IC mask layout, or mask design, is the representation of an integrated circuit in terms of planar geometric shapes which correspond to the patterns of metal, oxide, or semiconductor layers that make up the components of the integrated circuit. Originally the overall process was called tapeout as historically early ICs used graphical black crepe tape on mylar media for photo imaging (erroneously believed to reference magnetic data—the photo process greatly predated magnetic media). When using a standard process—where the interaction of the many chemical, thermal, and photographic variables is known and carefully controlled—the behaviour of the final integrated circuit depends largely on the positions and interconnections of the geometric shapes. Using a computer-aided layout tool, the layout engineer—or layout technician—places and connects all of the components that make up the chip such that they meet certain criteria� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Standard Cell
In semiconductor design, standard cell methodology is a method of designing application-specific integrated circuits (ASICs) with mostly digital-logic features. Standard cell methodology is an example of design abstraction, whereby a low-level very-large-scale integration (VLSI) layout is encapsulated into an abstract logic representation (such as a NAND gate). Cell-based methodology — the general class to which standard cells belong — makes it possible for one designer to focus on the high-level (logical function) aspect of digital design, while another designer focuses on the implementation (physical) aspect. Along with semiconductor manufacturing advances, standard cell methodology has helped designers scale ASICs from comparatively simple single-function ICs (of several thousand gates), to complex multi-million gate system-on-a-chip (SoC) devices. Construction of a standard cell A standard cell is a group of transistor and interconnect structures that provides a boolean ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PCell
PCell stands for parameterized cell, a concept used widely in the automated design of analog integrated circuits. A PCell represents a part or a component of the circuit whose structure is dependent on one or more parameters. Hence, it is a cell which is automatically generated by electronic design automation (EDA) software based on the values of these parameters. For example, one can create a transistor PCell and then use different instances of the same with different user defined lengths and widths. Vendors of EDA software sometimes use different names for the concept of parameterized cells, e.g. ''T-Cell'' and ''Magic Cell''. Application In electronic circuit designs, cells are basic units of functionality. A given cell may be placed or instantiated many times. A P-Cell is more flexible than a non-parameterized cell because different instances may have different parameter values and, therefore, different structures. For example, rather than having many different cell def ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Integrated Circuits
An integrated circuit or monolithic integrated circuit (also referred to as an IC, a chip, or a microchip) is a set of electronic circuits on one small flat piece (or "chip") of semiconductor material, usually silicon. Large numbers of tiny MOSFETs (metal–oxide–semiconductor field-effect transistors) integrate into a small chip. This results in circuits that are orders of magnitude smaller, faster, and less expensive than those constructed of discrete electronic components. The IC's mass production capability, reliability, and building-block approach to integrated circuit design has ensured the rapid adoption of standardized ICs in place of designs using discrete transistors. ICs are now used in virtually all electronic equipment and have revolutionized the world of electronics. Computers, mobile phones and other home appliances are now inextricable parts of the structure of modern societies, made possible by the small size and low cost of ICs such as modern compute ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Circuit Design
The process of circuit design can cover systems ranging from complex electronic systems down to the individual transistors within an integrated circuit. One person can often do the design process without needing a planned or structured design process for simple circuits. Still, teams of designers following a systematic approach with intelligently guided computer simulation are becoming increasingly common for more complex designs. In integrated circuit design automation, the term "circuit design" often refers to the step of the design cycle which outputs the schematics of the integrated circuit. Typically this is the step between logic design and physical design. Process Traditional circuit design usually involves several stages. Sometimes, a design specification is written after liaising with the customer. A technical proposal may be written to meet the requirements of the customer specification. The next stage involves synthesising on paper a schematic circuit diag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)