|
Celaya F
Celaya (; ) is a city and its surrounding municipality in the state of Guanajuato, Mexico, located in the southeast quadrant of the state. It is the third most populous city in the state, with a 2005 census population of 310,413. The municipality for which the city serves as municipal seat, had a population of 415,869. The city is located in the geographic center of the municipality, which has an areal extent of 553.18 km2 (213.58 sq mi) and includes many smaller outlying communities, the largest of which are San Miguel Octopan, Rincón de Tamayo and San Juan de la Vega. There are many smaller towns around Celaya including Rincón de Tamayo, Tarimoro, Villagrán, La Moncada, Panales Jamaica (Cañones), Panales Galera, La Calera, La Estancia, La Noria, Los Fierros, El Acebuche, Cacalote, and Charco Largo. It is also not far away from Cortazar, Salamanca, Salvatierra, Apaseo el Grande, Querétaro City and among others. The city was founded in 1570 as ''Villa de la Purisím ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bajío
El Bajío (the ''lowland'') is a cultural and geographical region within the central Mexican plateau which roughly spans from north-west of the Mexico City metropolitan area to the main silver mines in the northern-central part of the country. This includes (from south to north) the states of Querétaro, Guanajuato, parts of Jalisco (Centro, Los Altos de Jalisco), Aguascalientes and parts of Zacatecas, San Luis Potosí and Michoacán. Located at the border between Mesoamerica and Aridoamerica, El Bajío saw relatively few permanent settlements and big civilizations during Pre-Columbian history, being mostly inhabited by nomadic tribes known to the Aztecs as " The Chichimeca" peoples (''the barbarians''), another Nahua group from whom the Toltec and the Aztecs were probably descended. The tribes that inhabited El Bajío proved to be some of the hardest to conquer for the Spanish, but due to its strategic location in the Silver route, it also drew prominent attention from the Span ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tarimoro
Tarimoro is the municipal seat of the municipality of Tarimoro in the Mexican state of Guanajuato. History The original settlement was a community of Otomi people The Otomi (; es, Otomí ) are an indigenous people of Mexico inhabiting the central Mexican Plateau (Altiplano) region. The Otomi are an indigenous people of Mexico who inhabit a discontinuous territory in central Mexico. They are linguisticall ... who were later conquered by the '' Tarascós''. The latter named this place Tarimoro, which means "Place of willows." The town was founded back in the epic of colonization by Don Lucas of San Juan on January 3, 1563. In 1910, its name was changed to Ciudad Obregon Gonzalez, by decree of the state Congress, in honor of the then state governor, Joaquin Gonzalez Obregon. However, the official name was later changed back to Tarimoro. Geography and climate Tarimoro is located in Guanajuato. It is bordered to the north by Celaya, to the northwest by Apaseo del Alto, to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
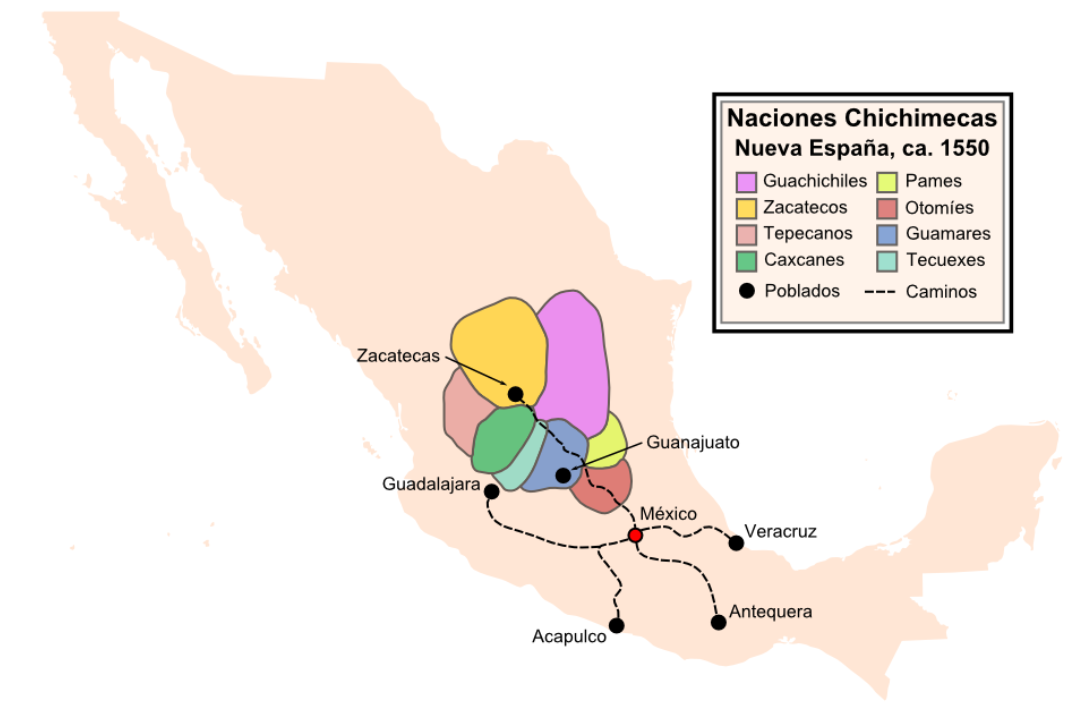
Chichimecas
Chichimeca () is the name that the Nahua peoples of Mexico generically applied to nomadic and semi-nomadic peoples who were established in present-day Bajio region of Mexico. Chichimeca carried the meaning as the Roman term "barbarian" that described Germanic tribes. The name, with its pejorative sense, was adopted by the Spanish Empire. For the Spanish, in the words of scholar Charlotte M. Gradie, "the Chichimecas were a wild, nomadic people who lived north of the Valley of Mexico. They had no fixed dwelling places, lived by hunting, wore little clothes and fiercely resisted foreign intrusion into their territory, which happened to contain silver mines the Spanish wished to exploit." In spite of not having temples or idols, they practiced animal sacrifice, and they were feared for their expertise and brutality in war. The Spanish invasion resulted in a "drastic population decline of all the peoples known collectively as Chichimecas, and to the eventual disappearance as peoples ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Purépecha People
The Purépecha (endonym pua, P'urhepecha ) are a group of indigenous people centered in the northwestern region of Michoacán, Mexico, mainly in the area of the cities of Cherán and Pátzcuaro. They are also known by the pejorative "Tarascan", an exonym, applied by outsiders and not one they use for themselves. The Purépecha occupied most of Michoacán but also some of the lower valleys of both Guanajuato and Jalisco. Celaya, Acambaro, Cerano, and Yurirapundaro. Now, the Purépecha live mostly in the highlands of central Michoacán, around Lakes Patzcuaro and Cuitzeo. History Prehispanic history It was one of the major empires of the Pre-Columbian era. The capital city was Tzintzuntzan. Purépecha architecture is noted for step pyramids in the shape of the letter "T". Pre-Columbian Purépecha artisans made feather mosaics that extensively used hummingbird feathers, which were highly regarded as luxury goods throughout the region. During the Pre-Colonial era, the Pur� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Street Vendors In The Celaya Train Station
A street is a public thoroughfare in a built environment. It is a public parcel of land adjoining buildings in an urban context, on which people may freely assemble, interact, and move about. A street can be as simple as a level patch of dirt, but is more often paved with a hard, durable surface such as tarmac, concrete, cobblestone or brick. Portions may also be smoothed with asphalt, embedded with rails, or otherwise prepared to accommodate non-pedestrian traffic. Originally, the word ''street'' simply meant a paved road ( la, via strata). The word ''street'' is still sometimes used informally as a synonym for ''road'', for example in connection with the ancient Watling Street, but city residents and urban planners draw a crucial modern distinction: a road's main function is transportation, while streets facilitate public interaction. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |