|
Cecaelia
The following is a list of Hybrid beasts in folklore, hybrid entities from the folklore record grouped morphologically. Hybrids not found in classical mythology but developed in the context of modern popular culture are listed in a separate section. For actual hybridization in zoology, see Hybrid (biology)#In different taxa, Hybrid (biology). Mythological Head of one animal, body of another * Alkonost – A creature from Russian folklore with the head of a woman with the body of a bird, said to make beautiful sounds that make anyone who hears them forget all that they know and not want anything more ever again. * Allocamelus – A Heraldic creature that has the head of a donkey and the body of a camel. * Anubis – The jackal-headed Egyptian God. * Atargatis – Human face, fish body. * Bai Ze – A creature from Chinese mythology with the head of a human and the body of a Cattle, cow with six horns and nine eyes. * Bastet – The cat-headed Egyptian Goddess. * Bird goddes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hybrid Beasts In Folklore
Hybrid beasts are creatures composed of parts from different animals, including humans, appearing in the folklore of a variety of cultures as legendary creatures. In burial sites Remains similar to those of mythological hybrids have been found in burial sites discovered by archaeologists. Known combinations include horse-cows, sheep-cows, and a six-legged sheep. The skeletons were formed by ancient peoples who joined together body parts from animal carcasses of different species. The practice is believed to have been done as an offering to their gods. Description These forms' motifs appear across cultures in many mythologies around the world. Such hybrids can be classified as partly human hybrids (such as mermaids or centaurs) or non-human hybrids combining two or more non-human animal species (such as the griffin or the chimera). Hybrids often originate as zoomorphic deities who, over time, are given an anthropomorphic aspect. Paleolithic Partly human hybrids appear in petro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fish
Fish are aquatic, craniate, gill-bearing animals that lack limbs with digits. Included in this definition are the living hagfish, lampreys, and cartilaginous and bony fish as well as various extinct related groups. Approximately 95% of living fish species are ray-finned fish, belonging to the class Actinopterygii, with around 99% of those being teleosts. The earliest organisms that can be classified as fish were soft-bodied chordates that first appeared during the Cambrian period. Although they lacked a true spine, they possessed notochords which allowed them to be more agile than their invertebrate counterparts. Fish would continue to evolve through the Paleozoic era, diversifying into a wide variety of forms. Many fish of the Paleozoic developed external armor that protected them from predators. The first fish with jaws appeared in the Silurian period, after which many (such as sharks) became formidable marine predators rather than just the prey of arthropods. Mos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brazilian Folklore
Brazilian mythology is the subset of Brazilian folklore with cultural elements of diverse origin found in Brazil, comprising folk tales, traditions, characters and beliefs regarding places, people, and entities. The category was originally restricted to indigenous elements, but has been extended to include: * Medieval iberic traditions brought by the Portuguese settlers, some of which are forgotten or very diminished in Portugal itself; as well as other European nations folklore, such as Italy, Germany and Poland. * African traditions brought by Africans to Brazil as slaves during the colonial times—including their religious beliefs; * Elements originated in Brazil by the contact of the three different traditions; * Contemporary elements that are re-elaborations of old traditions. Because Brazil is a melting pot of cultures, many elements of Brazilian mythology are shared by the traditions of other countries, especially its South American neighbors and Portugal. Prominent fig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coco (folklore)
The Coco or Coca (also known as the Cucuy, Cuco, Cuca, Cucu or Cucuí) is a mythical ghost-like monster, equivalent to the bogeyman, found in many Hispanophone and Lusophone countries. It can also be considered an Iberian version of a bugbear as it is a commonly used figure of speech representing an irrational or exaggerated fear. The Cucuy is a male being while Cuca is a female version of the mythical monster. The "monster" will come to the house of disobedient children and make them "disappear". Names and etymology The myth of the ''Coco'', or ''Cucuy'', originated in northern Portugal and Galicia. According to the Real Academia Española, the word ''coco'' derives from the Galician and Portuguese ''côco'' , which means "coconut". The word ''coco'' is used in colloquial speech to refer to the human head in Spanish. ''Coco'' also means "skull". The word ''cocuruto'' in Portuguese means "the crown of the head" or "the highest place" and with the same etymology in Galicia, ''cro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sheep
Sheep or domestic sheep (''Ovis aries'') are domesticated, ruminant mammals typically kept as livestock. Although the term ''sheep'' can apply to other species in the genus ''Ovis'', in everyday usage it almost always refers to domesticated sheep. Like all ruminants, sheep are members of the order Artiodactyla, the even-toed ungulates. Numbering a little over one billion, domestic sheep are also the most numerous species of sheep. An adult female is referred to as a ''ewe'' (), an intact male as a ''ram'', occasionally a ''tup'', a castrated male as a ''wether'', and a young sheep as a ''lamb''. Sheep are most likely descended from the wild mouflon of Europe and Asia, with Iran being a geographic envelope of the domestication center. One of the earliest animals to be domesticated for agricultural purposes, sheep are raised for fleeces, meat (lamb, hogget or mutton) and milk. A sheep's wool is the most widely used animal fiber, and is usually harvested by shearing. In Commonw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sphinx
A sphinx ( , grc, σφίγξ , Boeotian: , plural sphinxes or sphinges) is a mythical creature with the head of a human, the body of a lion, and the wings of a falcon. In Greek tradition, the sphinx has the head of a woman, the haunches of a lion, and the wings of a bird. She is mythicized as treacherous and merciless, and will kill and eat those who cannot answer her riddle. This deadly version of a sphinx appears in the myth and drama of Oedipus. Unlike the Greek sphinx, which was a woman, the Egyptian sphinx is typically shown as a man (an androsphinx ( grc, ανδρόσφιγξ)). In addition, the Egyptian sphinx was viewed as benevolent but having a ferocious strength similar to the malevolent Greek version. Both were thought of as guardians and often flank the entrances to temples. In European decorative art, the sphinx enjoyed a major revival during the Renaissance. Later, the sphinx image, initially very similar to the original Ancient Egyptian concept, was exported ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Temptation Of Saint Anthony (novel)
''The Temptation of Saint Anthony'' (French ''La Tentation de Saint Antoine'') is a dramatic poem in prose (often referred as a novel) by the French author Gustave Flaubert published in 1874. Flaubert spent his whole adult life working fitfully on the book. Origin In 1845, at age 24, Flaubert visited the Balbi Palace in Genoa, and was inspired by a painting of the same title, then attributed to Bruegel the Elder (now thought to be by one of his followers). Flaubert worked at the subject in three versions, completed in 1849, 1856 (with extracts published at that time) and 1872, before publishing the final version in 1874. It takes as its subject the famous temptation faced by Saint Anthony the Great, in the Egyptian desert, a theme often repeated in medieval and modern art. It is written in the form of a play script, detailing one night in the life of Anthony the Great, during which he is faced with great temptations. The work was illustrated by the French painter Odilon Re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
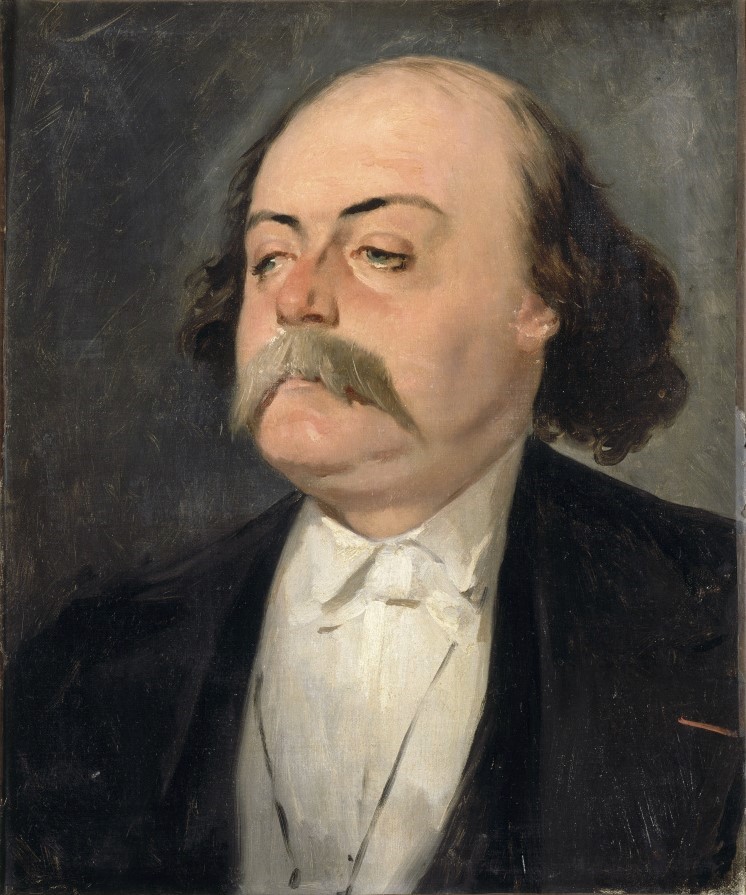
Gustave Flaubert
Gustave Flaubert ( , , ; 12 December 1821 – 8 May 1880) was a French novelist. Highly influential, he has been considered the leading exponent of literary realism in his country. According to the literary theorist Kornelije Kvas, "in Flaubert, realism strives for formal perfection, so the presentation of reality tends to be neutral, emphasizing the values and importance of style as an objective method of presenting reality". He is known especially for his debut novel ''Madame Bovary'' (1857), his ''Correspondence'', and his scrupulous devotion to his style and aesthetics. The celebrated short story writer Guy de Maupassant was a protégé of Flaubert. Life Early life and education Flaubert was born in Rouen, in the Seine-Maritime department of Upper Normandy, in northern France. He was the second son of Anne Justine Caroline (née Fleuriot; 1793–1872) and Achille-Cléophas Flaubert (1784–1846), director and senior surgeon of the major hospital in Rouen. He began writ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
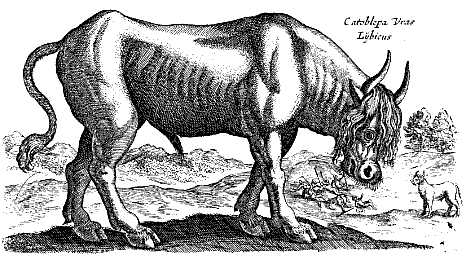
Catoblepas
The catoblepas (pl. catoblepones; from the Greek καταβλέπω (katablépō) "to look downwards") is a legendary creature from Ethiopia (Africa), first described by Pliny the Elder and later by Claudius Aelianus. It is said to resemble a cape buffalo, with its head always pointing downwards due to its great weight. Its stare or breath could either turn people into stone, or kill them. The catoblepas is often thought to be based on real-life encounters with wildebeest, such that some dictionaries say that the word is synonymous with "gnu". It is sometimes known as an African version of a Gorgon. Ancient and medieval descriptions Pliny the Elder (''Natural History'', 8.77) described the catoblepas as a mid-sized creature, sluggish, with a heavy head and a face always turned to the ground. He thought its gaze, like that of the basilisk, was lethal, making the heaviness of its head quite fortunate. Pomponius Mela (''Chorographia,'' 3.98) echoes the description given by Pliny t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bird Goddess
The term Bird goddess was coined by Marija Gimbutas with relation to figurines attributed to the neolithic Vinca culture. These figurines show female bodies combined with a bird's head. The interpretation as " goddess" is part of Gimbutas' program of feminist archaeology depicting the European neolithic as a "gynocentric" culture which would be ousted by the "patriarchal" Indo-European cultures with the onset of the Bronze Age. Griffen (2005) claims to have discovered a sign for the bird goddess in the Vinča signs. Gimbutas also identified a " Lady of the Beasts" (the female analogon of Pashupati), a bear goddess and a snake goddess. See also * Augur * Horus * Leda (mythology) *Language of the birds In Abrahamic and European mythology, medieval literature and occultism, the language of the birds is postulated as a mystical, perfect divine language, Adamic language, Enochian, angelic language or a mythical or magical language used by birds ... Literature *Gimbutas, Marija ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bastet
Bastet or Bast ( egy, bꜣstjt, cop, Ⲟⲩⲃⲁⲥⲧⲉ, Oubaste , Phoenician: 𐤀𐤁𐤎𐤕, romanized: ’bst, or 𐤁𐤎𐤕, romanized: bst) was a goddess of ancient Egyptian religion, worshipped as early as the Second Dynasty (2890 BCE). Her name also is rendered as B'sst, Baast, Ubaste, and Baset. In ancient Greek religion, she was known as Ailuros ( grc-koi, αἴλουρος "cat"). Bastet was worshipped in Bubastis in Lower Egypt, originally as a lioness goddess, a role shared by other deities such as Sekhmet. Eventually Bastet and Sekhmet were characterized as two aspects of the same goddess, with Sekhmet representing the powerful warrior and protector aspect and Bastet, who increasingly was depicted as a cat, representing a gentler aspect.Serpell, "Domestication and History of the Cat", p. 184. Name Bastet, the form of the name that is most commonly adopted by Egyptologists today because of its use in later dynasties, is a modern convention offering one pos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |