|
CDC20
The cell division cycle protein 20 homolog is an essential regulator of cell division that is encoded by the ''CDC20'' gene in humans. To the best of current knowledge its most important function is to activate the anaphase promoting complex (APC/C), a large 11-13 subunit complex that initiates chromatid separation and entrance into anaphase. The APC/CCdc20 protein complex has two main downstream targets. Firstly, it targets securin for destruction, enabling the eventual destruction of cohesin and thus sister chromatid separation. It also targets S and M-phase (S/M) cyclins for destruction, which inactivates S/M cyclin-dependent kinases (Cdks) and allows the cell to exit from mitosis. A closely related protein, Cdc20homologue-1 (Cdh1) plays a complementary role in the cell cycle. CDC20 appears to act as a regulatory protein interacting with many other proteins at multiple points in the cell cycle. It is required for two microtubule-dependent processes: nuclear movement prior to an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anaphase Promoting Complex
Anaphase-promoting complex (also called the cyclosome or APC/C) is an E3 ubiquitin ligase that marks target cell cycle proteins for degradation by the 26S proteasome. The APC/C is a large complex of 11–13 subunit proteins, including a cullin (Apc2) and RING (Apc11) subunit much like SCF. Other parts of the APC/C have unknown functions but are highly conserved. It was the discovery of the APC/C (and SCF) and their key role in eukaryotic cell-cycle regulation that established the importance of ubiquitin-mediated proteolysis in cell biology. Once perceived as a system exclusively involved in removing damaged protein from the cell, ubiquitination and subsequent protein degradation by the proteasome is now perceived as a universal regulatory mechanism for signal transduction whose importance approaches that of protein phosphorylation. In 2014, the APC/C was mapped in 3D at a resolution of less than a nanometre, which also uncovered its secondary structure. This finding could ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mad2
Mad2 (mitotic arrest deficient 2) is an essential spindle checkpoint protein. The spindle checkpoint system is a regulatory system that restrains progression through the metaphase-to-anaphase transition. The Mad2 gene was first identified in the yeast ''S. cerevisiae'' in a screen for genes which when mutated would confer sensitivity to microtubule poisons. The human orthologues of Mad2 (MAD2L1 and MAD2L2) were first cloned in a search for human cDNAs that would rescue the microtubule poison-sensitivity of a yeast strain in which a kinetochore binding protein was missing. The protein was shown to be present at unattached kinetochores and antibody inhibition studies demonstrated it was essential to execute a block in the metaphase-to-anaphase transition in response to the microtubule poison nocodazole. Subsequent cloning of the ''Xenopus laevis'' orthologue, facilitated by the sharing of the human sequence, allowed for the characterization of the mitotic checkpoint in egg extracts. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spindle Assembly Checkpoint
The spindle checkpoint, also known as the metaphase-to-anaphase transition, the spindle assembly checkpoint (SAC), the metaphase checkpoint, or the mitotic checkpoint, is a cell cycle checkpoint during mitosis or meiosis that prevents the separation of the duplicated chromosomes (anaphase) until each chromosome is properly attached to the spindle. To achieve proper segregation, the two kinetochores on the sister chromatids must be attached to opposite spindle poles (bipolar orientation). Only this pattern of attachment will ensure that each daughter cell receives one copy of the chromosome. The defining biochemical feature of this checkpoint is the stimulation of the anaphase-promoting complex by M-phase cyclin-CDK complexes, which in turn causes the proteolytic destruction of cyclins and proteins that hold the sister chromatids together. Overview and importance The beginning of metaphase is characterized by the connection of the microtubules to the kinetochores of the chromo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MAD2L1
Mitotic spindle assembly checkpoint protein MAD2A is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''MAD2L1'' gene. Function MAD2L1 is a component of the mitotic spindle assembly checkpoint that prevents the onset of anaphase until all chromosomes are properly aligned at the metaphase plate. MAD2L1 is related to the MAD2L2 gene located on chromosome 1. A MAD2 pseudogene has been mapped to chromosome 14. Interactions MAD2L1 has been shown to interact with: * ADAM17, * BUB1B, * CDC20, * CDC27 and * Estrogen receptor beta, * MAD2L2, * Mad1 Mad1 is a non-essential protein which in yeast has a function in the spindle assembly checkpoint (SAC). This checkpoint monitors chromosome attachment to spindle microtubules and prevents cells from starting anaphase until the spindle is built up ..., and * UBD. References Further reading * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * {{PDB Gallery, geneid=4085 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CDC16
Cell division cycle protein 16 homolog is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''CDC16'' gene. Function This gene encodes a component protein of the APC complex, which is composed of eight proteins and functions as a protein ubiquitin ligase. The APC complex is a cyclin degradation system that governs exit from mitosis. Each component protein of the APC complex is highly conserved among eukaryotic organisms. This protein and two other APC complex proteins, CDC23 and CDC27, contain a tetratricopeptide repeat (TPR), a protein domain that may be involved in protein-protein interaction. Multiple alternatively spliced variants, encoding the same protein, have been identified. Interactions CDC16 has been shown to interact with CDC27 and CDC20 The cell division cycle protein 20 homolog is an essential regulator of cell division that is encoded by the ''CDC20'' gene in humans. To the best of current knowledge its most important function is to activate the anaphase promoting ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BUB1B
Mitotic checkpoint serine/threonine-protein kinase BUB1 beta is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''BUB1B'' gene. Also known as BubR1, this protein is recognized for its mitotic roles in the spindle assembly checkpoint (SAC) and kinetochore-microtubule interactions that facilitate chromosome migration and alignment. BubR1 promotes mitotic fidelity and protects against aneuploidy by ensuring proper chromosome segregation between daughter cells. BubR1 is proposed to prevent tumorigenesis. Function This gene encodes a kinase involved in spindle checkpoint function and chromosome segregation. The protein has been localized to the kinetochore and plays a role in the inhibition of the anaphase-promoting complex/ cyclosome (APC/C), delaying the onset of anaphase and ensuring proper chromosome segregation. Impaired spindle checkpoint function has been found in many forms of cancer. Increased expression of BubR1 in mice extends a healthy lifespan. * Clinical Significance Bub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CDC27
Cell division cycle protein 27 homolog is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''CDC27'' gene. Function The protein encoded by this gene shares strong similarity with Saccharomyces cerevisiae protein Cdc27, and the gene product of Schizosaccharomyces pombe nuc 2. This protein is a component of anaphase-promoting complex (APC), which is composed of eight protein subunits and highly conserved in eucaryotic cells. APC catalyzes the formation of cyclin B-ubiquitin conjugate that is responsible for the ubiquitin-mediated proteolysis of B-type cyclins. This protein and 3 other members of the APC complex contain the TPR (tetratricopeptide repeat), a protein domain important for protein-protein interaction. This protein was shown to interact with mitotic checkpoint proteins including Mad2, p55CDC and BUBR1, and thus may be involved in controlling the timing of mitosis. Interactions CDC27 has been shown to interact with: * ANAPC10, * ANAPC11, * ANAPC1, * ANAPC4, * ANAPC5 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
FBXO5
F-box only protein 5 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''FBXO5'' gene. Function This gene encodes a member of the F-box protein family which is characterized by an approximately 40 amino acid motif, the F-box. The F-box proteins constitute one of the four subunits of the ubiquitin protein ligase complex called SCFs (SKP1-cullin-F-box), which function in phosphorylation-dependent ubiquitination. The F-box proteins are divided into 3 classes: Fbws containing WD-40 domains, Fbls containing leucine-rich repeats, and Fbxs containing either different protein-protein interaction modules or no recognizable motifs. The protein encoded by this gene belongs to the Fbxs class. This protein is similar to xenopus early mitotic inhibitor-1 (Emi1), which is a mitotic regulator that interacts with Cdc20 and inhibits the anaphase promoting complex. Moreover, Emi1 also assembles a CRL1 complex that targets RAD51 for ubiquitin-mediated degradation. Disease Gene and protein expressi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
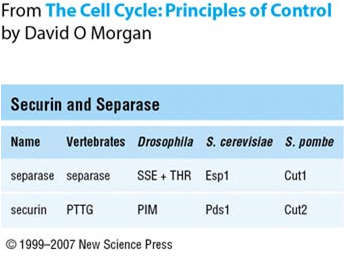
Securin
Securin is a protein involved in control of the metaphase-anaphase transition and anaphase onset. Following bi-orientation of chromosome pairs and inactivation of the spindle checkpoint system, the underlying regulatory system, which includes securin, produces an abrupt stimulus that induces highly synchronous chromosome separation in anaphase. Securin and Separase Securin is initially present in the cytoplasm and binds to separase, a protease that degrades the cohesin rings that link the two sister chromatids. Separase is vital for onset of anaphase. This securin-separase complex is maintained when securin is phosphorylated by Cdk1, inhibiting ubiquitination. When bound to securin, separase is not functional. In addition, both securin and separase are well-conserved proteins (Figure 1). Note that separase cannot function without initially forming the securin-separase complex. This is because securin helps properly fold separase into the functional conformation. However, yeast ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Securin
Securin is a protein involved in control of the metaphase-anaphase transition and anaphase onset. Following bi-orientation of chromosome pairs and inactivation of the spindle checkpoint system, the underlying regulatory system, which includes securin, produces an abrupt stimulus that induces highly synchronous chromosome separation in anaphase. Securin and Separase Securin is initially present in the cytoplasm and binds to separase, a protease that degrades the cohesin rings that link the two sister chromatids. Separase is vital for onset of anaphase. This securin-separase complex is maintained when securin is phosphorylated by Cdk1, inhibiting ubiquitination. When bound to securin, separase is not functional. In addition, both securin and separase are well-conserved proteins (Figure 1). Note that separase cannot function without initially forming the securin-separase complex. This is because securin helps properly fold separase into the functional conformation. However, yeast ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Separase
Separase, also known as separin, is a cysteine protease responsible for triggering anaphase by hydrolysing cohesin, which is the protein responsible for binding sister chromatids during the early stage of anaphase. In humans, separin is encoded by the ''ESPL1'' gene. History In ''S. cerevisiae'', separase is encoded by the ''esp1'' gene. Esp1 was discovered by Kim Nasmyth and coworkers in 1998. In 2021, structures of human separase were determined in complex with either securin or CDK1-cyclin B1-CKS1 using cryo-EM by scientists of the University of Geneva. Function Stable cohesion between sister chromatids before anaphase and their timely separation during anaphase are critical for cell division and chromosome inheritance. In vertebrates, sister chromatid cohesion is released in 2 steps via distinct mechanisms. The first step involves phosphorylation of STAG1 or STAG2 in the cohesin complex. The second step involves cleavage of the cohesin subunit SCC1 ( RAD21) by separase, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ANAPC7
Anaphase-promoting complex subunit 7 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''ANAPC7'' gene. Multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. Function This gene encodes a tetratricopeptide repeat containing component of the anaphase-promoting complex/cyclosome (APC/C), a large E3 ubiquitin ligase that controls cell cycle progression by targeting a number of cell cycle regulators such as B-type cyclins for 26S proteasome-mediated degradation through ubiquitination. The encoded protein is required for proper protein ubiquitination function of APC/C and for the interaction of APC/C with certain transcription coactivators. Interactions ANAPC7 has been shown to interact with ANAPC1, ANAPC4, CDC27 and CDC20 The cell division cycle protein 20 homolog is an essential regulator of cell division that is encoded by the ''CDC20'' gene in humans. To the best of current knowledge its most important function is to activate the anaphase promoti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |