|
Cathal Mac ûedo
Cathal mac ûedo Flaind Chathrach (died 627) was a King of Cashel in Munster from the Glendamnach sept of the Eoganachta. He was the son of ûed Fland Cathrach and grandson of Coirpre Cromm mac Crimthainn (died 577) a previous king of Cashel. He succeeded to the throne on the death of FûÙngen mac ûedo Duib in 618. According to an old saga poem ''Mû°r of Munster and the Violent Death of Cuanu mac Ailchine'', he married the widow of his predecessor Mû°r Muman (died 636) who was the daughter of ûed BennûÀn mac Crimthainn (died 618) of the Loch Lein Eoganachta of West Munster thereby assuring his right to rule at Cashel. After rescuing her sister Ruithchern from the UûÙ LiathûÀin who had captured her, the two sisters proceeded to lament the dead king FûÙngen mac ûedo Duib and the prosperity of his time for which they were rebuked by Cathal. Mû°r marries Ruithcern to LonûÀn mac Findig who is a close ally of Cathalãs, probably of the ûile. However one day the king bids him rise a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kings Of Cashel
The kings of Munster ( ga, RûÙ Mumhan), ruled from the establishment of Munster during the Irish Iron Age, until the High Middle Ages. According to Gaelic traditional history, laid out in works such as the ''Book of Invasions'', the earliest king of Munster was Bodb Derg of the Tuatha Dûˋ Danann. From the Gaelic peoples, an ûrainn kindred known as the DûÀirine (also known as Corcu LoûÙgde and represented today in seniority by the û hEidirsceoil), provided several early monarchs including Cû¤ RoûÙ. In a process in the ''Cath Maige Mucrama'', the ûrainn would lose out in the 2nd century AD to the Deirgtine, ancestors of the Eû°ganachta. Munster during this period was classified as part of ''Leath Moga'', or the southern-half, while other parts of Ireland were ruled mostly by the Connachta. After losing Osraige to the east, Cashel was established as the capital of Munster by the Eû°ganachta. This kindred ruled without interruption until the 10th century. Although the High Kings ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
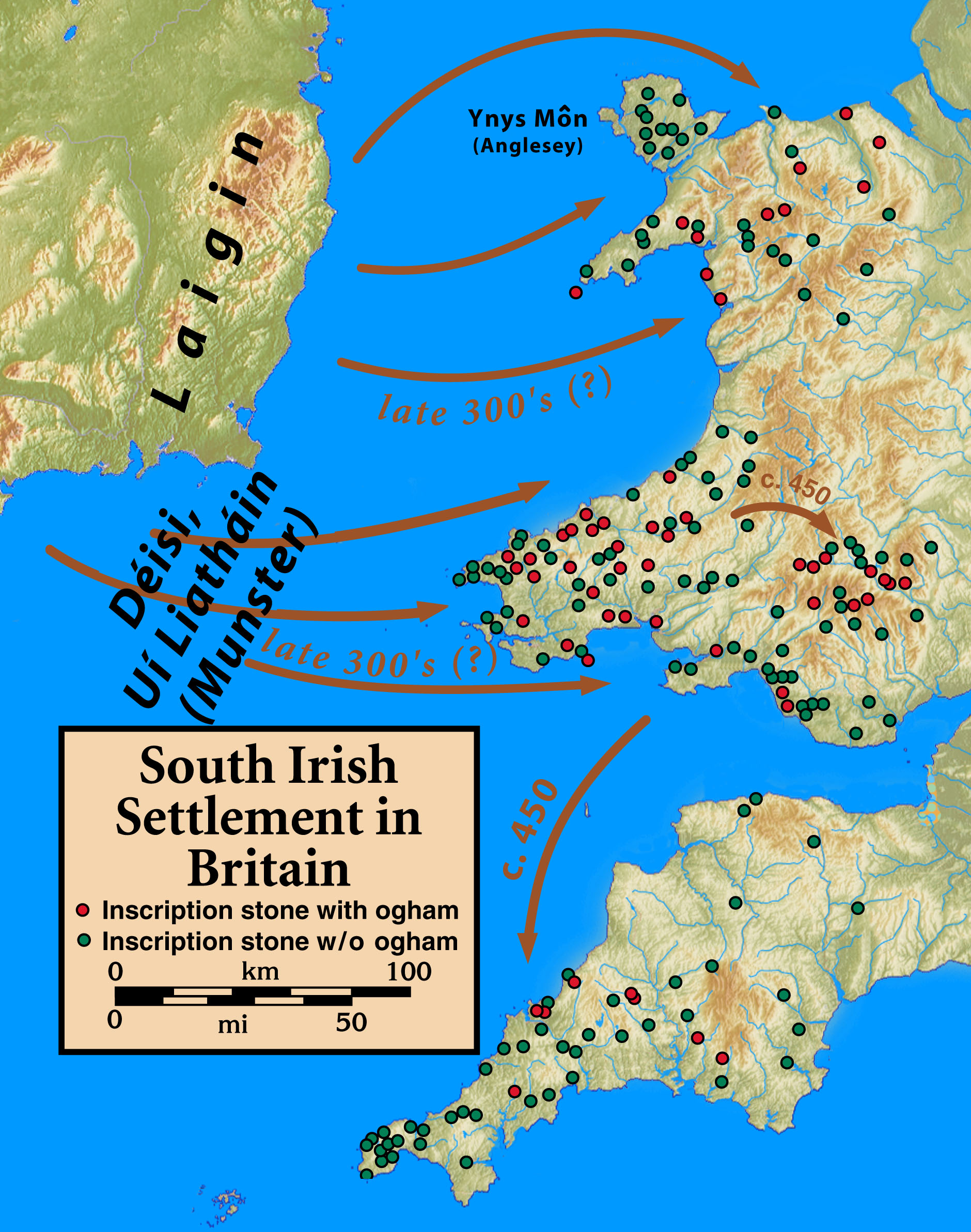
Dûˋisi
The ''Dûˋisi'' were a socially powerful class of peoples from Ireland that settled in Wales and western England between the ancient and early medieval period. The various peoples listed under the heading ''dûˋis'' shared the same status in Gaelic Ireland, and had little or no actual kinship, though they were often thought of as genetically related. During the Early Middle Ages some Dûˋisi groups and subgroups exerted great political influence in various parts of Ireland, and certain written sources suggest a connection to Britain as well. During early medieval Munster, the Dûˋisi were under the hegemony of the Eoganachta confederacy. Etymology Dûˋisi is an Old Irish term that is derives from the word ''dûˋis'', which meant in its original sense a "vassal" or "subject", a designated group of people who were rent-payers to a landowner.û Cathasaigh, pp. 1-33. Later, it became a proper noun for certain septs and their own subjects throughout Ireland.MacNeill, pp. 1-41. History and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
627 Deaths
6 (six) is the natural number following 5 and preceding 7. It is a composite number and the smallest perfect number. In mathematics Six is the smallest positive integer which is neither a square number nor a prime number; it is the second smallest composite number, behind 4; its proper divisors are , and . Since 6 equals the sum of its proper divisors, it is a perfect number; 6 is the smallest of the perfect numbers. It is also the smallest Granville number, or \mathcal-perfect number. As a perfect number: *6 is related to the Mersenne prime 3, since . (The next perfect number is 28.) *6 is the only even perfect number that is not the sum of successive odd cubes. *6 is the root of the 6-aliquot tree, and is itself the aliquot sum of only one other number; the square number, . Six is the only number that is both the sum and the product of three consecutive positive numbers. Unrelated to 6's being a perfect number, a Golomb ruler of length 6 is a "perfect ruler". Six is a con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
FaûÙlbe Flann Mac ûedo Duib
FaûÙlbe Flann mac ûedo Duib (died 639) was a King of Munster from the Eû°ganacht Chaisil branch of the Eoganachta. He succeeded Cathal mac ûedo Flaind Chathrach of the Glendamnach branch in 628. He was the younger brother of a previous king FûÙngen mac ûedo Duib (d. 618). His sobriquet Flann meant "blood-red". Career In 629, he fought the Battle of Carn Feradaig (Cahernarry, County Limerick) versus Guaire Aidne mac ColmûÀin (d.663) of the Ui Fiachrach Aidhne of Connachta. FaûÙlbe won the battle and Guaire was put to flight and his ally Conall mac MûÀele Dû¤ib of the UûÙ Maine and many Connaught nobles were slain. Guaire ruled at the height of Ui Fiachrach power in south Connaught and sought to recover the lost Connaught territories in Thomond. Byrne believes that the true expansion of the Deisi into County Clare dates from this battle. The other important event of his reign was the Battle of ûth Goan in the western Liffey plain fought in 636. In this battle FaûÙlbe interv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eû°ganachta
The Eû°ganachta or Eoghanachta () were an Irish dynasty centred on Cashel which dominated southern Ireland (namely the Kingdom of Munster) from the 6/7th to the 10th centuries, and following that, in a restricted form, the Kingdom of Desmond, and its offshoot Carbery, to the late 16th century. By tradition the dynasty was founded by Conall Corc but named after his ancestor ûogan, the firstborn son of the semi-mythological 3rd-century king Ailill Aulom. This dynastic clan-name, for it was never in any sense a 'surname,' should more accurately be restricted to those branches of the royal house which descended from Conall Corc, who established Cashel as his royal seat in the late 5th century. High Kingship issue Although the Eû°ganachta were powerful in Munster, they never provided Ireland with a High King. Serious challenges to the UûÙ Nûˋill were however presented by Cathal mac Finguine and Feidlimid mac Cremthanin. They were not widely recognized as High Kings or Kings of Tar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trinity College Dublin
, name_Latin = Collegium Sanctae et Individuae Trinitatis Reginae Elizabethae juxta Dublin , motto = ''Perpetuis futuris temporibus duraturam'' (Latin) , motto_lang = la , motto_English = It will last into endless future times , founder = Queen Elizabeth I , established = , named_for = Trinity, The Holy Trinity.The Trinity was the patron of The Dublin Guild Merchant, primary instigators of the foundation of the University, the arms of which guild are also similar to those of the College. , previous_names = , status = , architect = , architectural_style =Neoclassical architecture , colours = , gender = , sister_colleges = St. John's College, CambridgeOriel College, Oxford , freshman_dorm = , head_label = , head = , master = , vice_head_label = , vice_head = , warden ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kings Of Munster
The kings of Munster ( ga, RûÙ Mumhan), ruled from the establishment of Kingdom of Munster, Munster during the Irish Iron Age, until the High Middle Ages. According to Gaelic traditional history, laid out in works such as the ''Book of Invasions'', the earliest king of Munster was Bodb Derg of the Tuatha Dûˋ Danann. From the Gaelic peoples, an ûrainn kindred known as the DûÀirine (also known as Corcu LoûÙgde and represented today in seniority by the û hEidirsceoil), provided several early monarchs including Cû¤ RoûÙ. In a process in the ''Cath Maige Mucrama'', the ûrainn would lose out in the 2nd century AD to the Deirgtine, ancestors of the Eû°ganachta. Munster during this period was classified as part of ''Leath Cuinn and Leath Moga, Leath Moga'', or the southern-half, while other parts of Ireland were ruled mostly by the Connachta. After losing Osraige to the east, Cashel, County Tipperary, Cashel was established as the capital of Munster by the Eû°ganachta. This kindred r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cathal Cû¤-cen-mûÀthair
Cathal Cû¤-cen-mûÀthair mac CathaûÙl (died 665), often known as Cû¤-cen-mûÀthair, was an Irish King of Munster from around 661 until his death. He was a son of Cathal mac ûedo Flaind Chathrach (died c. 628) and belonged to the Glendamnach sept of the Eû°ganachta dynasty. The name Cû¤-cen-mûÀthair means the "motherless hound". Cû¤-cen-mûÀthair succeeded MûÀenach mac FûÙngin of the Eû°ganacht Chaisil, the Cashel branch of the kindred. A surviving poem attributed to Luccrech moccu Chûˋrai contains a list of his ancestors back to Adam. Cû¤-cen-mûÀthair died in 665 of a plague which killed many others as recorded in the Irish annals. The king lists have him followed as King of Munster by Colgû¤ mac FaûÙlbe Flaind of the Eû°ganacht Chaisil. Cû¤-cen-mûÀthair left at least two sons, Finguine mac Cathail (died 696) and Ailill mac Cathail Ailill mac Cathail Con-cen-mûÀthair (died 701) was a King of Munster from the Glendamnach branch of the Eû°ganachta. He was the son of Cathal Cû¤-cen- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MûÀel Dû¤in Mac ûedo BennûÀn
MûÀel Dû¤in mac ûedo BennûÀn (died 661) was a King of Iarmuman (west Munster) from the Eû°ganacht Locha Lûˋin branch of the Eoganachta. He was the son of ûed BennûÀn mac Crimthainn (died 618), who may have been King of all Munster. His uncle ûed DammûÀn (died 634) is called King of Iarmumu in his death obit giving MûÀel Dû¤in a possible reign of 633ã661. Some of the events of his reign concern a feud with the Glendamnach sept of the Eoganachta. The roots of this feud are found in an old saga poem Mû°r Muman and the Violent Death of Cuanu mac Ailchine. During the reign of Cathal mac ûedo Flaind Chathrach (died 627) of Munster, the husband of Aed Bennan's daughter Ruithchern, LonûÀn mac Findig, was murdered by Cuanu mac Ailchine (died 644) of the Fir Maige Fûˋne who abducts Ruithchern. They were on their way to seek shelter in Iarmuman and Cathal was blamed for not ensuring their safety. Warfare then ensued between the two septs of the Eoganachta. The battle of Cenn Con in Mu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ûile
ûile (; sga, ûle, ), commonly anglicised as Ely, was a medieval petty kingdom in the southern part of the modern county of Offaly and parts of North Tipperary in Ireland. The historic barony of Eliogarty was once a significant portion of the kingdom. Overview The clan or people of ûile claimed descent from Cian, a younger son of Ailill Aulom and brother of Eû°gan Mû°r, and thus had kinship with the Eû°ganachta. It has been suggested that the ûile were actually of Laigin origin, and that they may in fact have been the rulers of the Cashel area before the rise of the Eû°ganachta, as suggested by their role in Eû°ganachta origin tales, such as the ''Senchas FagbûÀla Caisil''. Their name is also associated with ''CruachûÀn BrûÙ ûile'' the original name of Croghan Hill. By the 12th-century it was much reduced in size, bounded to the north by the Kingdom of Mide, to the south by Cashel, to the east by the Kingdom of Ossory and the Mû¤scraige TûÙre to the west in Ormond. It cons ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Munster
Munster ( gle, an Mhumhain or ) is one of the provinces of Ireland, in the south of Ireland. In early Ireland, the Kingdom of Munster was one of the kingdoms of Gaelic Ireland ruled by a "king of over-kings" ( ga, rûÙ ruirech). Following the Norman invasion of Ireland, the ancient kingdoms were shired into Counties of Ireland#2.1 Pre-Norman sub-divisions, counties for administrative and judicial purposes. In later centuries, local government legislation has seen further sub-division of the historic counties. Munster has no official function for Local government in the Republic of Ireland, local government purposes. For the purposes of the International Organization for Standardization, ISO, the province is listed as one of the provincial sub-divisions of the State (ISO 3166-2:IE) and coded as "IE-M". Geographically, Munster covers a total area of and has a population of 1,364,098, with the most populated city being Cork (city), Cork. Other significant urban centres in the pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
UûÙ LiathûÀin
The UûÙ LiathûÀin (IPA: iùùlòýièhaùnòý were an early kingdom of Munster in southern Ireland. They belonged the same kindred as the UûÙ Fidgenti, and the two are considered together in the earliest sources, for example ''The Expulsion of the Dûˋisi'' (incidentally). The two have been given various origins among both the early or proto-Eû°ganachta and among the ûrainn or DûÀirine by different scholars working in a number of traditions, with no agreement ever reached or appearing reachable. It is entirely possible that they were the product of a combination of lineages from both these royal kindreds, or alternatively of another origin entirely. Eochu LiathûÀn ("Eochu the Grey"), son of DûÀire Cerbba, is the ancestor after which the UûÙ LiathûÀin is named. The small village of Castlelyons (CaisleûÀn û LiathûÀin) in East County Cork preserves the name of one of their last royal seats in the High Middle Ages, as does the name of Killaliathan Church, County Limerick. The two ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |