|
CataCXium F Sulf
CataCXium F sulf is a water-soluble organophosphorus compound derived from fluorene. The palladium complexes of the respective phosphine show an excellent activity in various palladium-catalyzed coupling reactions, including Suzuki reactions, Sonogashira couplings and Buchwald–Hartwig reactions. References * C.A. Fleckenstein; H. Plenio, Highly efficient Suzuki-Miyaura coupling of heterocyclic substrates through rational reaction design. ''Chemistry-A European Journal'' 2008, ''14(14)'', 4267–4279. * C.A. Fleckenstein; H. Plenio, Aqueous/organic cross coupling: Sustainable protocol for Sonogashira reactions of heterocycles. ''Green Chemistry'' 2008, ''10'', 563–570. * C.A. Fleckenstein; H. Plenio, Efficient Suzuki-Miyaura Coupling of (Hetero)aryl Chlorides with Thiophene- and Furanboronic Acids in Aqueous ''n''-Butanol. ''Journal of Organic Chemistry'' 2008, ''73'', 3236–3244. * C.A Fleckenstein; R. Kadyrov; H. Plenio, Efficient Large-Scale Synthesis of 9-Alkylfluorenyl P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organophosphorus Compound
Organophosphorus compounds are organic compounds containing phosphorus. They are used primarily in pest control as an alternative to chlorinated hydrocarbons that persist in the environment. Some organophosphorus compounds are highly effective insecticides, although some are extremely toxic to humans, including sarin and VX nerve agents. Organophosphorus chemistry is the corresponding science of the properties and reactivity of organophosphorus compounds. Phosphorus, like nitrogen, is in group 15 of the periodic table, and thus phosphorus compounds and nitrogen compounds have many similar properties. The definition of organophosphorus compounds is variable, which can lead to confusion. In industrial and environmental chemistry, an organophosphorus compound need contain only an organic substituent, but need not have a direct phosphorus-carbon (P-C) bond. Thus a large proportion of pesticides (e.g., malathion), are often included in this class of compounds. Phosphorus can adopt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fluorene
Fluorene , or 9''H''-fluorene is an organic compound with the formula (C6H4)2CH2. It forms white crystals that exhibit a characteristic, aromatic odor similar to that of naphthalene. It has a violet fluorescence, hence its name. For commercial purposes it is obtained from coal tar. It is insoluble in water and soluble in many organic solvents. Although sometimes classified as a polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon, the five-membered ring has no aromatic properties. Fluorene is mildly acidic. Synthesis, structure, and reactivity Although fluorene is obtained from coal tar, it can also be prepared by dehydrogenation of diphenylmethane. Alternatively, it can be prepared by the reduction of fluorenone with zinc or hypophosphorous acid–iodine. The fluorene molecule is nearly planar,D. M. Burns, John Iball (1954), ''Molecular Structure of Fluorene'' Nature volume 173, p. 635. although each of the two benzene rings is coplanar with the central carbon 9. Fluorene can be found after the i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palladium
Palladium is a chemical element with the symbol Pd and atomic number 46. It is a rare and lustrous silvery-white metal discovered in 1803 by the English chemist William Hyde Wollaston. He named it after the asteroid Pallas, which was itself named after the epithet of the Greek goddess Athena, acquired by her when she slew Pallas. Palladium, platinum, rhodium, ruthenium, iridium and osmium form a group of elements referred to as the platinum group metals (PGMs). They have similar chemical properties, but palladium has the lowest melting point and is the least dense of them. More than half the supply of palladium and its congener platinum is used in catalytic converters, which convert as much as 90% of the harmful gases in automobile exhaust (hydrocarbons, carbon monoxide, and nitrogen dioxide) into nontoxic substances (nitrogen, carbon dioxide and water vapor). Palladium is also used in electronics, dentistry, medicine, hydrogen purification, chemical applications, groundwate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palladium-catalyzed Coupling Reactions
In organic chemistry, a cross-coupling reaction is a reaction where two fragments are joined together with the aid of a metal catalyst. In one important reaction type, a main group organometallic compound of the type R-M (R = organic fragment, M = main group center) reacts with an organic halide of the type R'-X with formation of a new carbon–carbon bond in the product R-R'. Cross-coupling reaction are a subset of coupling reactions. It is often used in arylations. Richard F. Heck, Ei-ichi Negishi, and Akira Suzuki were awarded the 2010 Nobel Prize in Chemistry for developing palladium-catalyzed coupling reactions. Mechanism The mechanism generally involves reductive elimination of the organic substituents R and R' on a metal complex of the type LnMR(R') (where L is some arbitrary spectator ligand). The crucial intermediate LnMR(R') is formed in a two step process from a low valence precursor Ln. The oxidative addition of an organic halide (RX) to LnM gives LnMR(X). Subseq ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Suzuki Reaction
The Suzuki reaction is an organic reaction, classified as a cross-coupling reaction, where the coupling partners are a boronic acid and an organohalide and the catalyst is a palladium(0) complex. It was first published in 1979 by Akira Suzuki, and he shared the 2010 Nobel Prize in Chemistry with Richard F. Heck and Ei-ichi Negishi for their contribution to the discovery and development of palladium-catalyzed cross-couplings in organic synthesis. This reaction is also known as the Suzuki–Miyaura reaction or simply as the Suzuki coupling. It is widely used to synthesize poly olefins, styrenes, and substituted biphenyls. Several reviews have been published describing advancements and the development of the Suzuki reaction. The general scheme for the Suzuki reaction is shown below, where a carbon-carbon single bond is formed by coupling a halide (R1-X) with an organoboron species (R2-BY2) using a palladium catalyst and a base. Reaction mechanism The mechanism of the Suzuki r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
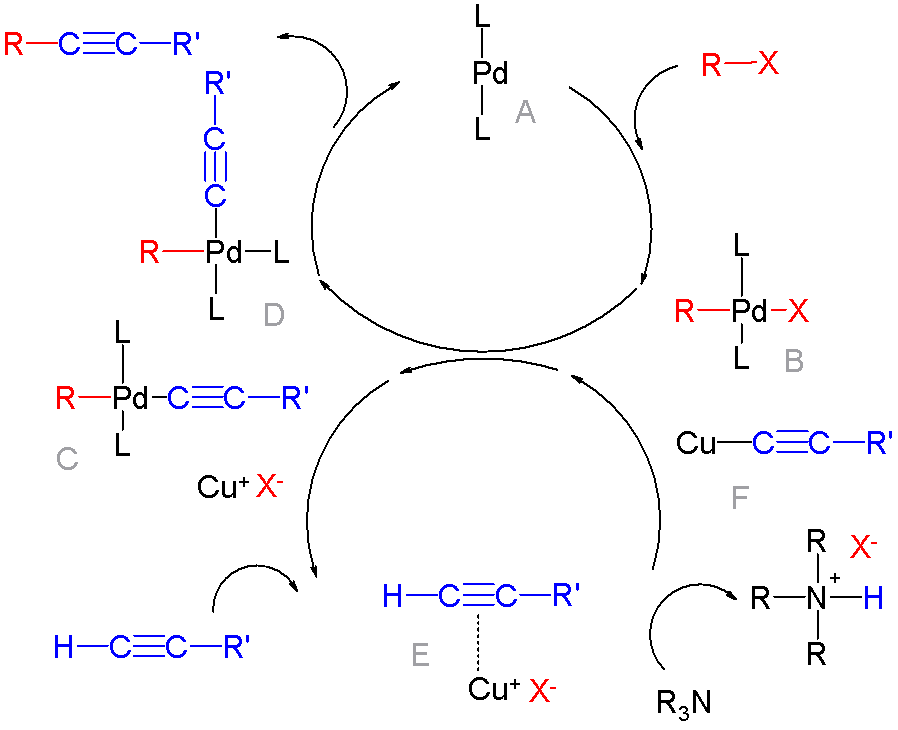
Sonogashira Coupling
The Sonogashira reaction is a cross-coupling reaction used in organic synthesis to form carbon–carbon bonds. It employs a palladium catalyst as well as copper co-catalyst to form a carbon–carbon bond between a terminal alkyne and an aryl or vinyl halide. :* : aryl or vinyl :* : arbitrary :* X: I, Br, Cl or OTf The Sonogashira cross-coupling reaction has been employed in a wide variety of areas, due to its usefulness in the formation of carbon–carbon bonds. The reaction can be carried out under mild conditions, such as at room temperature, in aqueous media, and with a mild base, which has allowed for the use of the Sonogashira cross-coupling reaction in the synthesis of complex molecules. Its applications include pharmaceuticals, natural products, organic materials, and nanomaterials. Specific examples include its use in the synthesis of tazarotene, which is a treatment for psoriasis and acne, and in the preparation of SIB-1508Y, also known as Altinicline, a nicotinic recep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sigma-Aldrich
Sigma-Aldrich (formally MilliporeSigma) is an American chemical, life science, and biotechnology company that is owned by the German chemical conglomerate Merck Group. Sigma-Aldrich was created in 1975 by the merger of Sigma Chemical Company and Aldrich Chemical Company. It grew through various acquisitions until it had over 9,600 employees and was listed on the Fortune 1000. The company is headquartered in St. Louis and has operations in approximately 40 countries. In 2015, the German chemical conglomerate Merck Group acquired Sigma-Aldrich for $17 billion. The company is currently a part of Merck's life science business and in combination with Merck's earlier acquired Millipore Corporation, Millipore, operates as MilliporeSigma. History Sigma Chemical Company of St. Louis and Aldrich Chemical Company of Milwaukee were both American specialty chemical companies when they merged in August 1975. The company grew throughout the 1980s and 1990s, with significant expansion in fac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Strem Chemicals
Strem Chemicals, Inc. is an employee-owned company specializing in fine chemicals in Newburyport, Massachusetts, United States. It was established in 1964 by Michael Strem, who remains president. While Michael Strem was a graduate student, he spent time in Dr. Irving Wender's laboratory learning to synthesize and use cobalt carbonyl. They discussed setting up a chemical company, which resulted in Strem Chemicals. Later, cobalt carbonyl became Strem Chemical's first commercial product. Strem Chemicals manufactures and markets specialty chemicals of high purity, provides custom synthesis and Current Good Manufacturing Practices, cGMP manufacturing services, and supplies about 4,500 specialty products in the area of metals, Inorganic compound, inorganics, organometallics and nanomaterials. Strem Chemicals supports the American Chemical Society Award for Distinguished Service in the Advancement of Inorganic Chemistry and the Canadian Society for Chemistry Award for Pure or Applied C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organometallic Chemistry
Organometallic chemistry is the study of organometallic compounds, chemical compounds containing at least one chemical bond between a carbon atom of an organic molecule and a metal, including alkali, alkaline earth, and transition metals, and sometimes broadened to include metalloids like boron, silicon, and selenium, as well. Aside from bonds to organyl fragments or molecules, bonds to 'inorganic' carbon, like carbon monoxide (metal carbonyls), cyanide, or carbide, are generally considered to be organometallic as well. Some related compounds such as transition metal hydrides and metal phosphine complexes are often included in discussions of organometallic compounds, though strictly speaking, they are not necessarily organometallic. The related but distinct term " metalorganic compound" refers to metal-containing compounds lacking direct metal-carbon bonds but which contain organic ligands. Metal β-diketonates, alkoxides, dialkylamides, and metal phosphine complexes are repres ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organophosphorus Compounds
Organophosphorus compounds are organic compounds containing phosphorus. They are used primarily in pest control as an alternative to chlorinated hydrocarbons that persist in the environment. Some organophosphorus compounds are highly effective insecticides, although some are extremely toxic to humans, including sarin and VX (nerve agent), VX nerve agents. Organophosphorus chemistry is the corresponding science of the properties and reactivity of organophosphorus compounds. Phosphorus, like nitrogen, is in pnictogen, group 15 of the periodic table, and thus phosphorus compounds and nitrogen compounds have many similar properties. The definition of organophosphorus compounds is variable, which can lead to confusion. In industrial and environmental chemistry, an organophosphorus compound need contain only an organic substituent, but need not have a direct phosphorus-carbon (P-C) bond. Thus a large proportion of pesticides (e.g., malathion), are often included in this class of compound ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

2.jpg)