|
Castle Dome
Castle Dome, or Castle Dome Peak is a prominent butte and high point of the Castle Dome Mountains northeast of Yuma, Arizona, in the northwestern Sonoran Desert. The butte lies approximately east of the historical Castle Dome Landing on the Colorado River (site submerged by the Imperial Reservoir). It is located above and east of US Route 95 and the Castle Dome mining district. Castle Dome is noteworthy for its recreational use for day hiking. It is also often coated in winter or spring snowstorms as a white landform, with its loss of white being determined by season and duration of storm temperatures. Castle Dome's height is . Mining and minerals Some noteworthy minerals from the Castle Dome Mountains region are vanadinite, wulfenite, baryte, and fluorite. Trails and unimproved road trails Some of the local trails are: King Valley Road, McPherson Pass Trail, Big Eye Wash Trail, Castle Dome Mountains, and Kofa Queen Canyon Trail. See also * Castle Dome Landing, Arizona ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Castle Dome Landing, Arizona
Castle Dome Landing, Arizona (also Castle Dome City) is a ghost town in the Castle Dome Mountains of Yuma County in the U.S. state of Arizona. It was first settled as a transport depot and mining camp around 1863 in what was then the Arizona Territory. History When the first Americans reached the Castle Dome Mountains in the early 1860s, there were already signs of previous mining activity. It was generally held that Native Americans had engaged in mining in the Castle Dome Mountains some years before and backpacked the ore south to a processing site on the banks of the Gila River, where remnants of adobe furnaces were found. As mineral deposits began to be discovered up and down the Colorado River in the early 1860s, numerous mining camps and steamboat ports grew into towns along the river. Heading north from Yuma, prospectors staked gold and silver claims along the river and in the surrounding mountains. The Castle Dome Mining Company, established in 1863 and owned by Con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Castle Dome Mountains
The Castle Dome Mountains (Tolkepaya Yavapai: Wi:hopuʼ) are a mountain range in Yuma County, Arizona, within the Kofa National Wildlife Refuge. Castle Dome Peak, the high point of the range, is a prominent butte and distinctive landmark. The peak is high, and is located at . Castle Dome was named by American soldiers at old Fort Yuma in the 1880s. Early Spanish explorers called the same peak ''Cabeza de Gigante'', "Giant's Head." History Mining The Castle Dome mining district is one of Yuma County's oldest and most productive mining locations. Its proximity to the Colorado River and relatively low rates of freight at the time permitted the mining of even low grades of ore which wouldn't have been profitable at other locations. In addition to silver and lead, the area is rich in numerous other minerals, including zinc, copper, gold, and many others. Total production from the Castle Dome mines included of lead, of silver, of zinc, of copper, of gold, and of placer gold pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arizona
Arizona ( ; nv, Hoozdo Hahoodzo ; ood, Alĭ ṣonak ) is a state in the Southwestern United States. It is the 6th largest and the 14th most populous of the 50 states. Its capital and largest city is Phoenix. Arizona is part of the Four Corners region with Utah to the north, Colorado to the northeast, and New Mexico to the east; its other neighboring states are Nevada to the northwest, California to the west and the Mexican states of Sonora and Baja California to the south and southwest. Arizona is the 48th state and last of the contiguous states to be admitted to the Union, achieving statehood on February 14, 1912. Historically part of the territory of in New Spain, it became part of independent Mexico in 1821. After being defeated in the Mexican–American War, Mexico ceded much of this territory to the United States in 1848. The southernmost portion of the state was acquired in 1853 through the Gadsden Purchase. Southern Arizona is known for its desert cl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vanadinite
Vanadinite is a mineral belonging to the apatite group of phosphates, with the chemical formula Pb5( V O4)3 Cl. It is one of the main industrial ores of the metal vanadium and a minor source of lead. A dense, brittle mineral, it is usually found in the form of red hexagonal crystals. It is an uncommon mineral, formed by the oxidation of lead ore deposits such as galena. First discovered in 1801 in Mexico, vanadinite deposits have since been unearthed in South America, Europe, Africa, and North America. Origins Vanadinite is an uncommon mineral, only occurring as the result of chemical alterations to a pre-existing material. It is therefore known as a secondary mineral. It is found in arid climates and forms by oxidation of primary lead minerals. Vanadinite is especially found in association with the lead sulfide, galena. Other associated minerals include wulfenite, limonite, and barite. It was originally discovered in Mexico by the Spanish mineralogist Andrés Manuel del Río ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Landforms Of Yuma County, Arizona
A landform is a natural or anthropogenic land feature on the solid surface of the Earth or other planetary body. Landforms together make up a given terrain, and their arrangement in the landscape is known as topography. Landforms include hills, mountains, canyons, and valleys, as well as shoreline features such as bays, peninsulas, and seas, including submerged features such as mid-ocean ridges, volcanoes, and the great ocean basins. Physical characteristics Landforms are categorized by characteristic physical attributes such as elevation, slope, orientation, stratification, rock exposure and soil type. Gross physical features or landforms include intuitive elements such as berms, mounds, hills, ridges, cliffs, valleys, rivers, peninsulas, volcanoes, and numerous other structural and size-scaled (e.g. ponds vs. lakes, hills vs. mountains) elements including various kinds of inland and oceanic waterbodies and sub-surface features. Mountains, hills, plateaux, and plains are t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yuma Desert
The Yuma Desert is a lower-elevation section of the Sonoran Desert in the southwestern United States and the northwest of Mexico. It lies in the Salton basin. The desert contains areas of sparse vegetation and has notable areas of sand dunes. With an average rainfall less than each year, it is among the harshest deserts in North America. Human presence is sparse throughout, the largest city being Yuma, Arizona, on the Colorado River and the border of California. Overview The desert includes the lower-elevation parts of the southwestern corner of Arizona, extending west to the Colorado River. On the other side of the river, in California, is the Colorado Desert region of the Sonoran Desert, also referred to as the Low Desert. Although the two regions are separated only by the Colorado River, numerous species of plant and animals live only on one side or the other, such as saguaro cactus, which occurs only east of the river. The Yuma Desert also includes the sandy plains of western ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buttes Of Arizona
__NOTOC__ In geomorphology, a butte () is an isolated hill with steep, often vertical sides and a small, relatively flat top; buttes are smaller landforms than mesas, plateaus, and tablelands. The word ''butte'' comes from a French word meaning knoll (but of any size); its use is prevalent in the Western United States, including the southwest where ''mesa'' (Spanish for "table") is used for the larger landform. Due to their distinctive shapes, buttes are frequently landmarks in plains and mountainous areas. To differentiate the two landforms, geographers use the rule of thumb that a mesa has a top that is wider than its height, while a butte has a top that is narrower than its height. Formation Buttes form by weathering and erosion when hard caprock overlies a layer of less resistant rock that is eventually worn away. The harder rock on top of the butte resists erosion. The caprock provides protection for the less resistant rock below from wind abrasion which leaves it standin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
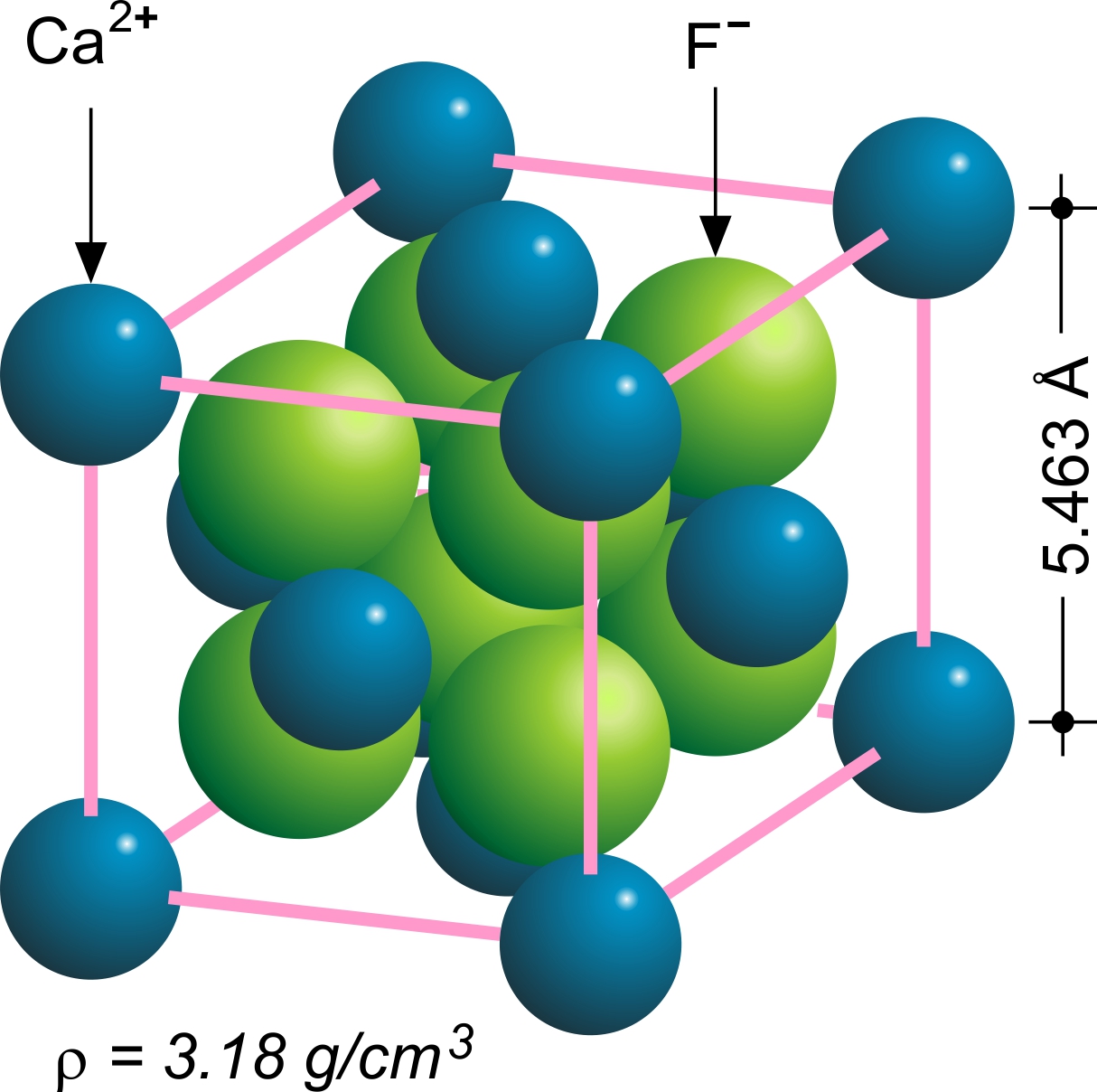
Fluorite
Fluorite (also called fluorspar) is the mineral form of calcium fluoride, CaF2. It belongs to the halide minerals. It crystallizes in isometric cubic habit, although octahedral and more complex isometric forms are not uncommon. The Mohs scale of mineral hardness, based on scratch hardness comparison, defines value 4 as fluorite. Pure fluorite is colourless and transparent, both in visible and ultraviolet light, but impurities usually make it a colorful mineral and the stone has ornamental and lapidary uses. Industrially, fluorite is used as a flux for smelting, and in the production of certain glasses and enamels. The purest grades of fluorite are a source of fluoride for hydrofluoric acid manufacture, which is the intermediate source of most fluorine-containing fine chemicals. Optically clear transparent fluorite lenses have low dispersion, so lenses made from it exhibit less chromatic aberration, making them valuable in microscopes and telescopes. Fluorite optics are also ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baryte
Baryte, barite or barytes ( or ) is a mineral consisting of barium sulfate ( Ba S O4). Baryte is generally white or colorless, and is the main source of the element barium. The ''baryte group'' consists of baryte, celestine (strontium sulfate), anglesite (lead sulfate), and anhydrite (calcium sulfate). Baryte and celestine form a solid solution (Ba,Sr)SO4. Names and history The radiating form, sometimes referred to as ''Bologna Stone'', attained some notoriety among alchemists for specimens found in the 17th century near Bologna by Vincenzo Casciarolo. These became phosphorescent upon being calcined. Carl Scheele determined that baryte contained a new element in 1774, but could not isolate barium, only barium oxide. Johan Gottlieb Gahn also isolated barium oxide two years later in similar studies. Barium was first isolated by electrolysis of molten barium salts in 1808 by Sir Humphry Davy in England. The American Petroleum Institute specification API 13/ISO 13500, which gove ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wulfenite
Wulfenite is a lead molybdate mineral with the formula Pb Mo O4. It can be most often found as thin tabular crystals with a bright orange-red to yellow-orange color, sometimes brown, although the color can be highly variable. In its yellow form it is sometimes called "yellow lead ore". It crystallizes in the tetragonal system, often occurring as stubby, pyramidal or tabular crystals. It also occurs as earthy, granular masses. It is found in many localities, associated with lead ores as a secondary mineral associated with the oxidized zone of lead deposits. It is also a secondary ore of molybdenum, and is sought by collectors. Discovery and occurrence Wulfenite was first described in 1845 for an occurrence in Bad Bleiberg, Carinthia, Austria. It was named for Franz Xavier von Wulfen (1728–1805), an Austrian mineralogist. It occurs as a secondary mineral in oxidized hydrothermal lead deposits. It occurs with cerussite, anglesite, smithsonite, hemimorphite, vanadinite, pyromor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hiking
Hiking is a long, vigorous walk, usually on trails or footpaths in the countryside. Walking for pleasure developed in Europe during the eighteenth century.AMATO, JOSEPH A. "Mind over Foot: Romantic Walking and Rambling." In ''On Foot: A History of Walking'', 101-24. NYU Press, 2004. Accessed March 1, 2021. http://www.jstor.org/stable/j.ctt9qg056.7. Religious pilgrimages have existed much longer but they involve walking long distances for a spiritual purpose associated with specific religions. "Hiking" is the preferred term in Canada and the United States; the term "walking" is used in these regions for shorter, particularly urban walks. In the United Kingdom and the Republic of Ireland, the word "walking" describes all forms of walking, whether it is a walk in the park or backpacking in the Alps. The word hiking is also often used in the UK, along with rambling , hillwalking, and fell walking (a term mostly used for hillwalking in northern England). The term bushwalking is end ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)