|
Castability
Castability is the ease of forming a quality casting. A very castable part design is easily developed, incurs minimal tooling costs, requires minimal energy, and has few rejections.Ravi, p. 2 Castability can refer to a part design or a material property.Ravi, p. 1 Part design Part design and geometry directly affect the castability, with volume, surface area and the number of features being the most important attributes. If the design has undercuts or interior cavities it decreases castability due to tooling complexity. Long thin sections in a design are hard to fill. Sudden changes in wall thickness reduce castability because it induces turbulence during filling; fillets should be added to avoid this. Annulars in the path of flow should be avoided because they can cause cold shuts or misruns. A design that causes isolated hot spots decreases castability. An ideal design would have progressive directional solidification from the thinnest section to the thickest.Ravi, p. 4. Locat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Misrun
A casting defect is an undesired irregularity in a metal casting process. Some defects can be tolerated while others can be repaired, otherwise they must be eliminated. They are broken down into five main categories: ''gas porosity'', ''shrinkage defects'', ''mould material defects'', ''pouring metal defects'', and ''metallurgical defects''. Terminology The terms "defect" and "" refer to two specific and separate things in castings. Defects are defined as conditions in a casting that must be corrected or removed, or the casting must be rejected. Discontinuities, also known as "imperfections", are defined as "interruptions in the physical continuity of the casting". Therefore, if the casting is less than perfect, but still useful and in tolerance, the imperfections should be deemed "discontinuities". Types There are many types of defects which result from many different causes. Some of the solutions to certain defects can be the cause for another type of defect. The following def ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cold Shut
A casting defect is an undesired irregularity in a metal casting process. Some defects can be tolerated while others can be repaired, otherwise they must be eliminated. They are broken down into five main categories: ''gas porosity'', ''shrinkage defects'', ''mould material defects'', ''pouring metal defects'', and ''metallurgical defects''. Terminology The terms "defect" and "" refer to two specific and separate things in castings. Defects are defined as conditions in a casting that must be corrected or removed, or the casting must be rejected. Discontinuities, also known as "imperfections", are defined as "interruptions in the physical continuity of the casting". Therefore, if the casting is less than perfect, but still useful and in tolerance, the imperfections should be deemed "discontinuities". Types There are many types of defects which result from many different causes. Some of the solutions to certain defects can be the cause for another type of defect. The following def ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hot Spot (casting)
A casting defect is an undesired irregularity in a metal casting process. Some defects can be tolerated while others can be repaired, otherwise they must be eliminated. They are broken down into five main categories: ''gas porosity'', ''shrinkage defects'', ''mould material defects'', ''pouring metal defects'', and ''metallurgical defects''. Terminology The terms "defect" and "" refer to two specific and separate things in castings. Defects are defined as conditions in a casting that must be corrected or removed, or the casting must be rejected. Discontinuities, also known as "imperfections", are defined as "interruptions in the physical continuity of the casting". Therefore, if the casting is less than perfect, but still useful and in tolerance, the imperfections should be deemed "discontinuities". Types There are many types of defects which result from many different causes. Some of the solutions to certain defects can be the cause for another type of defect. The following def ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Casting Defects
A casting defect is an undesired irregularity in a metal casting process. Some defects can be tolerated while others can be repaired, otherwise they must be eliminated. They are broken down into five main categories: ''gas porosity'', ''shrinkage defects'', ''mould material defects'', ''pouring metal defects'', and ''metallurgical defects''. Terminology The terms "defect" and "" refer to two specific and separate things in castings. Defects are defined as conditions in a casting that must be corrected or removed, or the casting must be rejected. Discontinuities, also known as "imperfections", are defined as "interruptions in the physical continuity of the casting". Therefore, if the casting is less than perfect, but still useful and in tolerance, the imperfections should be deemed "discontinuities". Types There are many types of defects which result from many different causes. Some of the solutions to certain defects can be the cause for another type of defect. The following def ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Casting
Casting is a manufacturing process in which a liquid material is usually poured into a mold, which contains a hollow cavity of the desired shape, and then allowed to solidify. The solidified part is also known as a ''casting'', which is ejected or broken out of the mold to complete the process. Casting materials are usually metals or various ''time setting'' materials that cure after mixing two or more components together; examples are epoxy, concrete, plaster and clay. Casting is most often used for making complex shapes that would be otherwise difficult or uneconomical to make by other methods. Heavy equipment like machine tool beds, ships' propellers, etc. can be cast easily in the required size, rather than fabricating by joining several small pieces. Casting is a 7,000-year-old process. The oldest surviving casting is a copper frog from 3200 BC. History Throughout history, metal casting has been used to make tools, weapons, and religious objects. Metal casting history and de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Material Properties
A materials property is an intensive property of a material, i.e., a physical property that does not depend on the amount of the material. These quantitative properties may be used as a metric by which the benefits of one material versus another can be compared, thereby aiding in materials selection. A property may be a constant or may be a function of one or more independent variables, such as temperature. Materials properties often vary to some degree according to the direction in the material in which they are measured, a condition referred to as anisotropy. Materials properties that relate to different physical phenomena often behave linearly (or approximately so) in a given operating range. Modeling them as linear functions can significantly simplify the differential constitutive equations that are used to describe the property. Equations describing relevant materials properties are often used to predict the attributes of a system. The properties are measured by standardi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Undercut (manufacturing)
In manufacturing, an undercut is a special type of recessed surface that is inaccessible using a straight tool. In turning, it refers to a recess in a diameter generally on the inside diameter of the part. In milling, it refers to a feature which is not visible when the part is viewed from the spindle. In molding, it refers to a feature that cannot be molded using only a single pull mold. In printed circuit board construction, it refers to the portion of the copper that is etched away under the photoresist. Turning On turned parts an undercut is also known as a ''neck'' or "relief groove". They are often used at the end of the threaded portion of a shaft or screw to provide clearance for the cutting tool. Molding Undercut - Any indentation or protrusion in a shape that will prevent its withdrawal from a one-piece mold. Milling In milling the spindle is where a cutting tool is mounted. In some situations material must be cut from a direction where the feature can not b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turbulence
In fluid dynamics, turbulence or turbulent flow is fluid motion characterized by chaotic changes in pressure and flow velocity. It is in contrast to a laminar flow, which occurs when a fluid flows in parallel layers, with no disruption between those layers. Turbulence is commonly observed in everyday phenomena such as surf, fast flowing rivers, billowing storm clouds, or smoke from a chimney, and most fluid flows occurring in nature or created in engineering applications are turbulent. Turbulence is caused by excessive kinetic energy in parts of a fluid flow, which overcomes the damping effect of the fluid's viscosity. For this reason turbulence is commonly realized in low viscosity fluids. In general terms, in turbulent flow, unsteady vortices appear of many sizes which interact with each other, consequently drag due to friction effects increases. This increases the energy needed to pump fluid through a pipe. The onset of turbulence can be predicted by the dimensionless Rey ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fillet (mechanics)
In mechanical engineering, a fillet is a rounding of an interior or exterior corner of a part design. An interior or exterior corner, with an angle or type of bevel, is called a " chamfer". Fillet geometry, when on an interior corner is a line of concave function, whereas a fillet on an exterior corner is a line of convex function (in these cases, fillets are typically referred to as rounds). Fillets commonly appear on welded, soldered, or brazed joints. Applications * Stress concentration is a problem of load-bearing mechanical parts which is reduced by employing fillets on points and lines of expected high stress. The fillets distribute the stress over a broader area and effectively make the parts more durable and capable of bearing larger loads. * For considerations in aerodynamics, fillets are employed to reduce interference drag where aircraft components such as wings, struts, and other surfaces meet one another. * For manufacturing, concave corners are sometimes fillet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Directional Solidification
Directional solidification (DS) and progressive solidification are types of solidification within castings. Directional solidification is solidification that occurs from farthest end of the casting and works its way towards the sprue. Progressive solidification, also known as parallel solidification,. is solidification that starts at the walls of the casting and progresses perpendicularly from that surface.. Theory - Most metals and alloys shrink as the material changes from a liquid state to a solid state. Therefore, if liquid material is not available to compensate for this shrinkage a '' shrinkage defect'' forms. When progressive solidification dominates over directional solidification a shrinkage defect will form. The geometrical shape of the mold cavity has a direct effect on progressive and directional solidification. At the end of tunnel-type geometries, divergent heat flow occurs, which causes that area of the casting to cool faster than surrounding areas; this is call ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parting Line
A parting line, in industrial casting of molds, is the border line in which draft angles change direction. One can check the parting line in the mould or product which divides the two half, i.e; the core and the cavity of a molded part. It is sometimes a starting point for the mold parting surface. In engineering drawing, a parting line is often abbreviated as PL. ASME's Y14.8 standard specifies a symbol for parting line. Engineering applications (seals, tight running molded parts) that require precision for shape control, call for removal of flash Flash, flashes, or FLASH may refer to: Arts, entertainment, and media Fictional aliases * Flash (DC Comics character), several DC Comics superheroes with super speed: ** Flash (Barry Allen) ** Flash (Jay Garrick) ** Wally West, the first Kid ...es. Many molders will repair or even replace the mold tooling so that the flash is reduced to an acceptable tolerance or eliminated altogether. Secondary operations to remove parting li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
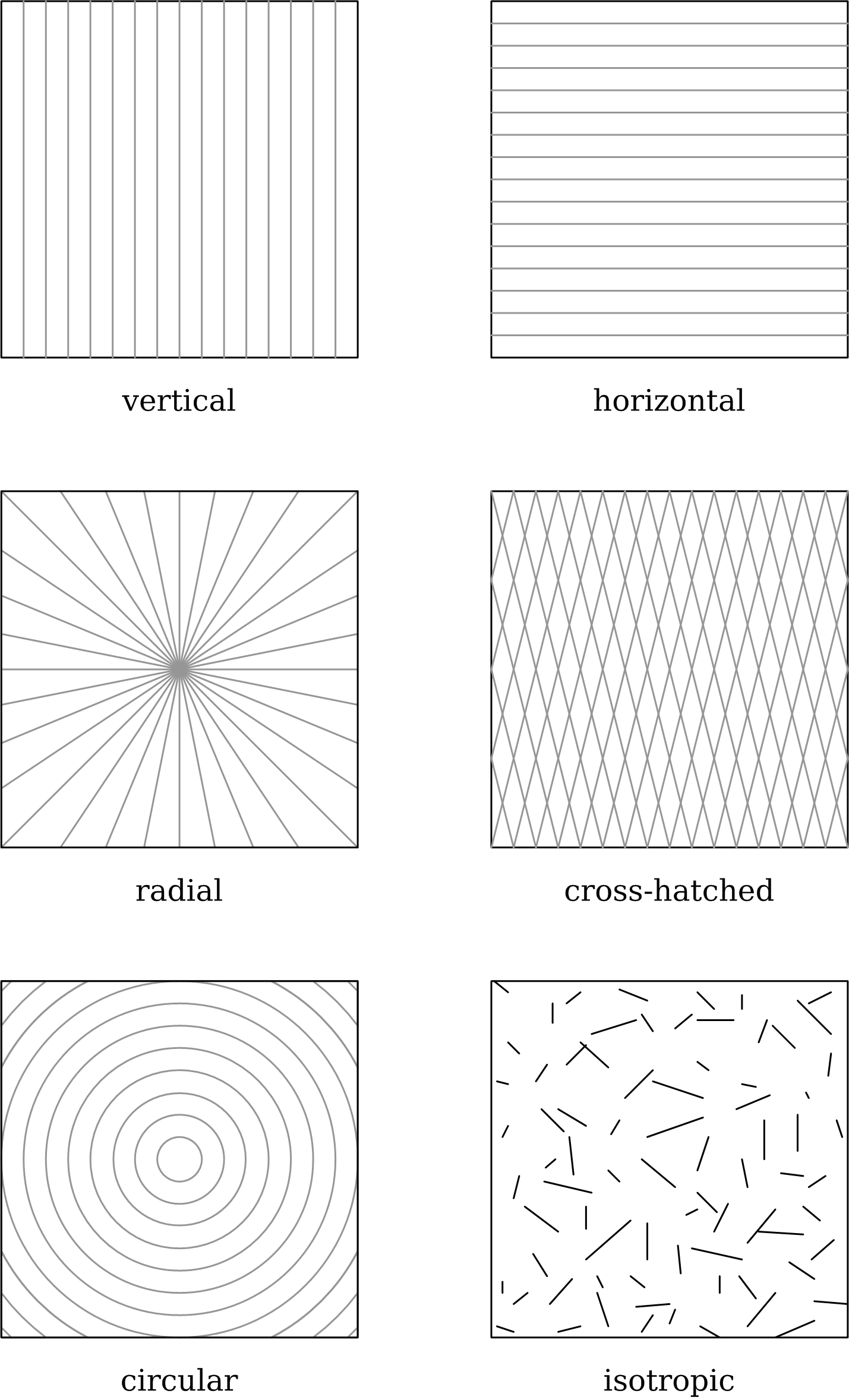
Surface Finish
Surface finish, also known as surface texture or surface topography, is the nature of a surface as defined by the three characteristics of lay, surface roughness, and waviness.. It comprises the small, local deviations of a surface from the perfectly flat ideal (a true plane). Surface texture is one of the important factors that control friction and transfer layer formation during sliding. Considerable efforts have been made to study the influence of surface texture on friction and wear during sliding conditions. Surface textures can be isotropic or anisotropic. Sometimes, stick-slip friction phenomena can be observed during sliding, depending on surface texture. Each manufacturing process (such as the many kinds of machining) produces a surface texture. The process is usually optimized to ensure that the resulting texture is usable. If necessary, an additional process will be added to modify the initial texture. The latter process may be grinding (abrasive cutting), polishing, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |