|
Carnot's Theorem (thermodynamics)
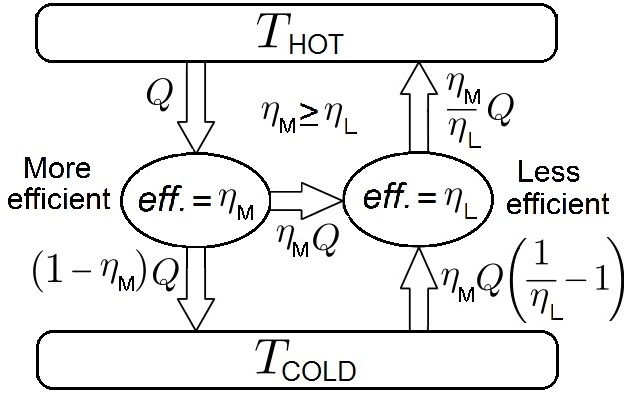
In thermodynamics, Carnot's theorem, developed in 1824 by Nicolas Léonard Sadi Carnot, also called Carnot's rule, is a principle that specifies limits on the maximum efficiency that any heat engine can obtain. Carnot's theorem states that all heat engines operating between the same two thermal or heat reservoirs can't have efficiencies greater than a reversible heat engine operating between the same reservoirs. A corollary of this theorem is that every reversible heat engine operating between a pair of heat reservoirs is equally efficient, regardless of the working substance employed or the operation details. Since a Carnot heat engine is also a reversible engine, the efficiency of all the reversible heat engines is determined as the efficiency of the Carnot heat engine that depends solely on the temperatures of its hot and cold reservoirs. The maximum efficiency (i.e., the Carnot heat engine efficiency) of a heat engine operating between cold and hot reservoirs, denoted as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thermodynamic Equations
Thermodynamics is expressed by a mathematical framework of ''thermodynamic equations'' which relate various thermodynamic quantities and physical properties measured in a laboratory or production process. Thermodynamics is based on a fundamental set of postulates, that became the laws of thermodynamics. Introduction One of the fundamental thermodynamic equations is the description of thermodynamic work in analogy to mechanical work, or weight lifted through an elevation against gravity, as defined in 1824 by French physicist Sadi Carnot. Carnot used the phrase motive power for work. In the footnotes to his famous ''On the Motive Power of Fire'', he states: “We use here the expression ''motive power'' to express the useful effect that a motor is capable of producing. This effect can always be likened to the elevation of a weight to a certain height. It has, as we know, as a measure, the product of the weight multiplied by the height to which it is raised.” With the inc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proof By Contradiction
In logic and mathematics, proof by contradiction is a form of proof that establishes the truth or the validity of a proposition, by showing that assuming the proposition to be false leads to a contradiction. Proof by contradiction is also known as indirect proof, proof by assuming the opposite, and ''reductio ad impossibile''. It is an example of the weaker logical refutation '' reductio ad absurdum''. A mathematical proof employing proof by contradiction usually proceeds as follows: #The proposition to be proved is ''P''. #We assume ''P'' to be false, i.e., we assume ''¬P''. #It is then shown that ''¬P'' implies falsehood. This is typically accomplished by deriving two mutually contradictory assertions, ''Q'' and ''¬Q'', and appealing to the Law of noncontradiction. #Since assuming ''P'' to be false leads to a contradiction, it is concluded that ''P'' is in fact true. An important special case is the existence proof by contradiction: in order to demonstrate the existence o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carnot Battery
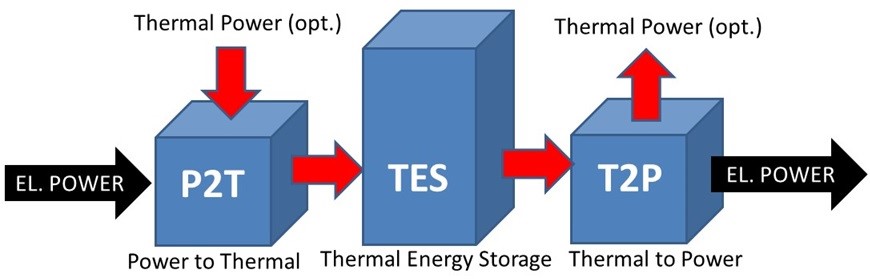
A Carnot battery is a type of energy storage system that stores electricity in thermal energy storage. During the charging process, electricity is converted into heat and kept in heat storage. During the discharging process, the stored heat is converted back into electricity. Moreover, “Marguerre” patented the concept of this technology 100 years ago but the development of this concept has only recently been revitalized for increasing the shares of energy delivered by renewable sources. On the other hand, “Andre Thess” invented the term of Carnot battery in 2018, before the first International Workshop on Carnot Batteries. The name "Carnot battery" comes from Carnot's theorem, which describes the maximum efficiency of converting heat into mechanical energy. The word "battery" indicates that the purpose of this technology is to store electricity. The discharge efficiency of Carnot batteries is limited by the Carnot efficiency. The German Aerospace Center (DLR) and Unive ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battery (electricity)
An electric battery is a source of electric power consisting of one or more electrochemical cells with external connections for powering electrical devices. When a battery is supplying power, its positive terminal is the cathode and its negative terminal is the anode. The terminal marked negative is the source of electrons that will flow through an external electric circuit to the positive terminal. When a battery is connected to an external electric load, a redox reaction converts high-energy reactants to lower-energy products, and the free-energy difference is delivered to the external circuit as electrical energy. Historically the term "battery" specifically referred to a device composed of multiple cells; however, the usage has evolved to include devices composed of a single cell. Primary (single-use or "disposable") batteries are used once and discarded, as the electrode materials are irreversibly changed during discharge; a common example is the alkaline battery use ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fuel Cell
A fuel cell is an electrochemical cell that converts the chemical energy of a fuel (often hydrogen fuel, hydrogen) and an oxidizing agent (often oxygen) into electricity through a pair of redox reactions. Fuel cells are different from most battery (electricity), batteries in requiring a continuous source of fuel and oxygen (usually from air) to sustain the chemical reaction, whereas in a battery the chemical energy usually comes from substances that are already present in the battery. Fuel cells can produce electricity continuously for as long as fuel and oxygen are supplied. The first fuel cells were invented by Sir William Robert Grove, William Grove in 1838. The first commercial use of fuel cells came more than a century later following the invention of the hydrogen–oxygen fuel cell by Francis Thomas Bacon in 1932. The alkaline fuel cell, also known as the Bacon fuel cell after its inventor, has been used in NASA space programs since the mid-1960s to generate power for sat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kelvin
The kelvin, symbol K, is the primary unit of temperature in the International System of Units (SI), used alongside its prefixed forms and the degree Celsius. It is named after the Belfast-born and University of Glasgow-based engineer and physicist William Thomson, 1st Baron Kelvin (1824–1907). The Kelvin scale is an absolute thermodynamic temperature scale, meaning it uses absolute zero as its null (zero) point. Historically, the Kelvin scale was developed by shifting the starting point of the much-older Celsius scale down from the melting point of water to absolute zero, and its increments still closely approximate the historic definition of a degree Celsius, but since 2019 the scale has been defined by fixing the Boltzmann constant to be exactly . Hence, one kelvin is equal to a change in the thermodynamic temperature that results in a change of thermal energy by . The temperature in degree Celsius is now defined as the temperature in kelvins minus 273.15, meaning ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heat
In thermodynamics, heat is defined as the form of energy crossing the boundary of a thermodynamic system by virtue of a temperature difference across the boundary. A thermodynamic system does not ''contain'' heat. Nevertheless, the term is also often used to refer to the thermal energy contained in a system as a component of its internal energy and that is reflected in the temperature of the system. For both uses of the term, heat is a form of energy. An example of formal vs. informal usage may be obtained from the right-hand photo, in which the metal bar is "conducting heat" from its hot end to its cold end, but if the metal bar is considered a thermodynamic system, then the energy flowing within the metal bar is called internal energy, not heat. The hot metal bar is also transferring heat to its surroundings, a correct statement for both the strict and loose meanings of ''heat''. Another example of informal usage is the term '' heat content'', used despite the fact that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
State Function
In the thermodynamics of equilibrium, a state function, function of state, or point function for a thermodynamic system is a mathematical function relating several state variables or state quantities (that describe equilibrium states of a system) that depend only on the current equilibrium thermodynamic state of the system (e.g. gas, liquid, solid, crystal, or emulsion), not the path which the system has taken to reach that state. A state function describes equilibrium states of a system, thus also describing the type of system. A state variable is typically a state function so the determination of other state variable values at an equilibrium state also determines the value of the state variable as the state function at that state. The ideal gas law is a good example. In this law, one state variable (e.g., pressure, volume, temperature, or the amount of substance in a gaseous equilibrium system) is a function of other state variables so is regarded as a state function. A state fu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thermodynamic Equilibrium
Thermodynamic equilibrium is an axiomatic concept of thermodynamics. It is an internal state of a single thermodynamic system, or a relation between several thermodynamic systems connected by more or less permeable or impermeable walls. In thermodynamic equilibrium, there are no net macroscopic flows of matter nor of energy within a system or between systems. In a system that is in its own state of internal thermodynamic equilibrium, no macroscopic change occurs. Systems in mutual thermodynamic equilibrium are simultaneously in mutual thermal, mechanical, chemical, and radiative equilibria. Systems can be in one kind of mutual equilibrium, while not in others. In thermodynamic equilibrium, all kinds of equilibrium hold at once and indefinitely, until disturbed by a thermodynamic operation. In a macroscopic equilibrium, perfectly or almost perfectly balanced microscopic exchanges occur; this is the physical explanation of the notion of macroscopic equilibrium. A thermody ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Entropy
Entropy is a scientific concept, as well as a measurable physical property, that is most commonly associated with a state of disorder, randomness, or uncertainty. The term and the concept are used in diverse fields, from classical thermodynamics, where it was first recognized, to the microscopic description of nature in statistical physics, and to the principles of information theory. It has found far-ranging applications in chemistry and physics, in biological systems and their relation to life, in cosmology, economics, sociology, weather science, climate change, and information systems including the transmission of information in telecommunication. The thermodynamic concept was referred to by Scottish scientist and engineer William Rankine in 1850 with the names ''thermodynamic function'' and ''heat-potential''. In 1865, German physicist Rudolf Clausius, one of the leading founders of the field of thermodynamics, defined it as the quotient of an infinitesimal amount of h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clausius Theorem
The Clausius theorem (1855), also known as the ''Clausius inequality'', states that for a thermodynamic system (e.g. heat engine or heat pump) exchanging heat with external thermal reservoirs and undergoing a thermodynamic cycle, :-\oint dS_\text = \oint \frac \leq 0, where \oint dS_\text is the total entropy change in the external thermal reservoirs (surroundings), \delta Q is an infinitesimal amount of heat that is from each reservoir and absorbed by the system (\delta Q > 0 if heat from the reservoir is absorbed by the system, and \delta Q 0 if heat from the reservoir is absorbed by the system, and \delta Q 0) per thermodynamic cycle while in reversible cases, no entropy is created or added to the reservoirs. If the amount of energy added by heating can be measured during the process, and the temperature can be measured during the process, then the Clausius inequality can be used to determine whether the process is reversible or irreversible by carrying out the integration ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coefficient Of Performance
The coefficient of performance or COP (sometimes CP or CoP) of a heat pump, refrigerator or air conditioning system is a ratio of useful heating or cooling provided to work (energy) required. Higher COPs equate to higher efficiency, lower energy (power) consumption and thus lower operating costs. The COP usually exceeds 1, especially in heat pumps, because, instead of just converting work to heat (which, if 100% efficient, would be a COP of 1), it pumps additional heat from a heat source to where the heat is required. Most air conditioners have a COP of 2.3 to 3.5. Less work is required to move heat than for conversion into heat, and because of this, heat pumps, air conditioners and refrigeration systems can have a coefficient of performance greater than one. However, this does not mean that they are more than 100% efficient, in other words, no heat engine can have a thermal efficiency of 100% or greater. For complete systems, COP calculations should include energy consumption o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |