|
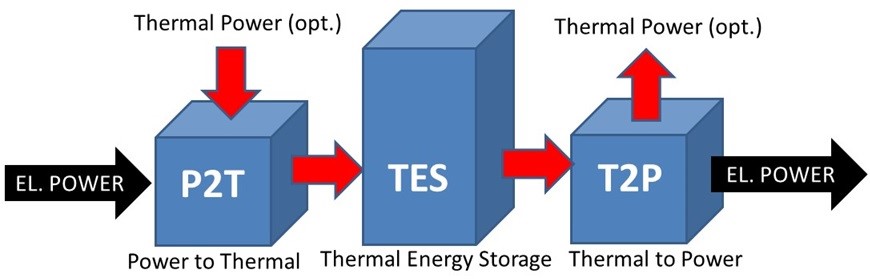
Carnot Battery
A Carnot battery is a type of energy storage system that stores electricity in thermal energy storage. During the charging process, electricity is converted into heat and kept in heat storage. During the discharging process, the stored heat is converted back into electricity. Moreover, “Marguerre” patented the concept of this technology 100 years ago but the development of this concept has only recently been revitalized for increasing the shares of energy delivered by renewable sources. On the other hand, “Andre Thess” invented the term of Carnot battery in 2018, before the first International Workshop on Carnot Batteries. The name "Carnot battery" comes from Carnot's theorem, which describes the maximum efficiency of converting heat into mechanical energy. The word "battery" indicates that the purpose of this technology is to store electricity. The discharge efficiency of Carnot batteries is limited by the Carnot efficiency. The German Aerospace Center (DLR) and Unive ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carnot Battery 01
Carnot may refer to: People *Carnot Posey (1818–1863), American lawyer and military officer People with the surname *Lazare Carnot (1753-1823), French mathematician and politician of the French Revolution *Louis Carnot (born 2001), French French footballer *Nicolas Léonard Sadi Carnot (1796-1832), French military scientist and physicist; son of Lazare Carnot * Hippolyte Carnot (1801-1888), French politician; son of Lazare Carnot *Marie François Sadi Carnot (1837-1894), French politician; President of France from 1887 to 1894 and son of Hippolyte Carnot *Marie-Adolphe Carnot (1839-1920), French mining engineer and chemist; son of Hippolyte Carnot * Paul Carnot (1869-1957), French physician; son of Marie-Adolphe Carnot * Stéphane Carnot (born 1972), former French footballer Places *Carnot, Central African Republic, a city * Carnot, Wisconsin, United States *Carnot-Moon, Pennsylvania, United States Other uses *Carnot cycle, in thermodynamics *Carnot heat engine, an idealised ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heat Pump
A heat pump is a device that can heat a building (or part of a building) by transferring thermal energy from the outside using a refrigeration cycle. Many heat pumps can also operate in the opposite direction, cooling the building by removing heat from the enclosed space and rejecting it outside. Units that only provide cooling are called air conditioners. When in heating mode, a refrigerant at outside temperature is being compressed. As a result, the refrigerant becomes hot. This thermal energy can be transferred to an indoor unit. After being moved outdoors again, the refrigerant is decompressed — evaporated. It has lost some of its thermal energy and returns colder than the environment. It can now take up the surrounding energy from the air or from the ground before the process repeats. Compressors, fans, and pumps run with electric energy. Common types are air-source heat pumps, ground-source heat pumps, water-source heat pumps and exhaust air heat pumps. They ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Steam Turbine
A steam turbine is a machine that extracts thermal energy from pressurized steam and uses it to do mechanical work on a rotating output shaft. Its modern manifestation was invented by Charles Parsons in 1884. Fabrication of a modern steam turbine involves advanced metalwork to form high-grade steel alloys into precision parts using technologies that first became available in the 20th century; continued advances in durability and efficiency of steam turbines remains central to the energy economics of the 21st century. The steam turbine is a form of heat engine that derives much of its improvement in thermodynamic efficiency from the use of multiple stages in the expansion of the steam, which results in a closer approach to the ideal reversible expansion process. Because the turbine generates rotary motion, it can be coupled to a generator to harness its motion into electricity. Such turbogenerators are the core of thermal power stations which can be fueled by fossil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heat Engine
In thermodynamics and engineering, a heat engine is a system that converts heat to mechanical energy, which can then be used to do mechanical work. It does this by bringing a working substance from a higher state temperature to a lower state temperature. A heat source generates thermal energy that brings the working substance to the higher temperature state. The working substance generates work in the working body of the engine while transferring heat to the colder sink until it reaches a lower temperature state. During this process some of the thermal energy is converted into work by exploiting the properties of the working substance. The working substance can be any system with a non-zero heat capacity, but it usually is a gas or liquid. During this process, some heat is normally lost to the surroundings and is not converted to work. Also, some energy is unusable because of friction and drag. In general, an engine is any machine that converts energy to mechanical work. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thermoelectric Materials
Thermoelectric materials show the thermoelectric effect in a strong or convenient form. The ''thermoelectric effect'' refers to phenomena by which either a temperature difference creates an electric potential or an electric current creates a temperature difference. These phenomena are known more specifically as the Seebeck effect (creating a voltage from temperature difference), Peltier effect (driving heat flow with an electric current), and Thomson effect (reversible heating or cooling within a conductor when there is both an electric current and a temperature gradient). While all materials have a nonzero thermoelectric effect, in most materials it is too small to be useful. However, low-cost materials that have a sufficiently strong thermoelectric effect (and other required properties) are also considered for applications including power generation and refrigeration. The most commonly used thermoelectric material is based on bismuth telluride (). Thermoelectric materials ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latent Heat Thermal Energy Storage
Energy storage is the capture of energy produced at one time for use at a later time to reduce imbalances between energy demand and energy production. A device that stores energy is generally called an accumulator or battery. Energy comes in multiple forms including radiation, chemical, gravitational potential, electrical potential, electricity, elevated temperature, latent heat and kinetic. Energy storage involves converting energy from forms that are difficult to store to more conveniently or economically storable forms. Some technologies provide short-term energy storage, while others can endure for much longer. Bulk energy storage is currently dominated by hydroelectric dams, both conventional as well as pumped. Grid energy storage is a collection of methods used for energy storage on a large scale within an electrical power grid. Common examples of energy storage are the rechargeable battery, which stores chemical energy readily convertible to electricity to operate a mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liquid Air
Liquid air is air that has been cooled to very low temperatures ( cryogenic temperatures), so that it has condensed into a pale blue mobile liquid. To thermally insulate it from room temperature, it is stored in specialized containers ( vacuum insulated flasks are often used). Liquid air can absorb heat rapidly and revert to its gaseous state. It is often used for condensing other substances into liquid and/or solidifying them, and as an industrial source of nitrogen, oxygen, argon, and other inert gases through a process called air separation. Properties Liquid air has a density of approximately . The density of a given air sample varies depending on the composition of that sample (e.g. humidity & concentration). Since dry gaseous air contains approximately 78% nitrogen, 21% oxygen, and 1% argon, the density of liquid air at standard composition is calculated by the percentage of the components and their respective liquid densities (see liquid nitrogen and liquid oxygen). Alth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rock (geology)
In geology, rock (or stone) is any naturally occurring solid mass or aggregate of minerals or mineraloid matter. It is categorized by the minerals included, its chemical composition, and the way in which it is formed. Rocks form the Earth's outer solid layer, the crust, and most of its interior, except for the liquid outer core and pockets of magma in the asthenosphere. The study of rocks involves multiple subdisciplines of geology, including petrology and mineralogy. It may be limited to rocks found on Earth, or it may include planetary geology that studies the rocks of other celestial objects. Rocks are usually grouped into three main groups: igneous rocks, sedimentary rocks and metamorphic rocks. Igneous rocks are formed when magma cools in the Earth's crust, or lava cools on the ground surface or the seabed. Sedimentary rocks are formed by diagenesis and lithification of sediments, which in turn are formed by the weathering, transport, and deposition of exis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Molten Salt
Molten salt is salt which is solid at standard temperature and pressure but enters the liquid phase due to elevated temperature. Regular table salt has a melting point of 801 °C (1474°F) and a heat of fusion of 520 J/g.Journal of Chemical Thermodynamicsbr>Proc. Roy. Soc. Bibliography C.F. Baes, ''The chemistry and thermodynamics of molten salt reactor fuels'', Proc. AIME Nuclear Fuel Reprocessing Symposium, Ames, Iowa, USA, 1969 (August 25) {{Authority control Energy storage Metallurgical processes Inorganic solvents Ionic liquids ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latent Heat
Latent heat (also known as latent energy or heat of transformation) is energy released or absorbed, by a body or a thermodynamic system, during a constant-temperature process — usually a first-order phase transition. Latent heat can be understood as energy in hidden form which is supplied or extracted to change the state of a substance without changing its temperature. Examples are latent heat of fusion and latent heat of vaporization involved in phase changes, i.e. a substance condensing or vaporizing at a specified temperature and pressure. The term was introduced around 1762 by Scottish chemist Joseph Black. It is derived from the Latin ''latere'' (''to lie hidden''). Black used the term in the context of calorimetry where a heat transfer caused a volume change in a body while its temperature was constant. In contrast to latent heat, sensible heat is energy transferred as heat, with a resultant temperature change in a body. Usage The terms ″sensible heat″ and ″l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sensible Heat
Sensible heat is heat exchanged by a body or thermodynamic system in which the exchange of heat changes the temperature of the body or system, and some macroscopic variables of the body or system, but leaves unchanged certain other macroscopic variables of the body or system, such as volume or pressure. Usage The term is used in contrast to a latent heat, which is the amount of heat exchanged that is hidden, meaning it occurs without change of temperature. For example, during a phase change such as the melting of ice, the temperature of the system containing the ice and the liquid is constant until all ice has melted. The terms latent and sensible are correlative. The sensible heat of a thermodynamic process may be calculated as the product of the body's mass (''m'') with its specific heat capacity (''c'') and the change in temperature (\Delta T): : Q_ = m c \Delta T \, . ''Sensible heat'' and ''latent heat'' are not special forms of energy. Rather, they describe exchanges of he ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liquefaction Of Gases
Liquefaction of gases is physical conversion of a gas into a liquid state (condensation). The liquefaction of gases is a complicated process that uses various compressions and expansions to achieve high pressures and very low temperatures, using, for example, turboexpanders. Uses Liquefaction processes are used for scientific, industrial and commercial purposes. Many gases can be put into a liquid state at normal atmospheric pressure by simple cooling; a few, such as carbon dioxide, require pressurization as well. Liquefaction is used for analyzing the fundamental properties of gas molecules (intermolecular forces), or for the storage of gases, for example: LPG, and in refrigeration and air conditioning. There the gas is liquefied in the '' condenser'', where the heat of vaporization is released, and evaporated in the '' evaporator,'' where the heat of vaporization is absorbed. Ammonia was the first such refrigerant, and is still in widespread use in industrial refrigeration ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |