|
Capture Of Delhi (1753)
The plunder of Old Delhi took place on 10 March 1753. Background The Mughal emperor had taken back the domain of Awadh and Allahabad from Safdar Jang, and to avenge his humiliation, Safdar Jang rebelled and attacked Delhi. Battle On 13 May Safdar Jang was dismissed as wazir and appointed in his place Intixam, with Imad as Mir Bakshi. On Suraj's advice, Safdar Jang reacted by appointing Akbar Ādilshāh as emperor. On 14 May the Jats sacked Chārbāg, Bāg-e-kultāt and Hakīm Munīm Bridge, and the next day Jaisinghpura, burning several areas. On 16 May the Jats attacked Delhi and defeated Sādil Khan and Raja Devidatta in a battle. On 17 May, the Jats captured Feroz Shah Kotla. In the fight against the rohillas, the Jats rode bulls and threw cannonballs with bare hands. Najib Khan was wounded and 400 Rohilla pathans died. Aftermath Imad-ul-Mulk being the de-facto ruler of Delhi called for help from the Marathas and instigated them to attack Jat territory. The Marathas laid sieg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Delhi
Delhi, officially the National Capital Territory (NCT) of Delhi, is a city and a union territory of India containing New Delhi, the capital of India. Straddling the Yamuna river, primarily its western or right bank, Delhi shares borders with the state of Uttar Pradesh in the east and with the state of Haryana in the remaining directions. The NCT covers an area of . According to the 2011 census, Delhi's city proper population was over 11 million, while the NCT's population was about 16.8 million. Delhi's urban agglomeration, which includes the satellite cities of Ghaziabad, Faridabad, Gurgaon and Noida in an area known as the National Capital Region (NCR), has an estimated population of over 28 million, making it the largest metropolitan area in India and the second-largest in the world (after Tokyo). The topography of the medieval fort Purana Qila on the banks of the river Yamuna matches the literary description of the citadel Indraprastha in the Sanskrit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Old Delhi
Old Delhi or Purani Dilli is an area in the Central Delhi district of Delhi, India. It was founded as a walled city named Shahjahanabad in 1648, when Shah Jahan (the Mughal emperor at the time) decided to shift the Mughal capital from Agra. The construction of the city was completed in 1648, and it remained the capital of the Mughal Empire until its fall in 1857, when the British Raj took over as paramount power in India. It was once filled with mansions of nobles and members of the royal court, along with elegant mosques and gardens. It serves as the symbolic heart of metropolitan Delhi and is known for its bazaars, street food, shopping locations and its Islamic architecture; Jama Masjid being the most notable example, standing tall in the midst of the old city. Only a few havelis are left and maintained. Upon the 2012 trifurcation of the Municipal Corporation of Delhi, Old Delhi became administered by the North Delhi Municipal Corporation History The site of ''Sh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Military History Of Delhi
A military, also known collectively as armed forces, is a heavily armed, highly organized force primarily intended for warfare. It is typically authorized and maintained by a sovereign state, with its members identifiable by their distinct military uniform. It may consist of one or more military branches such as an army, navy, air force, space force, marines, or coast guard. The main task of the military is usually defined as defence of the state and its interests against external armed threats. In broad usage, the terms ''armed forces'' and ''military'' are often treated as synonymous, although in technical usage a distinction is sometimes made in which a country's armed forces may include both its military and other paramilitary forces. There are various forms of irregular military forces, not belonging to a recognized state; though they share many attributes with regular military forces, they are less often referred to as simply ''military''. A nation's military may ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
18th Century In Delhi
18 (eighteen) is the natural number following 17 and preceding 19. In mathematics * Eighteen is a composite number, its divisors being 1, 2, 3, 6 and 9. Three of these divisors (3, 6 and 9) add up to 18, hence 18 is a semiperfect number. Eighteen is the first inverted square-prime of the form ''p''·''q''2. * In base ten, it is a Harshad number. * It is an abundant number, as the sum of its proper divisors is greater than itself (1+2+3+6+9 = 21). It is known to be a solitary number, despite not being coprime to this sum. * It is the number of one-sided pentominoes. * It is the only number where the sum of its written digits in base 10 (1+8 = 9) is equal to half of itself (18/2 = 9). * It is a Fine number. In science Chemistry * Eighteen is the atomic number of argon. * Group 18 of the periodic table is called the noble gases. * The 18-electron rule is a rule of thumb in transition metal chemistry for characterising and predicting the stability of metal complexes. In re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1757 In India
Events in the year 1757 in India. Events National income - ₹9,322 million *January – Recapture of Calcutta. * Battle of Plassey.''Everyman's Dictionary of Dates''; 6th ed. J. M. Dent, 1971; p. 261 References India India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the so ... Years of the 18th century in India {{India-year-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conflicts In 1753
Conflict may refer to: Arts, entertainment, and media Films * ''Conflict'' (1921 film), an American silent film directed by Stuart Paton * ''Conflict'' (1936 film), an American boxing film starring John Wayne * ''Conflict'' (1937 film), a Swedish drama film directed by Per-Axel Branner * ''Conflict'' (1938 film), a French drama film directed by Léonide Moguy * ''Conflict'' (1945 film), an American suspense film starring Humphrey Bogart * ''Catholics: A Fable'' (1973 film), or ''The Conflict'', a film starring Martin Sheen * ''Judith'' (1966 film) or ''Conflict'', a film starring Sophia Loren * ''Samar'' (1999 film) or ''Conflict'', a 1999 Indian film by Shyam Benegal Games * ''Conflict'' (series), a 2002–2008 series of war games for the PS2, Xbox, and PC * ''Conflict'' (video game), a 1989 Nintendo Entertainment System war game * '' Conflict: Middle East Political Simulator'', a 1990 strategy computer game Literature and periodicals * ''Conflict'' (novel) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Capture Of Delhi (1771)
The Capture of Delhi was a battle in 1771 when the forces of the Maratha Empire led by Mahadaji Shinde captured Delhi along with the Red Fort, and giving Mughal Emperor Shah Alam II the throne back with treaty. The Marathas captured Delhi from Najib Khan who wads put in charge by the Afghans. With this battle Marathas regained their lost supremacy in North India after the Third Battle of Panipat and conquered much of the lost territories which they lost after the Third Battle of Panipat. In the Third Battle of Panipat, the Maratha Empire suffered a serious blow at the hands of the Muslim axis of the Durrani Empire, Nawab of Awadh, and Rohillas under Najib ad-Dawlah. After the death of Peshwa Balaji Baji Rao Bhat, Madhavrao I became Peshwa under the regency of Raghunathrao Bhat. Mahadji Shinde's victory over Jats of Mathura, Rajputs of Rajasthan and Pashtun-Rohillas of Rohilkhand (in the western part of present-day Uttar Pradesh state) re-established the Marathas in the north ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Delhi (other)
Battle of Delhi may refer to: * Siege of Delhi, 1303, fought between the Mongol Chagatai Khanate and the Delhi Sultanate * Battle of Delhi (1398), fought between the Timurids and the Tughlaq dynasty * Battle of Tughlaqabad (1556), also known as the Battle of Delhi, fought between the Mughals and Hemu * Battle of Delhi (1737), fought between the Mughal Empire and Maratha Empire * Battle of Delhi (1757), fought between the Maratha Empire and Rohilla Afghans * Battle of Delhi (1764), fought between Bharatpur State and Mughal Empire * Capture of Delhi (1771) fought between Marathas under Mahadji Shinde and Rohillas under Najib ad-Dawlah * Battle of Delhi (1783), fought between the Sikhs and the Mughal Empire * Battle of Delhi (1803), fought between the Maratha Empire and British East India Company * Siege of Delhi (1804), fought between the Maratha Empire and British East India Company * Siege of Delhi in 1857, a battle fought between British East India Company and Indian Rebels Se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Najib Khan
Najib ad-Dawlah ( ps, نجيب الدوله), also known as Najib Khan Yousafzai ( ps, نجيب خان), was a Rohilla Yousafzai Afghan who earlier served as a Mughal serviceman but later deserted the cause of the Mughals and joined Ahmed Shah Abdali in 1757 in his attack on Delhi. He was also a House chief of Rohilkhand, and in the 1740s founded the city of Najibabad in Bijnor district, India. He was instrumental in winning the Third Battle of Panipat. He began his career in 1743 as an immigrant from the village Swabi, District Swabi Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, as a soldier. He was an employee of Imad-ul-Mulk but later deserted the cause of the Mughals and joined Ahmed Shah Abdali in 1757 in his attack on Delhi. He was then appointed as ''Mir Bakshi'' of the Mughal emperor by Abdali. Later in his career he was known as Najib ad-Dawlah, Amir al-Umra, Shuja ad-Dawlah. From 1757 to 1770, he was governor of Saharanpur, ruling over Dehradun. Many architectural relics of the period of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Feroz Shah Kotla
The Feroz Shah Kotla or Kotla ("fortress", "citadel") was a fortress built by Feroz Shah Tughlaq to house his version of Delhi city called Firozabad. A pristine polished sandstone Topra Ashokan pillar from the 3rd century BC rises from the palace's crumbling remains, one of many pillars of Ashoka left by the Mauryan emperor; it was moved from Topra Kalan in Pong Ghati of Yamunanagar district in Haryana to Delhi under orders of Firoz Shah Tughlaq of Delhi Sultanate, and re-erected in its present location in 1356. The original inscription on the obelisk is primarily in Brahmi script but language was Prakrit, with some Pali and Sanskrit added later. The inscription was successfully translated in 1837 by James Prinsep. This and other ancient ''lats'' (pillars, obelisk) have earned Firoz Shah Tughlaq and Delhi Sultanate fame for its architectural patronage. Other than the Ashokan Pillar, the Fort complex also houses the Jami Masjid (Mosque), a ''Baoli'' and a large garden complex. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
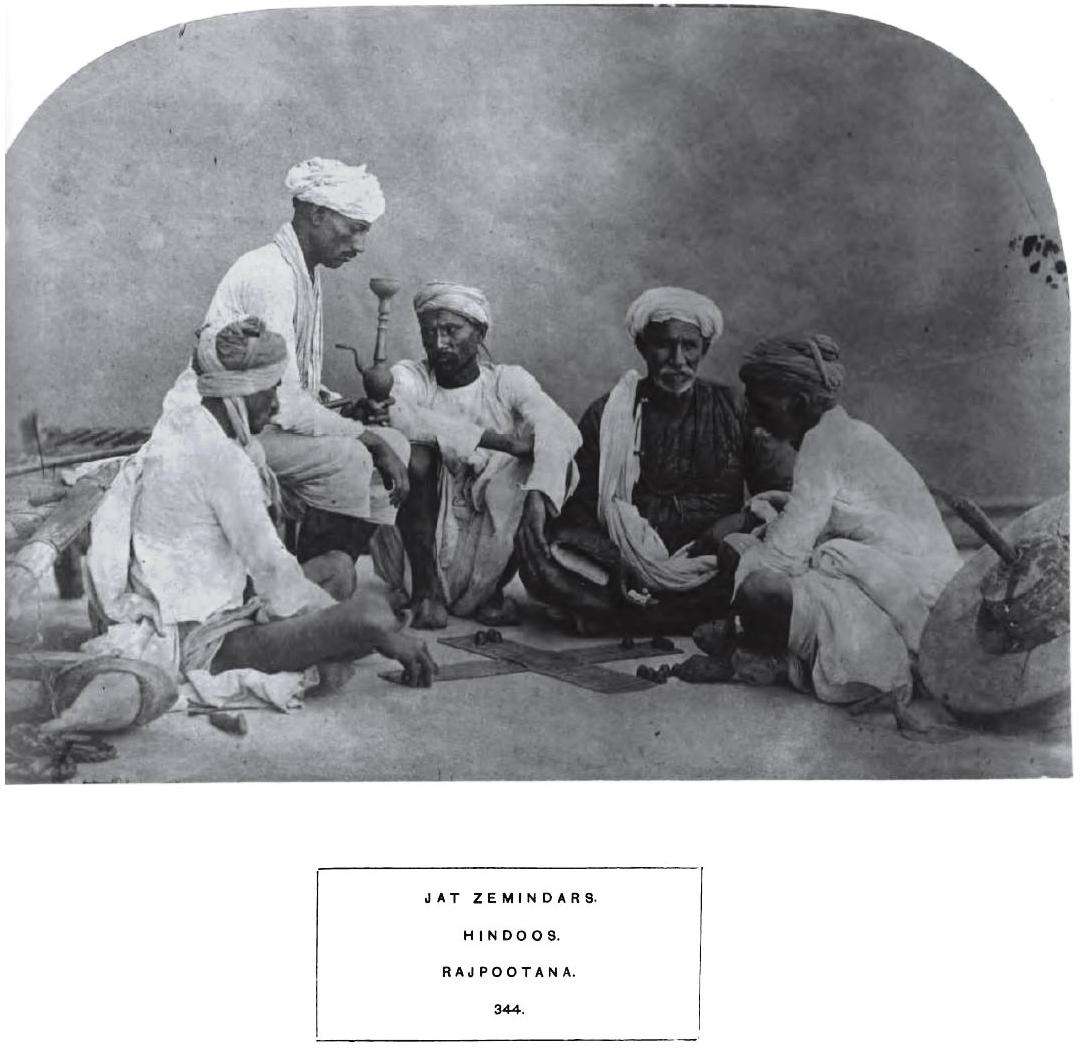
Jat People
The Jat people ((), ()) are a traditionally agricultural community in Northern India and Pakistan. Originally pastoralists in the lower Indus river-valley of Sindh, Jats migrated north into the Punjab region in late medieval times, and subsequently into the Delhi Territory, northeastern Rajputana, and the western Gangetic Plain in the 17th and 18th centuries. Quote: "Hiuen Tsang gave the following account of a numerous pastoral-nomadic population in seventh-century Sin-ti (Sind): 'By the side of the river.. f Sind along the flat marshy lowlands for some thousand li, there are several hundreds of thousands very great manyfamilies ..hichgive themselves exclusively to tending cattle and from this derive their livelihood. They have no masters, and whether men or women, have neither rich nor poor.' While they were left unnamed by the Chinese pilgrim, these same people of lower Sind were called Jats' or 'Jats of the wastes' by the Arab geographers. The Jats, as 'dromedary men.' we ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Safdar Jang
Abul Mansur Mirza Muhammad Muqim Ali Khan (c. 1708 – 5 October 1754), better known as Safdar Jang, was a major figure at the Mughal court during the declining years of the Mughal Empire. He became the second Nawab of Awadh when he succeeded Saadat Ali Khan I (his maternal uncle and father-in-law) in 1739. All future Nawabs of Oudh were patriarchal descendants of Safdar Jang. Biography He was a descendant of Qara Yusuf of the Kara Koyunlu. In 1739, he succeeded his father-in-law and maternal uncle, Burhan-ul-Mulk Saadat Ali Khan I to the throne of Oudh and ruled from 19 March 1739 to 5 October 1754.. The Mughal Emperor Muhammad Shah gave him the title of "Safdar Jang". Safdar Jang was an able administrator. He was not only effective in keeping control of Awadh, but also managed to render valuable assistance to the weakened Emperor Muhammad Shah. He was soon given governorship of Kashmir as well, and became a central figure at the Delhi court. During the later years of Muhamm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |