|
Capetians
The Capetian dynasty (; french: Capétiens), also known as the House of France, is a dynasty of Frankish origin, and a branch of the Robertians. It is among the largest and oldest royal houses in Europe and the world, and consists of Hugh Capet, the founder of the dynasty, and his male-line descendants, who ruled in France without interruption from 987 to 1792, and again from 1814 to 1848. The senior line ruled in France as the House of Capet from the election of Hugh Capet in 987 until the death of Charles IV in 1328. That line was succeeded by cadet branches, the Houses of Valois and then Bourbon, which ruled without interruption until the French Revolution abolished the monarchy in 1792. The Bourbons were restored in 1814 in the aftermath of Napoleon's defeat, but had to vacate the throne again in 1830 in favor of the last Capetian monarch of France, Louis Philippe I, who belonged to the House of Orléans. Cadet branches of the Capetian House of Bourbon house are still r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robertians
The Robertians (sometimes called the Robertines in modern scholarship) are the proposed Frankish family which was ancestral to the Capetian dynasty, and thus to the royal families of France and of many other countries. The Capetians appear first in the records as powerful nobles serving under the Carolingian dynasty of Charlemagne in West Francia, which later became France. As their power increased, they came into conflict with the older royal family and attained the crown several times before the eventual start of the continuous rule of the descendants of Hugh Capet (ruled 987–996). Hugh's paternal ancestral family, the Robertians, appear in documents that can trace them back to his great-grandfather Robert the Strong (d. 866). His origins remain unclear, but medieval records hint at an origin in East Francia, in present-day Germany, an area then still also ruled by the Carolingians. In particular, Regino of Prüm (died 915 CE) states that Robert the Strong's son Odo was said ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Armorial Of The Capetian Dynasty
Most of the members of the Capetian dynasty bore a version of the arms of France. The arms of France were adopted by the Capetian kings only in the twelfth century. Consequently, the cadet branches that had branched off in earlier periods (Burgundy, Vermandois, Dreux and Courtenay) bore entirely different arms. Today, many coat of arms of places in France are derived from the royal arms of the French king. French royal family Crowns of the princes of the blood Basic Marks of Difference France Ancient The most basic marks of difference used by the Capetians were the label, bordure and bend. Charges and variations were added by cadets with the expansion of the dynasty. The cross and saltire were used as marks of distinction by the spiritual peers of France. France Modern Under the House of Bourbon the bend gules gradually evolved into a baton couped, while the label argent and bordure gules were associated with the dukes of Orleans and Anjou, respectively. Cadet Branch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
King Of France
France was ruled by Monarch, monarchs from the establishment of the West Francia, Kingdom of West Francia in 843 until the end of the Second French Empire in 1870, with several interruptions. Classical French historiography usually regards Clovis I () as the first king of France, however historians today consider that such a kingdom did not begin until the establishment of West Francia. Titles The kings used the title "King of the Franks" ( la, Rex Francorum) until the late twelfth century; the first to adopt the title of "King of France" (Latin: ''Rex Franciae''; French language, French: ''roi de France'') was Philip II of France, Philip II in 1190 (r. 1180–1223), after which the title "King of the Franks" gradually lost ground. However, ''Francorum Rex'' continued to be sometimes used, for example by Louis XII of France, Louis XII in 1499, by Francis I of France, Francis I in 1515, and by Henry II of France, Henry II in about 1550; it was also used on coins up to the e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic, Pacific and Indian Oceans. Its metropolitan area extends from the Rhine to the Atlantic Ocean and from the Mediterranean Sea to the English Channel and the North Sea; overseas territories include French Guiana in South America, Saint Pierre and Miquelon in the North Atlantic, the French West Indies, and many islands in Oceania and the Indian Ocean. Due to its several coastal territories, France has the largest exclusive economic zone in the world. France borders Belgium, Luxembourg, Germany, Switzerland, Monaco, Italy, Andorra, and Spain in continental Europe, as well as the Netherlands, Suriname, and Brazil in the Americas via its overseas territories in French Guiana and Saint Martin. Its eighteen integral regions (five of which are overseas) span a combined area of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
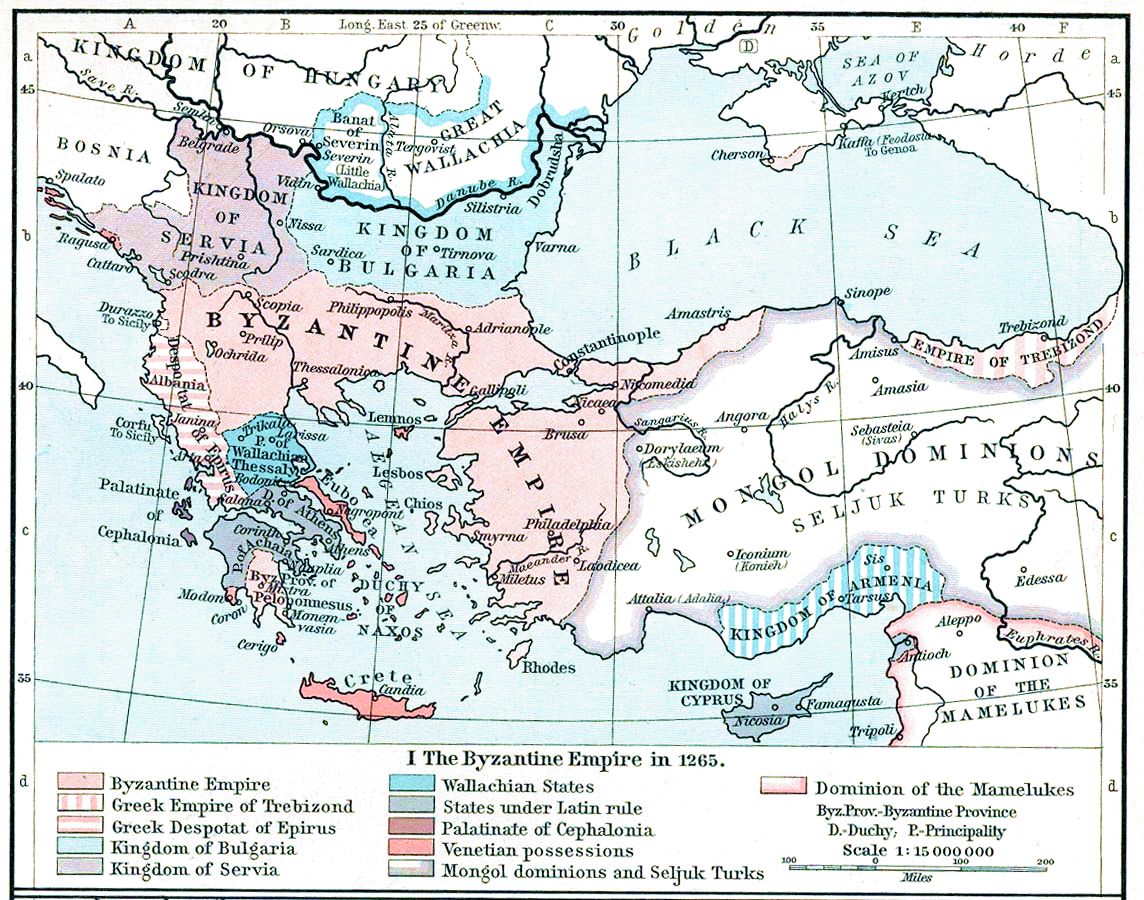
King Of Thessalonica
The King of Thessalonica was the ruler of the Kingdom of Thessalonica, one of the crusader states founded in Greece in the aftermath of the Fourth Crusade (1202–1204). The King of Thessalonica was not an independent ruler; the Kingdom of Thessalonica was one of several vassal states created by the crusaders, subservient to the new Latin Empire of Constantinople, which had supplanted the Byzantine Empire. The kingdom proved to be short-lived, with Thessalonica being captured by Theodore Komnenos Doukas of Epirus in 1224, just twenty years after the kingdom had been founded. The last king, Demetrius of Montferrat, escaped into exile and upon his death ceded the title to Frederick II, Holy Roman Emperor, who some years later ceded it back to Demetrius's family. Their line of titular Kings of Thessalonica ended with the marriage of Yolande of Montferrat to Byzantine emperor Andronikos II Palaiologos in 1284, at which point titular ownership of Thessalonica passed back to the By ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
King Of Hungary
The King of Hungary ( hu, magyar király) was the ruling head of state of the Kingdom of Hungary from 1000 (or 1001) to 1918. The style of title "Apostolic King of Hungary" (''Apostoli Magyar Király'') was endorsed by Pope Clement XIII in 1758 and used afterwards by all Monarchs of Hungary. The term "King of Hungary" is typically capitalized only as a title applied to a specific person; however, within this article, the terms "Kings of Hungary" or "Junior Kings" (etc.) are also shown in capital letters, as in the manner of philosophical writing which capitalizes concepts such as Truth, Kindness and Beauty. Establishment of the title Before 1000 AD, Hungary was not recognized as a kingdom and the ruler of Hungary was styled Grand Prince of the Hungarians. The first King of Hungary, Stephen I. was crowned on 25 December 1000 (or 1 January 1001) with the crown Pope Sylvester II had sent him and with the consent of Otto III, Holy Roman Emperor. Fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingdom Of Northern Lusitania
The Kingdom of Northern Lusitania ( Portuguese: ''Reino da Lusitânia Setentrional'') was a kingdom proposed by Napoleon in 1807 for the king of Etruria, Charles Louis, located in the North of Portugal. In 1807 Portugal refused Napoleon's demand to accede to the Continental System of embargo against the United Kingdom. Napoleon, having signed the Treaty of Fontainebleau on 27 October 1807, with Spain, defined the occupation of Portugal, proposing that the country would be divided into three different states: *the ''Kingdom of Northern Lusitania'' (in the north of Portugal, between the rivers Douro and Minho and including main cities as Porto and Braga; named after the Roman province of Lusitania and to be ruled by the deposed king of Etruria, Charles II; *''Portugal'' (reduced to the region between the rivers Douro and Tagus, including the capital city of Lisbon; to be ruled directly by France); *the ''Principality of the Algarves'' (corresponding to all southern Portugal, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
King Of Sicily
The monarchs of Sicily ruled from the establishment of the County of Sicily in 1071 until the "perfect fusion" in the Kingdom of the Two Sicilies in 1816. The origins of the Sicilian monarchy lie in the Norman conquest of southern Italy which occurred between the 11th and 12th century. Sicily, which was ruled as an Islamic emirate for at least two centuries, was invaded in 1071 by Norman House of Hauteville, who conquered Palermo and established a feudal county. The House of Hauteville completed their conquest of Sicily in 1091. In 1130, the County of Sicily and the County of Apulia, ruled by different branches of the House of Hauteville, merged as the Kingdom of Sicily, and Count Roger II was crowned king by Antipope Anacletus II. In 1282, after the Sicilian Vespers, the kingdom split into separate states: the properly named "Ultra Sicily" (''Siciliae ultra Pharum'', Latin for "Sicily over the Strait") and "Hither Sicily" (''Siciliae citra'', commonly called "the Kin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
King Of Sardinia
The following is a list of rulers of Sardinia, in particular, of the monarchs of the Kingdom of Sardinia and Corsica from 1323 and then of the Kingdom of Sardinia from 1479 to 1861. Early history Owing to the absence of written sources, little is known of the history of the Nuraghic civilization which constructed impressive megalithic structures between the 18th and the 12th centuries BCE. The first accounts of Sardinia are from Greek sources, but relate more to myth than to historical reality; an African or Iberian hero, Norax, named the city of Nora; Sardo, a son of Hercules, gave the island its name; one of his nephews, Iolaus, founded the city of Olbia. Greek colonization of the city of Olbia has been confirmed by recent archaeological excavations. Towards the end of the 6th century BC, Sardinia was conquered by the Carthaginians and in 238 BC it was occupied by the Romans for c.1000 years, with a period under the dominion of the Vandals in the 5th and 6th centuries ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingdom Of Albania (medieval)
The Kingdom of Albania (, lat, Regnum Albaniae) was established by Charles of Anjou in the Albanian territories he conquered from the Byzantine Empire in 1271, with the help of the local Albanian nobility. The Kingdom of Albania was declared in late February 1272. The kingdom extended from the region of Durazzo (Dyrrhachium, modern Durrës) south along the coast to Butrint. A major attempt to advance further in direction of Constantinople failed at the Siege of Berat (1280–1281). A Byzantine counteroffensive soon ensued, which drove the Angevins out of the interior by 1281. The Sicilian Vespers further weakened the position of Charles, and the Kingdom was soon reduced by the Byzantines to a small area around Durazzo. The Angevins held out here, however, until 1368, when the city was captured by Karl Thopia. In 1392, Karl Thopia's son surrendered the city to the Republic of Venice. History Background During the conflict between the Despotate of Epirus and the Empire o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
King Of Poland
Poland was ruled at various times either by dukes and princes (10th to 14th centuries) or by kings (11th to 18th centuries). During the latter period, a tradition of free election of monarchs made it a uniquely electable position in Europe (16th to 18th centuries). The first known Polish ruler is Duke Mieszko I, who adopted Christianity under the authority of Rome in the year 966. He was succeeded by his son, Bolesław I the Brave, who greatly expanded the boundaries of the Polish state and ruled as the first king in 1025. The following centuries gave rise to the mighty Piast dynasty, consisting of both kings such as Mieszko II Lambert, Przemysł II or Władysław I the Elbow-high and dukes like Bolesław III Wrymouth. The dynasty ceased to exist with the death of Casimir III the Great in 1370. In the same year, the Capetian House of Anjou became the ruling house with Louis I as king of both Poland and Hungary. His daughter, Jadwiga, later married Jogaila, the pagan Grand ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |