|
Candoluminescence
Candoluminescence is the light given off by certain materials at elevated temperatures (usually when exposed to a flame) that has an intensity at some wavelengths which can, through chemical action in flames, be higher than the blackbody emission expected from incandescence at the same temperature.H.F. Ivey, "Candoluminescence and radical-excited luminescence," ''Journal of Luminescence'' 8:4, pp. 271–307 (1974) The phenomenon is notable in certain transition-metal and rare-earth oxide materials (ceramics) such as zinc oxide, cerium(IV) oxide and thorium dioxide. History The existence of the candoluminescence phenomenon and the underlying mechanism have been the subject of extensive research and debate since the first reports of it in the 1800s. The topic was of particular interest before the introduction of electric lighting, when most artificial light was produced by fuel combustion. The main alternative explanation for candoluminescence is that it is simply "selective" thermal e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gas Mantle
A Coleman white gas lantern mantle glowing at full brightness An incandescent gas mantle, gas mantle or Welsbach mantle is a device for generating incandescent bright white light when heated by a flame. The name refers to its original heat source in gas lights which illuminated the streets of Europe and North America in the late 19th century. ''Mantle'' refers to the way it hangs like a cloak above the flame. Gas mantles were also used in portable camping lanterns, pressure lanterns and some oil lamps. Gas mantles are usually sold as fabric items, which, because of impregnation with metal nitrates, burns away to leave a rigid but fragile mesh of metal oxides when heated during initial use; these metal oxides produce light from the heat of the flame whenever used. Thorium dioxide was commonly a major component; being radioactive, it has led to concerns about the safety of those involved in manufacturing mantles. Normal use, however, poses minimal health risk. Mechanism l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Limelight
Limelight (also known as Drummond light or calcium light)James R. Smith (2004). ''San Francisco's Lost Landmarks'', Quill Driver Books. is a type of stage lighting once used in theatres and music halls. An intense illumination is created when a flame fed by oxygen and hydrogen is directed at a cylinder of quicklime (calcium oxide), which can be heated to before melting. The light is produced by a combination of incandescence and candoluminescence. Although it has long since been replaced by electric lighting, the term has nonetheless survived, as someone in the public eye is still said to be "in the limelight". The actual lamps are called "limes", a term which has been transferred to electrical equivalents. History Discovery and invention The limelight effect was discovered in the 1820s by Goldsworthy Gurney, based on his work with the "oxy-hydrogen blowpipe", credit for which is normally given to Robert Hare. In 1825, a Scottish engineer, Thomas Drummond (1797–1840), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Light
Light or visible light is electromagnetic radiation that can be perceived by the human eye. Visible light is usually defined as having wavelengths in the range of 400–700 nanometres (nm), corresponding to frequencies of 750–420 terahertz, between the infrared (with longer wavelengths) and the ultraviolet (with shorter wavelengths). In physics, the term "light" may refer more broadly to electromagnetic radiation of any wavelength, whether visible or not. In this sense, gamma rays, X-rays, microwaves and radio waves are also light. The primary properties of light are intensity, propagation direction, frequency or wavelength spectrum and polarization. Its speed in a vacuum, 299 792 458 metres a second (m/s), is one of the fundamental constants of nature. Like all types of electromagnetic radiation, visible light propagates by massless elementary particles called photons that represents the quanta of electromagnetic field, and can be analyzed as both waves and par ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fluorescence
Fluorescence is the emission of light by a substance that has absorbed light or other electromagnetic radiation. It is a form of luminescence. In most cases, the emitted light has a longer wavelength, and therefore a lower photon energy, than the absorbed radiation. A perceptible example of fluorescence occurs when the absorbed radiation is in the ultraviolet region of the electromagnetic spectrum (invisible to the human eye), while the emitted light is in the visible region; this gives the fluorescent substance a distinct color that can only be seen when the substance has been exposed to UV light. Fluorescent materials cease to glow nearly immediately when the radiation source stops, unlike phosphorescent materials, which continue to emit light for some time after. Fluorescence has many practical applications, including mineralogy, gemology, medicine, chemical sensors (fluorescence spectroscopy), fluorescent labelling, dyes, biological detectors, cosmic-ray detection, vacu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catalytic Converter
A catalytic converter is an exhaust emission control device that converts toxic gases and pollutants in exhaust gas from an internal combustion engine into less-toxic pollutants by catalyzing a redox reaction. Catalytic converters are usually used with internal combustion engines fueled by gasoline or diesel, including lean-burn engines, and sometimes on kerosene heaters and stoves. The first widespread introduction of catalytic converters was in the United States automobile market. To comply with the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency's stricter regulation of exhaust emissions, most gasoline-powered vehicles starting with the 1975 model year are equipped with catalytic converters. These "two-way" converters combine oxygen with carbon monoxide (CO) and unburned hydrocarbons (HC) to produce carbon dioxide (CO2) and water (H2O). Although two-way converters on gasoline engines were rendered obsolete in 1981 by "three-way" converters that also reduce oxides of nitrogen (); they ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Incandescent Light Bulb
An incandescent light bulb, incandescent lamp or incandescent light globe is an electric light with a wire filament heated until it glows. The filament is enclosed in a glass bulb with a vacuum or inert gas to protect the filament from oxidation. Current is supplied to the filament by terminals or wires embedded in the glass. A bulb socket provides mechanical support and electrical connections. Incandescent bulbs are manufactured in a wide range of sizes, light output, and voltage ratings, from 1.5 volts to about 300 volts. They require no external regulating equipment, have low manufacturing costs, and work equally well on either alternating current or direct current. As a result, the incandescent bulb became widely used in household and commercial lighting, for portable lighting such as table lamps, car headlamps, and flashlights, and for decorative and advertising lighting. Incandescent bulbs are much less efficient than other types of electric lighting, converting les ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Coblentz
William Weber Coblentz (November 20, 1873 – September 15, 1962) was an American physicist notable for his contributions to infrared radiometry and spectroscopy. Early life, education, and employment William Coblentz was born in North Lima, Ohio to parents of German and Swiss descent. His mother (Catherine) died when Coblentz was just under three, leaving him temporarily with a family of just his younger brother (Oscar) and their father (David). However, the father remarried about 2 years later, and Coblentz appears to have admired his second mother (Amelia). Throughout Coblentz's childhood and adolescence, his family lived on farms, but apparently were never able to buy one of their own. The family's extremely modest circumstances led to a somewhat-delayed education for Coblentz, who did not finish high school (Youngstown, Ohio) until 1896, when he was 22 years old. Coblentz entered the Case School of Applied Science, now Case Western Reserve University in the fall of 1896, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Herbert E
Herbert may refer to: People Individuals * Herbert (musician), a pseudonym of Matthew Herbert Name * Herbert (given name) * Herbert (surname) Places Antarctica * Herbert Mountains, Coats Land * Herbert Sound, Graham Land Australia * Herbert, Northern Territory, a rural locality * Herbert, South Australia. former government town * Division of Herbert, an electoral district in Queensland * Herbert River, a river in Queensland * County of Herbert, a cadastral unit in South Australia Canada * Herbert, Saskatchewan, Canada, a town * Herbert Road, St. Albert, Canada New Zealand * Herbert, New Zealand, a town * Mount Herbert (New Zealand) United States * Herbert, Illinois, an unincorporated community * Herbert, Michigan, a former settlement * Herbert Creek, a stream in South Dakota * Herbert Island, Alaska Arts, entertainment, and media Fictional entities * Herbert (Disney character) * Herbert Pocket (''Great Expectations'' character), Pip's close friend and roommate in the Cha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles Proteus Steinmetz
Charles Proteus Steinmetz (born Karl August Rudolph Steinmetz, April 9, 1865 – October 26, 1923) was a German-born American mathematician and electrical engineer and professor at Union College. He fostered the development of alternating current that made possible the expansion of the electric power industry in the United States, formulating mathematical theories for engineers. He made ground-breaking discoveries in the understanding of hysteresis that enabled engineers to design better electromagnetic apparatus equipment, especially electric motors for use in industry. At the time of his death, Steinmetz held over 200 patents. A genius in both mathematics and electronics, he did work that earned him the nicknames "Forger of Thunderbolts" and "The Wizard of Schenectady". Steinmetz's equation, Steinmetz solids, Steinmetz curves, and Steinmetz equivalent circuit are all named after him, as are numerous honors and scholarships, including the IEEE Charles Proteus Steinm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
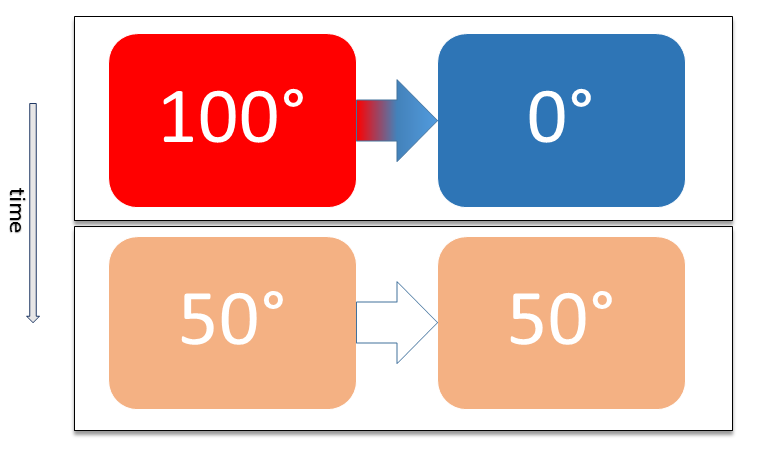
Thermal Equilibrium
Two physical systems are in thermal equilibrium if there is no net flow of thermal energy between them when they are connected by a path permeable to heat. Thermal equilibrium obeys the zeroth law of thermodynamics. A system is said to be in thermal equilibrium with itself if the temperature within the system is spatially uniform and temporally constant. Systems in thermodynamic equilibrium are always in thermal equilibrium, but the converse is not always true. If the connection between the systems allows transfer of energy as 'change in internal energy' but does not allow transfer of matter or transfer of energy as work, the two systems may reach thermal equilibrium without reaching thermodynamic equilibrium. Two varieties of thermal equilibrium Relation of thermal equilibrium between two thermally connected bodies The relation of thermal equilibrium is an instance of equilibrium between two bodies, which means that it refers to transfer through a selectively permeable p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thermalisation
In physics, thermalisation is the process of physical bodies reaching thermal equilibrium through mutual interaction. In general the natural tendency of a system is towards a state of equipartition of energy and uniform temperature that maximizes the system's entropy. Thermalisation, thermal equilibrium, and temperature are therefore important fundamental concepts within statistical physics, statistical mechanics, and thermodynamics; all of which are a basis for many other specific fields of scientific understanding and engineering application. Examples of thermalisation include: * the achievement of equilibrium in a plasma. * the process undergone by high-energy neutrons as they lose energy by collision with a moderator. The hypothesis, foundational to most introductory textbooks treating quantum statistical mechanics, assumes that systems go to thermal equilibrium (thermalisation). The process of thermalisation erases local memory of the initial conditions. The eigenstate th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catalysis
Catalysis () is the process of increasing the rate of a chemical reaction by adding a substance known as a catalyst (). Catalysts are not consumed in the reaction and remain unchanged after it. If the reaction is rapid and the catalyst recycles quickly, very small amounts of catalyst often suffice; mixing, surface area, and temperature are important factors in reaction rate. Catalysts generally react with one or more reactants to form intermediates that subsequently give the final reaction product, in the process of regenerating the catalyst. Catalysis may be classified as either homogeneous, whose components are dispersed in the same phase (usually gaseous or liquid) as the reactant, or heterogeneous, whose components are not in the same phase. Enzymes and other biocatalysts are often considered as a third category. Catalysis is ubiquitous in chemical industry of all kinds. Estimates are that 90% of all commercially produced chemical products involve catalysts at some s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)