|
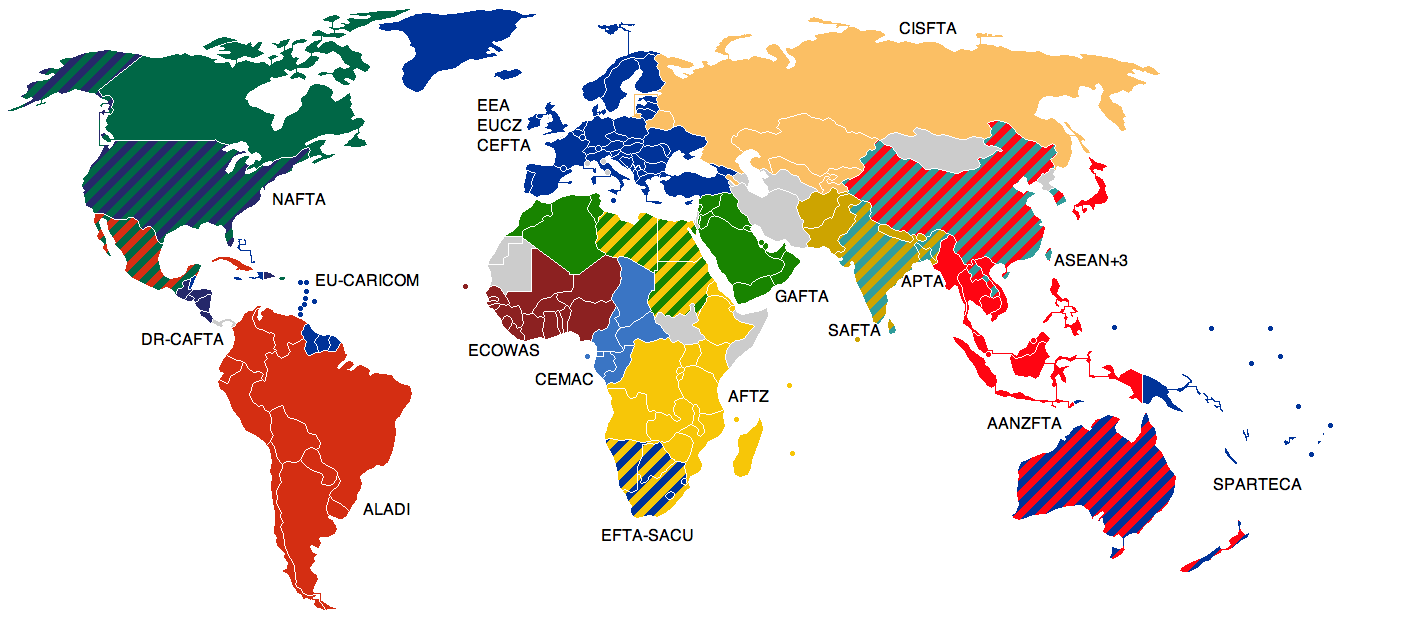
Canada–European Free Trade Association Free Trade Agreement
The Canada–European Free Trade Association Free Trade Agreement is a trade agreement between Canada and the member states of the European Free Trade Association (Iceland, Norway, Switzerland and Liechtenstein). Signed in Davos, Switzerland on January 26, 2008, it came into effect on July 1, 2009. The agreement is aimed at eliminating all tariffs on goods between Canada and EFTA members. In 1999, Canada entered into free trade negotiations with the EFTA. Negotiations concluded successfully in June 2007, and the FTA between Canada and the EFTA States was signed on January 26, 2008. Bilateral Agreements on Agriculture between Canada and each EFTA State were appended to the CEFTA. Both came into effect on July 1, 2009. The agreement eliminates almost all tariffs, with certain agricultural and fishery products being excluded from immediate tariff elimination. Bilateral trade totaled $10.7 billion in 2006 (With Canadian imports from the EFTA valued at $7.6 billion and Exports to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ACCESS
Access may refer to: Companies and organizations * ACCESS (Australia), an Australian youth network * Access (credit card), a former credit card in the United Kingdom * Access Co., a Japanese software company * Access Healthcare, an Indian BPO services provider * Access International Advisors, a hedge fund * AirCraft Casualty Emotional Support Services * Arab Community Center for Economic and Social Services * Access, the Alphabet division containing Google Fiber * Access, the Southwest Ohio Regional Transit Authority's paratransit service Sailing * Access 2.3, a sailing keelboat * Access 303, a sailing keelboat * Access Liberty, a sailing keelboat Television * ''Access Hollywood'', formerly ''Access'', an American entertainment newsmagazine * ''Access'' (British TV programme), a British entertainment television programme * ''Access'' (Canadian TV series), a Canadian television series (1974–1982) * Access TV, a former Canadian educational television channel (1973–2011) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Economy Of Iceland
The economy of Iceland is small and subject to high volatility. In 2011, gross domestic product was US$12 billion, but by 2018 it had increased to a nominal GDP of US$27 billion. With a population o350,000 this is $55,000 per capita, based on purchasing power parity (PPP) estimates.Source: Statistics Iceland. The financial crisis of 2007–2010 produced a decline in GDP and employment that has since been reversed entirely by a recovery aided by a tourism boom starting in 2010. Tourism accounted for more than 10% of Iceland's GDP in 2017. After a period of robust growth, Iceland's economy is slowing down according to an economic outlook for the years 2018–2020 published by Arion Research in April 2018. Iceland has a mixed economy with high levels of free trade and government intervention. However, government consumption is less than other Nordic countries. Hydro-power is the primary source of home and industrial electrical supply in Iceland. In the 1990s Iceland undertook extens ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Treaties Concluded In 2008
A treaty is a formal, legally binding written agreement between actors in international law. It is usually made by and between sovereign states, but can include international organizations, individuals, business entities, and other legal persons. A treaty may also be known as an international agreement, protocol, covenant, convention, pact, or exchange of letters, among other terms. However, only documents that are legally binding on the parties are considered treaties under international law. Treaties vary on the basis of obligations (the extent to which states are bound to the rules), precision (the extent to which the rules are unambiguous), and delegation (the extent to which third parties have authority to interpret, apply and make rules). Treaties are among the earliest manifestations of international relations, with the first known example being a border agreement between the Sumerian city-states of Lagash and Umma around 3100 BC. International agreements were used in s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Treaties Of Liechtenstein
A treaty is a formal, legally binding written agreement between actors in international law. It is usually made by and between sovereign states, but can include international organizations, individuals, business entities, and other legal persons. A treaty may also be known as an international agreement, protocol, covenant, convention, pact, or exchange of letters, among other terms. However, only documents that are legally binding on the parties are considered treaties under international law. Treaties vary on the basis of obligations (the extent to which states are bound to the rules), precision (the extent to which the rules are unambiguous), and delegation (the extent to which third parties have authority to interpret, apply and make rules). Treaties are among the earliest manifestations of international relations, with the first known example being a border agreement between the Sumerian city-states of Lagash and Umma around 3100 BC. International agreements were used in so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Treaties Of Norway
A treaty is a formal, legally binding written agreement between actors in international law. It is usually made by and between sovereign states, but can include international organizations, individuals, business entities, and other legal persons. A treaty may also be known as an international agreement, protocol, covenant, convention, pact, or exchange of letters, among other terms. However, only documents that are legally binding on the parties are considered treaties under international law. Treaties vary on the basis of obligations (the extent to which states are bound to the rules), precision (the extent to which the rules are unambiguous), and delegation (the extent to which third parties have authority to interpret, apply and make rules). Treaties are among the earliest manifestations of international relations, with the first known example being a border agreement between the Sumerian city-states of Lagash and Umma around 3100 BC. International agreements were used in so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Treaties Of Iceland
A treaty is a formal, legally binding written agreement between actors in international law. It is usually made by and between sovereign states, but can include international organizations, individuals, business entities, and other legal persons. A treaty may also be known as an international agreement, protocol, covenant, convention, pact, or exchange of letters, among other terms. However, only documents that are legally binding on the parties are considered treaties under international law. Treaties vary on the basis of obligations (the extent to which states are bound to the rules), precision (the extent to which the rules are unambiguous), and delegation (the extent to which third parties have authority to interpret, apply and make rules). Treaties are among the earliest manifestations of international relations, with the first known example being a border agreement between the Sumerian city-states of Lagash and Umma around 3100 BC. International agreements were used in so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Free-trade Area
A free-trade area is the region encompassing a trade bloc whose member countries have signed a free trade agreement (FTA). Such agreements involve cooperation between at least two countries to reduce trade barriers, import quotas and tariffs, and to increase trade of goods and services with each other. If natural persons are also free to move between the countries, in addition to a free-trade agreement, it would also be considered an open border. It can be considered the second stage of economic integration. Customs unions are a special type of free-trade area. All such areas have internal arrangements which parties conclude in order to liberalize and facilitate trade among themselves. The crucial difference between customs unions and free-trade areas is their approach to third parties. While a customs union requires all parties to establish and maintain identical external tariffs with regard to trade with non-parties, parties to a free-trade area are not subject to this requiremen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Market Access
In international trade, market access is a company's ability to enter a foreign market by selling its goods and services in another country. Market access is not the same as free trade, because market access is normally subject to conditions or requirements (such as tariffs or quotas), whereas under ideal free trade conditions goods and services can circulate across borders without any barriers to trade. Expanding market access is therefore often a more achievable goal of trade negotiations than achieving free trade. Market access concessions and limitations to market access differ greatly between trade in goods and trade in services. While market access for goods mainly involves measures at the border such as customs duties or quantitative restrictions, market access for services relates more to the application of domestic regulation behind the border. Moreover, in a world of proliferating regionalism, preferential market access for goods and services also have distinctive charact ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rules Of Origin
Rules of origin are the rules to attribute a country of origin to a product in order to determine its "economic nationality". The need to establish rules of origin stems from the fact that the implementation of trade policy measures, such as tariffs, quotas, trade remedies, in various cases, depends on the country of origin of the product at hand. Rules of origin have become a challenging topic in international trade, not only because they constitute a highly technical area of rule-making, but also because their designation and application have not been harmonized across the world. The lack of harmony is even more remarkable in the era of regionalism, when more and more free trade agreements (FTAs) are concluded, creating the spaghetti bowl effect. Definition of rules of origin The most comprehensive definition for rules of origin is found in the International Convention on the Simplification and Harmonization of Customs procedures (Kyoto Convention), which entered into forc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Free Trade Agreements Of Canada
The free trade agreements of Canada represents Canada's cooperation in multinational trade pacts and plays a large role in the Canadian economy. Canada is regularly described as a trading nation, considering its total trade is worth more than two-thirds of its GDP (the second highest level in the G7, after Germany). Of that total trade, roughly 75% is done with countries that are part of free-trade agreements with Canada—primarily the United States through the Canada–United States–Mexico Agreement (CUSMA), and its predecessor the North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA). By the end of 2014, Canadas bilateral trade hit Can$1 trillion for the first time. Overview Canada is a founding member of the World Trade Organization (WTO) since 1 January 1995. The ''North American Free Trade Agreement'' (NAFTA), which is held with Canada by the United States and Mexico, came into force on 1 January 1994, creating the largest free-trade region in the world by GDP. By 2014, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canada's Global Markets Action Plan
The Global Markets Action Plan (GMAP) was Prime Minister Stephen Harper's government strategy to generate employment opportunities for Canadians by expanding Canadian businesses and investment in other countries in a highly competitive global environment. After Ed Fast was appointed Minister of International Trade in 2011, Harper asked him for a blueprint prioritizing trade in Canada's foreign policy. On November 27, 2013, Fast delivered a comprehensive report on a ''Global Markets Action Plan''. History Harper's government was highly concerned to maintain Canada's competitive position in international trade, which is equivalent to more than 60 percent of Canada's annual gross domestic product; one out of five jobs was created by the global market presence. In 2007, the government launched its Global Commerce Strategy for expanding Canada's trade network, strengthening its competitive position in its traditional markets, and extending its reach to new emerging markets. The stra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Economy Of Switzerland
The economy of Switzerland is one of the world's most advanced and highly-developed free-market economies. The service sector has come to play a significant economic role, particularly the Swiss banking industry and tourism. The economy of Switzerland ranked first in the world since 2015 Global Innovation Index and third in the 2020 Global Competitiveness Report. According to United Nations data for 2016, Switzerland is the third richest landlocked country in the world after Liechtenstein and Luxembourg. Together with the latter and Norway, they are the only three countries in the world with a GDP per capita (nominal) above US$70,000 that are neither island nations nor ministates. History 19th century Switzerland as a federal state was established in 1848. Before that time, the city-cantons of Zurich, Geneva, and Basel in particular began to develop economically based on industry and trade, while the rural regions of Switzerland remained poor and underdeveloped. While ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |