|
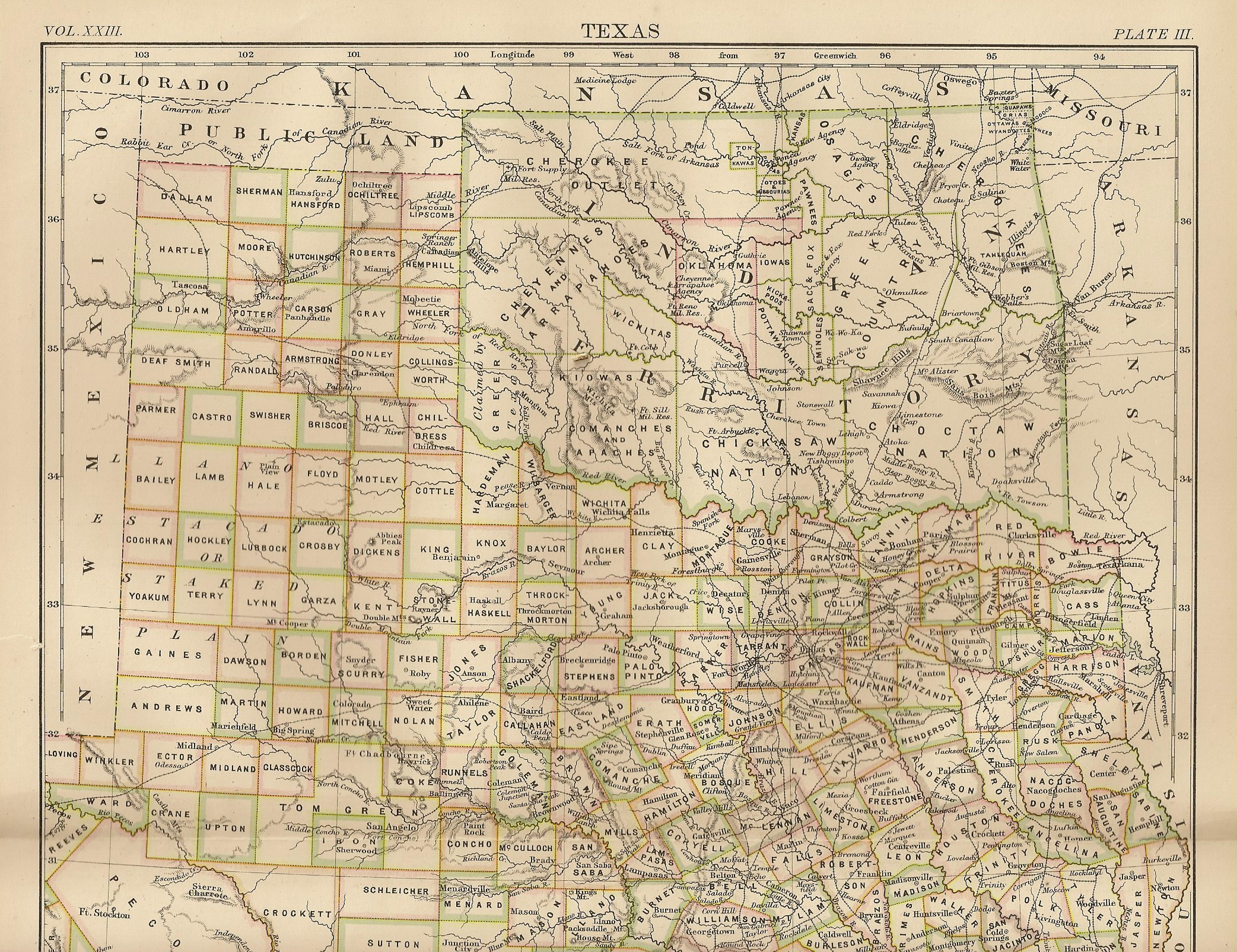
Camp Napoleon Council
The Camp Napoleon Council was a meeting of Native American tribes in today's Oklahoma that resulted in an intertribal compact. The council took place at Cottonwood Camp on May 24, 1865 near present-day Verden in Grady County. Background By early 1865, the Civil War had turned decisively against the Confederate States of America. Until then the Confederate military had provided support to maintain the Indian Territory as a buffer between Texas and the United States. However, after 1864, the South had been forced to withdraw its military forces and supplies to defend its states west of the Mississippi River. Except for the Native American troops serving the Confederate Army under General Stand Watie, the shooting war was virtually over in the Indian Territory. Pro-Confederate Indians agreed that a council of the Five Civilized Tribes, the Prairie Indians, and the Plains Indians should be held to end intertribal hostilities and to negotiate terms for their return to the United Sta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oklahoma
Oklahoma (; Choctaw language, Choctaw: ; chr, ᎣᎧᎳᎰᎹ, ''Okalahoma'' ) is a U.S. state, state in the South Central United States, South Central region of the United States, bordered by Texas on the south and west, Kansas on the north, Missouri on the northeast, Arkansas on the east, New Mexico on the west, and Colorado on the northwest. Partially in the western extreme of the Upland South, it is the List of U.S. states and territories by area, 20th-most extensive and the List of U.S. states and territories by population, 28th-most populous of the 50 United States. Its residents are known as Oklahomans and its capital and largest city is Oklahoma City. The state's name is derived from the Choctaw language, Choctaw words , 'people' and , which translates as 'red'. Oklahoma is also known informally by its List of U.S. state and territory nicknames, nickname, "Sooners, The Sooner State", in reference to the settlers who staked their claims on land before the official op ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Choctaw
The Choctaw (in the Choctaw language, Chahta) are a Native American people originally based in the Southeastern Woodlands, in what is now Alabama and Mississippi. Their Choctaw language is a Western Muskogean language. Today, Choctaw people are enrolled in three federally recognized tribes: the Choctaw Nation of Oklahoma, Mississippi Band of Choctaw Indians, and Jena Band of Choctaw Indians in Louisiana. The Choctaw were first noted by Europeans in French written records of 1675. Their mother mound is Nanih Waiya, a great earthwork platform mound located in central-east Mississippi. Early Spanish explorers of the mid-16th century in the Southeast encountered ancestral Mississippian culture villages and chiefs. The Choctaw coalesced as a people in the 17th century and developed at least three distinct political and geographical divisions: eastern, western, and southern. These different groups sometimes created distinct, independent alliances with nearby European powers. These i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Treaties Of Indigenous Peoples Of North America
A treaty is a formal, legally binding written agreement between actors in international law. It is usually made by and between sovereign states, but can include international organizations, individuals, business entities, and other legal persons. A treaty may also be known as an international agreement, protocol, covenant, convention, pact, or exchange of letters, among other terms. However, only documents that are legally binding on the parties are considered treaties under international law. Treaties vary on the basis of obligations (the extent to which states are bound to the rules), precision (the extent to which the rules are unambiguous), and delegation (the extent to which third parties have authority to interpret, apply and make rules). Treaties are among the earliest manifestations of international relations, with the first known example being a border agreement between the Sumerian city-states of Lagash and Umma around 3100 BC. International agreements were used in so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Science And Arts Of Oklahoma
The University of Science and Arts of Oklahoma (USAO) is a public liberal arts college in Chickasha, Oklahoma. It is the only public college in Oklahoma with a strictly liberal arts–focused curriculum and is a member of the Council of Public Liberal Arts Colleges. USAO is an undergraduate-only institution and grants bachelor's degrees in a variety of subject areas. The school was founded in 1908 as a school for women and from 1912 to 1965 was known as Oklahoma College for Women. It became coeducational in 1965 and today educates approximately 800 students. In 2001, the entire Oklahoma College for Women campus was listed as a national historic district., 2001, Accessed January 31, 2015. History After Oklahoma was admitted to statehood in 1907, the new state legislature was tasked with establishing institutions of higher education in the former Indian Territory. Statistics gathered by the State Superintendent of Education showed that many young women from Oklahoma chose to at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fort Smith Council
The Fort Smith Council (September 21, 1865), also known as the Indian Council, was a series of meetings held at Fort Smith, Arkansas from September 8–21, 1865, that were organized by the United States Commissioner of Indian Affairs, Dennis N. Cooley, for Indian tribes east of the Rockies (and particularly those living in what was then defined as Indian Territory).Hartzog, Martha. ''Fort Smith Council''. accessed February 3, 2017. Other members of Cooley's party representing the U. S. government were: Elijah Sells, Superintendent of Indian Affairs for the Southern Superintendency; William Harney, an Army officer who had spent most of the Civil War in Europe; |
Cheyenne
The Cheyenne ( ) are an Indigenous people of the Great Plains. Their Cheyenne language belongs to the Algonquian language family. Today, the Cheyenne people are split into two federally recognized nations: the Southern Cheyenne, who are enrolled in the Cheyenne and Arapaho Tribes in Oklahoma, and the Northern Cheyenne, who are enrolled in the Northern Cheyenne Tribe of the Northern Cheyenne Indian Reservation in Montana. The Cheyenne comprise two Native American tribes, the Só'taeo'o or Só'taétaneo'o (more commonly spelled as Suhtai or Sutaio) and the Tsétsêhéstâhese (also spelled Tsitsistas, The term for the Cheyenne homeland is ''Tsiihistano''. Language The Cheyenne of Montana and Oklahoma speak the Cheyenne language, known as ''Tsêhésenêstsestôtse'' (common spelling: Tsisinstsistots). Approximately 800 people speak Cheyenne in Oklahoma. There are only a handful of vocabulary differences between the two locations. The Cheyenne alphabet contains 14 letters. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arapahoe
The Arapaho (; french: Arapahos, ) are a Native American people historically living on the plains of Colorado and Wyoming. They were close allies of the Cheyenne tribe and loosely aligned with the Lakota and Dakota. By the 1850s, Arapaho bands formed two tribes, namely the Northern Arapaho and Southern Arapaho. Since 1878, the Northern Arapaho have lived with the Eastern Shoshone on the Wind River Reservation in Wyoming and are federally recognized as the Arapahoe Tribe of the Wind River Reservation. The Southern Arapaho live with the Southern Cheyenne in Oklahoma. Together, their members are enrolled as the federally recognized Cheyenne and Arapaho Tribes. Names It is uncertain where the word 'Arapaho' came from. Europeans may have derived it from the Pawnee word for "trader", ''iriiraraapuhu'', or it may have been a corruption of a Crow word for "tattoo", ''alapúuxaache''. The Arapaho autonym is or ("our people" or "people of our own kind"). They refer to their tribe as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kiowa
Kiowa () people are a Native American tribe and an indigenous people of the Great Plains of the United States. They migrated southward from western Montana into the Rocky Mountains in Colorado in the 17th and 18th centuries,Pritzker 326 and eventually into the Southern Plains by the early 19th century. In 1867, the Kiowa were moved to a reservation in southwestern Oklahoma. Today, they are federally recognized as Kiowa Indian Tribe of Oklahoma with headquarters in Carnegie, Oklahoma. , there were 12,000 members. The Kiowa language (Cáuijògà), part of the Tanoan language family, is in danger of extinction, with only 20 speakers as of 2012."Kiowa Tanoan" ''Ethnologue.'' Retrieved 21 June 2012. Name In the Kiowa language, Kiowa call themselves[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Comanche
The Comanche or Nʉmʉnʉʉ ( com, Nʉmʉnʉʉ, "the people") are a Native American tribe from the Southern Plains of the present-day United States. Comanche people today belong to the federally recognized Comanche Nation, headquartered in Lawton, Oklahoma. The Comanche language is a Numic language of the Uto-Aztecan family. Originally, it was a Shoshoni dialect, but diverged and became a separate language. The Comanche were once part of the Shoshone people of the Great Basin. In the 18th and 19th centuries, Comanche lived in most of present-day northwestern Texas and adjacent areas in eastern New Mexico, southeastern Colorado, southwestern Kansas, and western Oklahoma. Spanish colonists and later Mexicans called their historical territory ''Comanchería''. During the 18th and 19th centuries, Comanche practiced a nomadic horse culture and hunted, particularly bison. They traded with neighboring Native American peoples, and Spanish, French, and American colonists and set ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Osage Nation
The Osage Nation ( ) ( Osage: 𐓁𐒻 𐓂𐒼𐒰𐓇𐒼𐒰͘ ('), "People of the Middle Waters") is a Midwestern Native American tribe of the Great Plains. The tribe developed in the Ohio and Mississippi river valleys around 700 BC along with other groups of its language family. They migrated west after the 17th century, settling near the confluence of the Missouri and Mississippi rivers, as a result of Iroquois invading the Ohio Valley in a search for new hunting grounds. The term "Osage" is a French version of the tribe's name, which can be roughly translated as "calm water". The Osage people refer to themselves in their indigenous Dhegihan Siouan language as 𐓏𐒰𐓓𐒰𐓓𐒷 ('), or "Mid-waters". By the early 19th century, the Osage had become the dominant power in the region, feared by neighboring tribes. The tribe controlled the area between the Missouri and Red rivers, the Ozarks to the east and the foothills of the Wichita Mountains to the south. They depe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caddo
The Caddo people comprise the Caddo Nation of Oklahoma, a federally recognized tribe headquartered in Binger, Oklahoma. They speak the Caddo language. The Caddo Confederacy was a network of Indigenous peoples of the Southeastern Woodlands, who historically inhabited much of what is now East Texas, west Louisiana, southwestern Arkansas, and southeastern Oklahoma. Prior to European contact, they were the Caddoan Mississippian culture, who constructed huge earthwork mounds at several sites in this territory, flourishing about 800 to 1400 CE. In the early 19th century, Caddo people were forced to a reservation in Texas. In 1859, they were removed to Indian Territory. Government and civic institutions The Caddo Nation of Oklahoma was previously known as the Caddo Tribe of Oklahoma. The tribal constitution provides for election of an eight-person council, with a chairperson. Some 6,000 people are enrolled in the nation, with 3,044 living within the state of Oklahoma. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |