|
Camille Pelletan
Charles Camille Pelletan (28 June 1846 – 4 June 1915) was a French politician, historian and journalist, Minister of Marine (France), Minister of Marine in Emile Combes' ''Bloc des gauches'' (Left-Wing Blocks) cabinet from 1902 to 1905. He was part of the left-wing of the Republican, Radical and Radical-Socialist Party, created in 1902. Biography Pelletan was born in Paris, the son of Eugène Pelletan (1813–1884), a writer of some distinction and a noted opponent of the Second French Empire, Second Empire. Camille Pelletan was educated in Paris, passed as licentiate in laws, and studied at the ''École Nationale des Chartes'' where he was qualified as an "archiviste paléographe". At the age of twenty he became an active journalist, and a bitter critic of the Imperial Government. After the Franco-Prussian War, war of 1870-71 he took a leading place among the Radical Party (France), Radicals, as an opponent of the "Opportunist Republicans" who continued the policy of Léon Gam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pelletan Camille
Pelletan is a French surname. Notable people with the surname include: * Camille Pelletan (1846–1915), French politician and journalist * Eugène Pelletan (1813–1884), French writer, journalist and politician * Louis Pelletan, Governor General of Pondicherry in the Second French Colonial Empire * Philippe-Jean Pelletan (1747–1829), French surgeon and member of the French Academy of Sciences See also * Pelletan Point, a headland of Graham Land, Antarctica {{surname French-language surnames ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alfred Gaulier
Alfred Gaulier (10 November 1829 – 17 January 1898) was a French journalist and politician. His father was a cavalry officer and he seemed destined for a military career. At the time of the coup that brought Napoleon III to power he was a sub-lieutenant in the infantry. He signed a document voting against the coup, and was forced to resign. After a difficult period, he found work as a journalist throughout the remainder of the Second French Empire and the early years of the French Third Republic. He was a radical republican, and was elected deputy for the Seine department from 1886 to 1889. Early years Alfred Nicolas Gaulier was born on 10 November 1829 in Paris. His parents were Jean-Baptiste Gaulier (b. 1772), retired cavalry squadron leader, Knight of Saint-Louis and Officer of the Legion of Honour, and Anne Antoinette Gouget (b. 1802). His grandfather, René Gaulier, was a carpenter. His father had participated in most of the campaigns of the French First Republic and F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Naval Ministers Of France
One of France's Secretaries of State under the Ancien Régime was entrusted with control of the French Navy (Secretary of State of the Navy (France).) In 1791, this title was changed to Minister of the Navy. Before January 1893, this position also had responsibility for France's colonies, and was usually known as Minister of the Navy and Colonies, a role thereafter taken by the Minister of the Overseas. In 1947 the naval ministry was absorbed into the Ministry of Defence, with the exception of merchant marine affairs which had been split in 1929 to the separate Ministry of Merchant Marine. History The two French royal fleets (the Ponant fleet and Levant fleet) were put under the control of Colbert from 1662, whilst he was "intendant des finances" and "minister of state" – but not "secretary of state" : he only became secretary of state in 1669 after having bought his way into the post. From then on, right up to the French Revolution, a secretary of state had responsibili ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Republican, Radical And Radical-Socialist Party (historical)
The Republican, Radical and Radical-Socialist Party (french: Parti républicain, radical et radical-socialiste) is a liberal and formerly social-liberal political party in France. It is also often referred to simply as the Radical Party (french: Parti radical), or to prevent confusion with other French Radical parties as the ''Parti radical valoisien'' (after its headquarters on the rue de Valois), abbreviated to Rad, PR, PRV, or historically PRRRS. Founded in 1901, it is the oldest active political party in France. Coming from the Radical Republican tradition, the Radical Party upheld the principles of private property, social justice and secularism. The Radicals were originally a left-wing group, but with the emergence of the French Section of the Workers' International (SFIO) in 1905 they shifted gradually towards the political centre. In 1926, its right wing split off to form the Unionist (or National) Radicals. In 1972, the left wing of the party split off to form the centr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dreyfus Affair
The Dreyfus affair (french: affaire Dreyfus, ) was a political scandal that divided the French Third Republic from 1894 until its resolution in 1906. "L'Affaire", as it is known in French, has come to symbolise modern injustice in the Francophone world, and it remains one of the most notable examples of a complex miscarriage of justice and antisemitism. The role played by the press and public opinion proved influential in the conflict. The scandal began in December 1894 when Captain Alfred Dreyfus was convicted of treason. Dreyfus was a 35-year-old Alsatian French artillery officer of Jewish descent. He was falsely convicted and sentenced to life imprisonment for communicating French military secrets to the German Embassy in Paris, and was imprisoned on Devil's Island in French Guiana, where he spent nearly five years. In 1896, evidence came to light—primarily through an investigation made by Georges Picquart, head of counter-espionage—which identified the real culprit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1898 French Legislative Election
Legislative elections were held in France on 8 and 22 May 1898. The government of Jules Méline, who had been premier since April 1896, had relied on the support of Conservatives, contrary to the convention of republican concentration, according to which no government should rely on the support of monarchists and Bonapartists in the Chamber of Deputies if it could not rely on a republican majority. The elections were dominated by the Dreyfus Affair, and saw several notable supporters of Dreyfus (Joseph Reinach, Jean Jaurès, Jules Guesde) lose their seats. Twenty-two professed anti-Semites were also elected, including Édouard Drumont. Overall, however, the election saw the defeat of Méline and his supporters: the Radicals were victorious, allowing Henri Brisson to form a republican government.Gildea, R., ''Children of the Revolution'', London, 2008, p275 Results References External linksMap of Deputies elected in 1898 according to their group in the House, including overs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1893 French Legislative Election
The 1893 general election was held on 20 August and 3 September 1893. The Republicans were victorious and gained an increased majority, and President Sadi Carnot invited Jean Casimir-Perier to form a government. However, there was increasing tension between the Radicals and the Moderates in the ruling coalition, which had manifested itself in the passage of a protectionist tariff law with right-wing support in January 1892. After the election, following the bombing of the Chamber of Deputies by the anarchist Auguste Vaillant on 9 December 1893, Casimir-Perier rushed through the ''lois scélérates'' with the support of the Right. Casimir-Perier was elected to the presidency on 24 June 1894, following the assassination of President Carnot by the Italian anarchist Sante Geronimo Caserio. In January 1895, however, he resigned, and was replaced by Félix Faure, again with the support of the Right. Casimir-Perier's government was followed by a series of moderate governments with r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1889 French Legislative Election
The 1889 general election was held on 22 September and 6 October 1889, during the Boulanger affair. It resulted in a victory for the Republicans, and a thorough defeat for the Boulangists. Results , - style="background-color:#E9E9E9; text-align:center;" , - , colspan="6" , , - ! colspan="3" style="text-align:left;" , Parties and coalitions ! Votes ! % ! Seats , - , rowspan="4" style="background-color:#FFC6D5;border-bottom-style:hidden;" , , style="background-color:;", , style="text-align:left;", Democratic Union , 2,974,565 , 37.4 , 214 , - , style="background-color:#E0B0FF;", , style="text-align:left;", Independent Radicals , 1,375,935 , 17.3 , 69 , - , style="background-color:#DE0000;", , style="text-align:left;", Radical Socialists , , , 57 , - , style="background-color:;", , style="text-align:left;", Liberal Republican Union , 516,970 , 6.5 , 14 , - style="background-color:#FFC6D5;" , colspan="3" style="text-align:left;", Anti-Boulangis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Département In France
In the administrative divisions of France, the department (french: département, ) is one of the three levels of government under the national level ("territorial collectivities"), between the administrative regions and the communes. Ninety-six departments are in metropolitan France, and five are overseas departments, which are also classified as overseas regions. Departments are further subdivided into 332 arrondissements, and these are divided into cantons. The last two levels of government have no autonomy; they are the basis of local organisation of police, fire departments and, sometimes, administration of elections. Each department is administered by an elected body called a departmental council ( ing. lur.. From 1800 to April 2015, these were called general councils ( ing. lur.. Each council has a president. Their main areas of responsibility include the management of a number of social and welfare allowances, of junior high school () buildings and technical staff, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bouches-du-Rhône
Bouches-du-Rhône ( , , ; oc, Bocas de Ròse ; "Mouths of the Rhône") is a department in Southern France. It borders Vaucluse to the north, Gard to the west and Var to the east. The Mediterranean Sea lies to the south. Its prefecture and largest city is Marseille; other important cities include Aix-en-Provence, Arles, Martigues and Aubagne. Marseille, France's second-largest city, has one of the largest container ports in the country. It prizes itself as France's oldest city, founded by Greek settlers from Phocaea around 600 BC. Bouches-du-Rhône is the most populous department of the Provence-Alpes-Côte d'Azur region, with 2,043,110 inhabitants as of 2019.Populations légales 2019: 13 Bouches-du-Rhône INSEE It has an area of . Its [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1885 French Legislative Election
Legislative elections were held in France on 4 and 18 October 1885. Following the deaths of Napoléon, Prince Imperial and the Comte de Chambord, the monarchists and Bonapartists formed a conservative electoral alliance under the leadership of the Baron de Mackau. In the first round of the election, the conservatives won 176 seats, whereas the Opportunist Republicans - partly because radical and moderate Republicans ran against each other, underestimating the danger from the right - only won 127. However, in the second round the radical and moderate Republicans agreed that the worse-placed Republican candidates would withdraw, and Republicans won 244 seats to the conservatives' 25, leading to a Republican victory.Gildea, R., ''Children of the Revolution'', London, 2008, p. 257 Henri Brisson remained prime minister immediately after the election, but resigned in December following his defeat in the presidential election to the incumbent, Jules Grévy. Brisson was replaced by Charl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
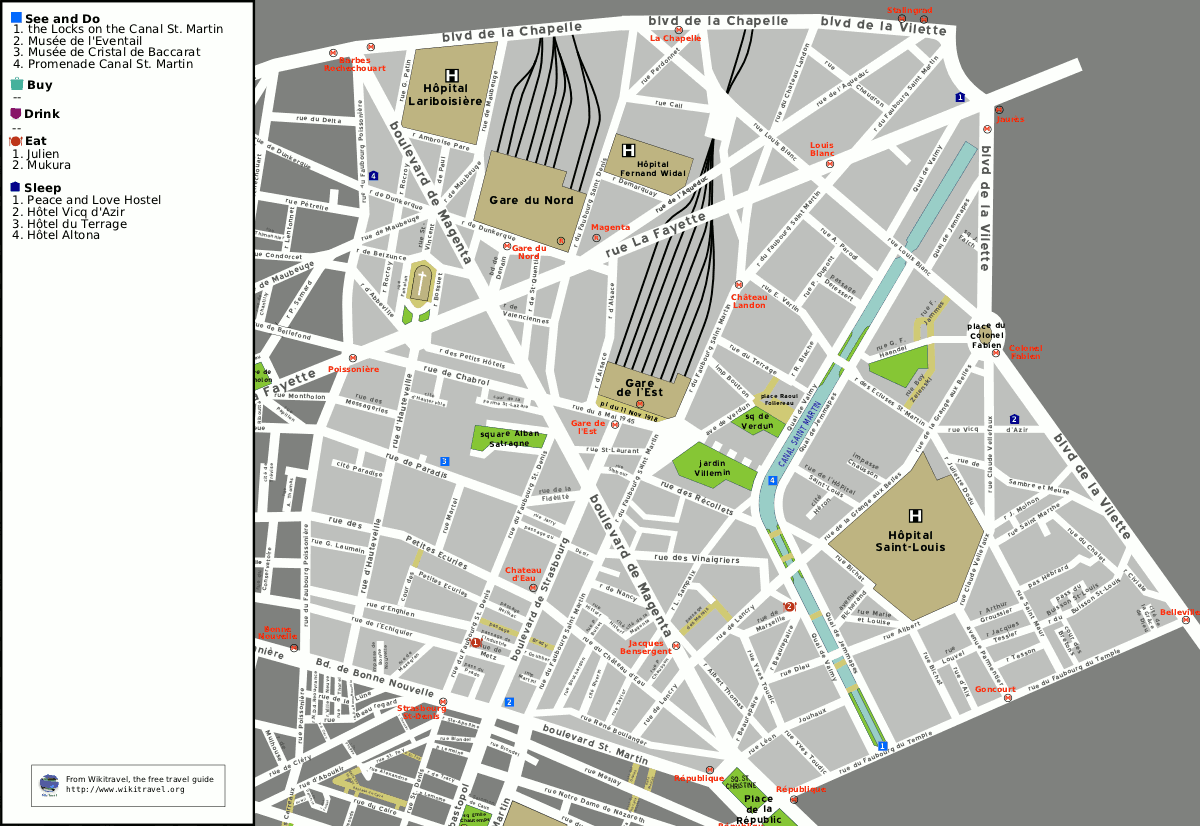
10th Arrondissement Of Paris
The 10th arrondissement of Paris (''Xe arrondissement'') is one of the 20 arrondissements of the capital city of France. In spoken French, this arrondissement is referred to as ''dixième'' ("10th arrondissement of Paris" = "dixième arrondissement de Paris"). The arrondissement, called Entrepôt (warehouse), is situated on the right bank of the River Seine. The arrondissement contains two of Paris's six main railway stations: the Gare du Nord and the Gare de l'Est. Built during the 19th century, these two termini are among the busiest in Europe. The 10th arrondissement also contains a large portion of the Canal Saint-Martin, linking the northeastern parts of Paris with the River Seine. Geography The land area of the arrondissement is 2.892 km2 (1.117 sq. miles, or 715 acres), and it had a 1999 population of 89,695. The 10th arrondissement is often referred to as ''l'Entrepôt''. Like all Parisian arrondissements, it is divided into four quartiers (districts):All demogra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)