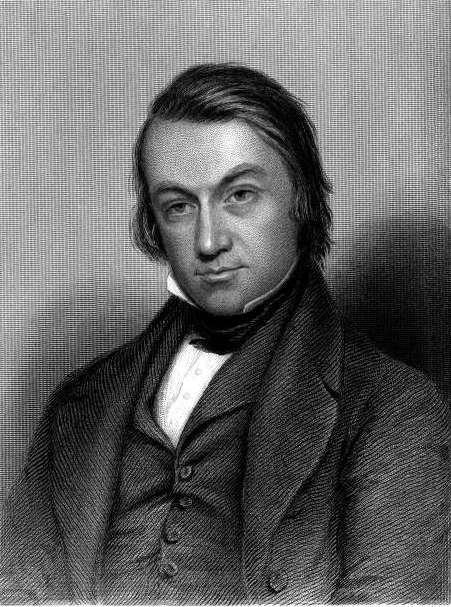|
Caledonian Asylum
The Royal Caledonian School was a residential home and school for Scottish people, Scottish orphans, initially in London and subsequently in Bushey, Hertfordshire. History The Caledonian Asylum was launched by members of the Highland Society of London in 1815 to provide a home and education for Scottish children in London who had been orphaned in the Napoleonic Wars. John Galt (novelist), John Galt, the novelist, became secretary to the Asylum in 1815. The first Asylum was at 16 Cross Street, Hatton Garden, London from December 1819 until 1828 when it relocated to Copenhagen Fields, Islington. Its long residence in Islington resulted in the naming of Caledonian Market and the Caledonian Road (London), Caledonian Road. In 1852 Victoria of the United Kingdom, Queen Victoria became Patronage#Charity, Patron and the Asylum was renamed the Royal Caledonian Schools, although legally it was and still is the "Caledonian Asylum". At that time it catered for about 70 boys and 50 girls. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Patronage
Patronage is the support, encouragement, privilege, or financial aid that an organization or individual bestows on another. In the history of art, arts patronage refers to the support that kings, popes, and the wealthy have provided to artists such as musicians, painters, and sculptors. It can also refer to the right of bestowing offices or Benefice, church benefices, the business given to a store by a regular customer, and the patron saint, guardianship of saints. The word "patron" derives from the la, patronus ("patron"), one who gives benefits to his clients (see Patronage in ancient Rome). In some countries the term is used to describe political patronage or patronal politics, which is the use of state resources to reward individuals for their electoral support. Some patronage systems are legal, as in the Canadian tradition of the Prime Minister to appoint Senate of Canada, senators and the heads of a number of commissions and agencies; in many cases, these appointments go to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Defunct Schools In Hertfordshire
{{Disambiguation ...
Defunct (no longer in use or active) may refer to: * ''Defunct'' (video game), 2014 * Zombie process or defunct process, in Unix-like operating systems See also * * :Former entities * End-of-life product * Obsolescence Obsolescence is the state of being which occurs when an object, service, or practice is no longer maintained or required even though it may still be in good working order. It usually happens when something that is more efficient or less risky r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
James Thomson (B
James, Jamie, Jim, or Jimmy Thomson may refer to: Arts and letters * James Thomson (architect, born 1852) (1852–1927), Scottish architect, city architect of Dundee * James Thomson (poet, born 1700) (1700–1748), Scottish poet and playwright * James Thomson (weaver poet) (1763–1832), Scottish poet * James Thomson (poet, born 1834) (1834–1882), Scottish poet and essayist * James Thomson (engraver) (1788–1850), English engraver, known for his portraits * James Thomson (journalist) (1852–1934), Australian journalist and newspaper owner * James Thomson (minister) (1768–1855), Scottish editor of the ''Encyclopædia Britannica'' * James M. Thomson (newspaper publisher) (1878–1959), American newspaper publisher * Jamie Thomson (author) (born 1958), author of gamebooks Politicians * James Thomson (Australian politician) (1856–?), New South Wales politician * James Thomson (London politician) (born 1966), Common Councilman, Walbrook ward * James Thomson (Manitoba politicia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Melbourne
Melbourne ( ; Boonwurrung/Woiwurrung: ''Narrm'' or ''Naarm'') is the capital and most populous city of the Australian state of Victoria, and the second-most populous city in both Australia and Oceania. Its name generally refers to a metropolitan area known as Greater Melbourne, comprising an urban agglomeration of 31 local municipalities, although the name is also used specifically for the local municipality of City of Melbourne based around its central business area. The metropolis occupies much of the northern and eastern coastlines of Port Phillip Bay and spreads into the Mornington Peninsula, part of West Gippsland, as well as the hinterlands towards the Yarra Valley, the Dandenong and Macedon Ranges. It has a population over 5 million (19% of the population of Australia, as per 2021 census), mostly residing to the east side of the city centre, and its inhabitants are commonly referred to as "Melburnians". The area of Melbourne has been home to Aboriginal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malcolm McEacharn
Sir Malcolm Donald McEacharn (8 February 1852 – 10 March 1910) was Mayor of Melbourne from 1897 to 1900. He was a well-known Australian shipping magnate in the early part of the twentieth century and successfully stood for the Division of Melbourne at the inaugural federal election, held in 1901. Early life McEacharn was born in London on 8 February 1852 to a master mariner Malcolm and his wife Ann, née Gay, both from the Isle of Islay, Scotland. His father died in a shipwreck two years later, and, as the son of a dead sailor, the Royal Caledonian School in Islington cared for and educated him for seven years when he was of school age. In 1866, at age 14, he joined a London shipping office named Rucker, Offor & Co. He began his own shipbroking business in 1873 at age 21. Two years later he partnered with Andrew McIlwraith, to found McIlwraith, McEacharn & Co. in London. He married his first wife Ann Peirson, from a landowning family near Pickering, in Goathland, North ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles Mackay (author)
Charles Mackay (27 March 1814 – 24 December 1889) was a Scottish poet, journalist, author, anthologist, novelist, and songwriter, remembered mainly for his book ''Extraordinary Popular Delusions and the Madness of Crowds''. Early life Charles Mackay was born in Perth, Scotland. His father, George Mackay, was a bombardier in the Royal Artillery, and his mother Amelia Cargill died shortly after his birth. Mackay was educated at the Caledonian Asylum, in London. In 1828 he was placed by his father at a school in Brussels, on the Boulevard de Namur, shortly taken over by William James Joseph Drury; and studied languages. In 1830 he was engaged as a private secretary to William Cockerill, the ironmaster, near Liège, began writing in French in the ''Courrier Belge'', and sent English poems to a local newspaper called ''The Telegraph''. In the summer of 1830 he visited Paris, and he spent 1831 with Cockerill at Aix-la-Chapelle. In May 1832 his father brought him back to London ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Purcell School
The Purcell School for Young Musicians is a specialist music school for children, located in the town of Bushey, south Hertfordshire, England, and is the oldest specialist music school in the UK. The school was awarded the UNESCO Mozart Medal in 2003, which was received on behalf of the school by Prince Charles, who is a patron of the school. Sir Simon Rattle is honorary president of the school. Many of the pupils subsequently study at top conservatories across the country including: the Royal College of Music, the Royal Academy of Music and the Guildhall School of Music and Drama. In 2015, the School became the first Fazioli Pianoforti Centre of Excellence. The School's pupils are funded largely by the Government's Music and Dance Scheme, along with the School's own scholarship funds. It has a consistent success in national and international competitions and has an extensive programme of outreach and community work. The majority of pupils progress to music conservatoires altho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Queens' School
Queens' School, near Watford, Hertfordshire, is a partially selective secondary school and sixth form with academy status. It currently is a specialist science and sports college. History The story of Queens' begins with two schools in Watford in the early 20th century. Watford Central School was founded in 1912 in buildings in Derby Road vacated by Watford Grammar School for Boys when it moved to its present site in West Watford. In 1950, the central school became a new grammar school on the northwest side of Aldenham Road, Bushey, called Bushey Grammar School. The buildings vacated in Derby road were then occupied by the Central Primary School.''Queens' School: The first Ten Years'', Queens' School, 1976. Alexandra School was founded in 1901 in Judge Street, North Watford. (These buildings later became an annexe to the Watford School of Art.) In January 1966 the school moved to the southeast side of Aldenham road, opposite Bushey Grammar School. The pedestrian underpass u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caledonian Estate
The Caledonian Estate is a Grade II listed, early Edwardian estate towards the northern end of the Caledonian Road in Islington, London. It is situated next to Pentonville Prison. The Estate was built on the site of the classical Caledonian Asylum from which the Road took its name. Pevsner describes the building as having been constructed between 1900 and 1907, though English Heritage describes it as having been built between 1904 and 1906. A pamphlet produced by the London County Council notes that, though the Council had accepted an offer from the Asylum for the land by January 1901, construction could not begin until December 1904 as the trustees of the school needed time to erect new buildings elsewhere. The architect was James Greenwood Stephenson (1872–1950); and was designed during his time in the Housing of the Working Classes Branch of the London County Council Architect's Department. Susan Beattie states that it is one of the two "most successful" flatted e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pentonville Prison
HM Prison Pentonville (informally "The Ville") is an English Category B men's prison, operated by His Majesty's Prison Service. Pentonville Prison is not in Pentonville, but is located further north, on the Caledonian Road in the Barnsbury area of the London Borough of Islington, north London. In 2015 the justice secretary, Michael Gove, described Pentonville as "the most dramatic example of failure" within the prisons estate. The prison today Pentonville is a local prison, holding Category B/C adult males remanded by local magistrates' courts and the Crown Court, and those serving short sentences or beginning longer sentences. The prison is divided into these main wings: * A wing: Remand and convicted * J wing: Induction wing * C wing: Remands and convicted prisoners * D wing: Remands and convicted * E wing: Remands and convicted * F wing: Detoxification Unit (F4 F5 Vulnerable Prisoners) * G wing: remands and convicted (G5 enhanced only) G wing has an education departmen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

_(31023042187)_CROP.jpg)