|
Cachoeira Do Cai Dam
The Cachoeira do Cai Dam ( pt, Barragem de Cachoeira do Cai}) is a planned hydroelectric dam on the Jamanxim River in the state of Pará, Brazil, with a capacity of . Location The Cachoeira do Cai Dam is proposed to be built on the Jamanxim River in the state of Pará, in the Tapajós river basin. It would adjoin the Sawré Muybu Indigenous Territory, which lies between the Jamanxim and the Tapajós in the region above the point where the two rivers converge. The hydroelectric power plant would be part of the proposed Tapajós hydroelectric complex on the Tapajós and Jamanxim rivers. Others are the São Luiz do Tapajós (6,133 MW), Jatobá (2,338 MW), Cachoeira dos Patos (528 MW) and Jamanxim (881 MW), all under study, as well as the less advanced proposals for the Jardim do Ouro (227 MW) and Chacorão (3,336 MW). Technical The project is a joint venture of Eletrobras, Eletronorte, Construções e Comércio Camargo Côrrea, EDF Consultoria em ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jamanxim River
The Jamanxim River is a river of Pará state in north-central Brazil. Originating in the Serra do Cachimbo, it is a tributary of the Tapajós, into which it flows a few kilometers upstream from Itaituba. Course The river flows through the Tapajós-Xingu moist forests ecoregion. It flows through the Itaituba I National Forest, a sustainable use conservation area established in 1998. The river basin also contains part of the Rio Novo National Park, a conservation unit created in 2006. Hydroelectric potential Its hydroelectric potential, along with that of the Tapajós, was assessed by Eletronorte (Centrais Elétricas do Norte do Brasil S.A.), the regional power authority, identifying nine potential dam sites, including four along the Jamanxim. at Cachoeira dos Patos, (estimated at 28 MW); Cachoeira do Caí, (estimated at 802 MW); at Jardim do Ouro and at Jamanxim (estimated at 881 MW). If all were constructed, these dams would flood a total of 103,700 ha, including 33,216 ha o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chacorão Dam
The Chacorão Dam (or Chocorão Dam, pt, Barragem de Chacorão) is a proposed dam on the Tapajós river in the state of Pará, Brazil. It would flood a section of rapids in the river, making them navigable by barges carrying soybeans to ports on the Amazon River. The dam would include locks for the barges and a hydroelectric power plant. It is controversial since it would flood a large area of an indigenous territory. Location The proposed Chacorão Dam would be built on the Tapajós river in the state of Pará. The hydroelectric power plant would be part of the proposed Tapajós hydroelectric complex on the Tapajos and Jamanxim rivers. Others are the São Luiz do Tapajós (6,133 MW), Jatobá (2,338 MW), Cachoeira dos Patos (528 MW), Jamanxim (881 MW) and Cachoeira do Cai (802 MW) plants, all under study, as well as the less advanced proposal for the Jardim do Ouro (227 MW). The São Luiz do Tapajós, Jatobá and Chacorão dams on the Tapaj ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dams In Pará
A dam is a barrier that stops or restricts the flow of surface water or underground streams. Reservoirs created by dams not only suppress floods but also provide water for activities such as irrigation, human consumption, industrial use, aquaculture, and navigability. Hydropower is often used in conjunction with dams to generate electricity. A dam can also be used to collect or store water which can be evenly distributed between locations. Dams generally serve the primary purpose of retaining water, while other structures such as floodgates or levees (also known as dikes) are used to manage or prevent water flow into specific land regions. The earliest known dam is the Jawa Dam in Jordan, dating to 3,000 BC. The word ''dam'' can be traced back to Middle English, and before that, from Middle Dutch, as seen in the names of many old cities, such as Amsterdam and Rotterdam. History Ancient dams Early dam building took place in Mesopotamia and the Middle East. Dams were us ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydroelectric Power Stations In Brazil
Hydroelectricity, or hydroelectric power, is electricity generated from hydropower (water power). Hydropower supplies one sixth of the world's electricity, almost 4500 TWh in 2020, which is more than all other renewable sources combined and also more than nuclear power. Hydropower can provide large amounts of low-carbon electricity on demand, making it a key element for creating secure and clean electricity supply systems. A hydroelectric power station that has a dam and reservoir is a flexible source, since the amount of electricity produced can be increased or decreased in seconds or minutes in response to varying electricity demand. Once a hydroelectric complex is constructed, it produces no direct waste, and almost always emits considerably less greenhouse gas than fossil fuel-powered energy plants. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
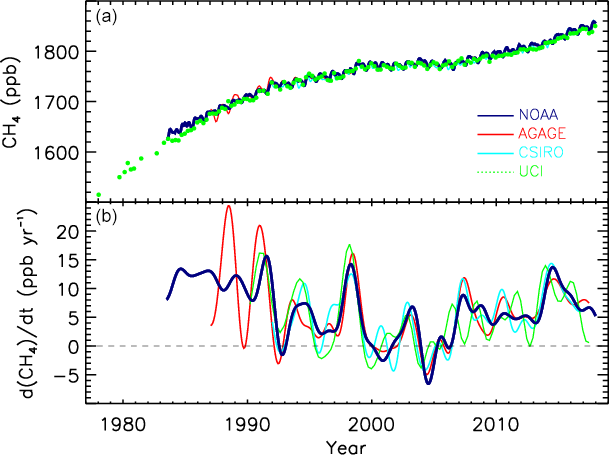
Methane Emissions
Increasing methane emissions are a major contributor to the rising concentration of greenhouse gases in Earth's atmosphere, and are responsible for up to one-third of near-term global heating. During 2019, about 60% (360 million tons) of methane released globally was from human activities, while natural sources contributed about 40% (230 million tons). Reducing methane emissions by capturing and utilizing the gas can produce simultaneous environmental and economic benefits. Since the Industrial Revolution, methane concentrations in the atmosphere have more than doubled, and about 20 percent of the warming the planet has experienced can be attributed to the gas. About one-third (33%) of anthropogenic emissions are from gas release during the extraction and delivery of fossil fuels; mostly due to gas venting and gas leaks from both active fossil fuel infrastructure and orphan wells. Russia is the world's top methane emitter from oil and gas. Animal agriculture is a similarly lar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Itaituba II National Forest
Itaituba II National Forest ( pt, Floresta Nacional de Itaituba II) is a national forest in the state of Pará, Brazil. Location The Itaituba II National Forest is in the Amazon biome. It has an area of . It covers parts of the municipalities of Itaituba and Trairão in the state of Pará. The Itaituba I and Itaituba II National Forests together cover . The management plan for the two forests defined a zone of sustainable forestry management of , of which were allocated to three forestry concessions. History The Itaituba II National Forest was created by decree nº 2.482 of 2 February 1998. It is administered by the Chico Mendes Institute for Biodiversity Conservation (ICMBio). It is classed as IUCN protected area category VI (protected area with sustainable use of natural resources) with the objective of sustainable multiple use of forest resources and scientific research, with emphasis on methods for sustainable exploitation of native forests. Law 12678 of 25 June 2012 ame ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Itaituba I National Forest
Itaituba I National Forest ( pt, Floresta Nacional de Itaituba I) is a national forest in the state of Pará, Brazil. Location The Itaituba I National Forest is in the Amazon biome. It has an area of . It covers parts of the municipalities of Itaituba and Trairão in the state of Pará. The forest is in the Tapajos residual plateau and in the Tapajos river basin, on the right bank of that river. The forest may be accessed by land via BR-163 and BR-230, the main federal highways in the region, or by boat via the Tapajós and Jamanxim rivers, and tributaries such as the Igarapé do Botica and the Ratão. There are some airstrips in and around the forest. Tributaries of the Tapajos include the Cururu, das Tropas, Cupari and Jamanxim. The Jamanxim, which rises in the Serra do Cachimbo in the extreme south of the state, has fast-flowing passages and areas where it sprawls into backwaters, making travel by large boats difficult along most of its length. Its main tributaries are th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jamanxim National Park
The Jamanxim National Park ( pt, Parque Nacional do Jamanxim) is a national park in the state of Pará, Brazil. Location The Jamanxim National Park covers of Amazon rainforest. It is in parts of the municipalities of Altamira, Itaituba and Trairão in the state of Pará. The Trairão National Forest lies to the north. The park mostly lies in the Jamanxim-Xingu depression, with relatively flat terrain ranging from in altitude. The Southern Pará plateau rises to . Two small areas of the Tapajós Plateau in the west contain hills rising from . The park contains the sub-basins of the Jamanxim, Tocantins and Aruri rivers within the Tapajós basin. It also holds very small parts of the Ratão and Iriri basins. Average annual rainfall is . Temperatures range from with an average of . Vegetation includes open rainforest with vines and palms trees, dense submontane rainforest with emergent canopy and dense alluvial rainforest with uniform canopy. The trees include species wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eletronorte
Eletrobras (, full name: Centrais Elétricas Brasileiras S.A.) is a major Brazilian electric utilities company. The company's headquarters are located in Rio de Janeiro. It is Latin America's biggest power utility company, tenth largest in the world, and is also the fourth largest clean energy company in the world. Eletrobras holds stakes in a number of Brazilian electric companies, so that it generates about 40% and transmits 69% of Brazil's electric supply. The company's generating capacity is about 51,000 MW, mostly in hydroelectric plants. The Brazilian federal government owned 52% stake in Eletrobras until June 2022, the rest of the shares traded on B3 (stock exchange), B3. The stock is part of the Índice Bovespa, Ibovespa index. It is also traded on the Nasdaq, Nasdaq Stock Market and on the Madrid Stock Exchange. History Eletrobras was established in 1962 during João Goulart's presidency. Operations Eletrobras is an electric power holding company. It is the larges ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eletrobras
Eletrobras (, full name: Centrais Elétricas Brasileiras S.A.) is a major Brazilian electric utilities company. The company's headquarters are located in Rio de Janeiro. It is Latin America's biggest power utility company, tenth largest in the world, and is also the fourth largest clean energy company in the world. Eletrobras holds stakes in a number of Brazilian electric companies, so that it generates about 40% and transmits 69% of Brazil's electric supply. The company's generating capacity is about 51,000 MW, mostly in hydroelectric plants. The Brazilian federal government owned 52% stake in Eletrobras until June 2022, the rest of the shares traded on B3. The stock is part of the Ibovespa index. It is also traded on the Nasdaq Stock Market and on the Madrid Stock Exchange. History Eletrobras was established in 1962 during João Goulart's presidency. Operations Eletrobras is an electric power holding company. It is the largest generation and transmission company in Bra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jardim Do Ouro Dam
The Jardim do Ouro Dam ( pt, Barragem Jardim do Ouro Dam) is a proposed hydroelectric dam on the Jamanxim River in the state of Pará, Brazil. The dam would have a reservoir and capacity of . It has not been studied on detail due to relatively low return on investment compared to other projects in the region. Location The Jardim do Ouro Dam is proposed to be built on the Jamanxim River The Jamanxim River is a river of Pará state in north-central Brazil. Originating in the Serra do Cachimbo, it is a tributary of the Tapajós, into which it flows a few kilometers upstream from Itaituba. Course The river flows through the Tapaj ... in the state of Pará, in the Tapajós river basin. It would be built in the municipality of Itaituba. The hydroelectric power plant will be part of the proposed Tapajos hydroelectric complex on the Tapajós and Jamanxim rivers. Others are the São Luiz do Tapajós (6,133 MW), Jatobá (2,338 MW), Cachoeira do Cai (802 MW), Ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pará
Pará is a Federative units of Brazil, state of Brazil, located in northern Brazil and traversed by the lower Amazon River. It borders the Brazilian states of Amapá, Maranhão, Tocantins (state), Tocantins, Mato Grosso, Amazonas (Brazilian state), Amazonas and Roraima. To the northwest are the borders of Guyana and Suriname, to the northeast of Pará is the Atlantic Ocean. The capital and largest city is Belém, which is located at the mouth of the Amazon. The state, which is home to 4.1% of the Brazilian population, is responsible for just 2.2% of the Brazilian GDP. Pará is the most populous state of the North Region, Brazil, North Region, with a population of over 8.6 million, being the ninth-most populous state in Brazil. It is the second-largest state of Brazil in area, at , second only to Amazonas (Brazilian state), Amazonas upriver. Its most famous icons are the Amazon River and the Amazon Rainforest. Pará produces Natural rubber, rubber (extracted from natural rubber tree ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |