|
CPLEX
IBM ILOG CPLEX Optimization Studio (often informally referred to simply as CPLEX) is an optimization software package. In 2004, the work on CPLEX earned the first INFORMS Impact Prize. History The CPLEX Optimizer was named for the simplex method as implemented in the C programming language, although today it also supports other types of mathematical optimization and offers interfaces other than C. It was originally developed by Robert E. Bixby and sold commercially from 1988 by CPLEX Optimization Inc. This was acquired by ILOG in 1997 and ILOG was subsequently acquired by IBM in January 2009. CPLEX continues to be actively developed by IBM. Features The IBM ILOG CPLEX Optimizer solves integer programming problems, very large linear programming problems using either primal or dual variants of the simplex method or the barrier interior point method, convex and non-convex quadratic programming problems, and convex quadratically constrained problems (solved via second-order ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ILOG
ILOG S.A. was an international software company purchased and incorporated into IBM announced in January, 2009. It created enterprise software products for supply chain, business rule management, visualization and optimization. The main product line for Business Rules Management Systems (BRMS) has been rebranded as IBM Operational Decision Management. Many of the related components retain the ILOG brand as a part of their name. The software developed by the ILOG software company supports several software platforms, including COBOL, C++, C#, .NET, Java, AJAX and Adobe Flex / AIR. Founded in 1987 in Paris, France, ILOG had its main headquarters in Gentilly, France, and Sunnyvale, California. It also had main offices in Australia, China, Germany, Japan, Singapore and the United Kingdom. Through its acquisition of CPLEX Optimization Inc. in 1997, ILOG became the owner of the CPLEX mathematical programming software, and ILOG's acquisition of LogicTools in 2007 made ILOG the o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mathematical Optimization Software
Given a transformation between input and output values, described by a mathematical function ''f'', optimization deals with generating and selecting a best solution from some set of available alternatives, by systematically choosing input values from within an allowed set, computing the output of the function, and recording the best output values found during the process. Many real-world problems can be modeled in this way. For example, the inputs can be design parameters of a motor, the output can be the power consumption, or the inputs can be business choices and the output can be the obtained profit. An optimization problem, in this case a minimization problem, can be represented in the following way :''Given:'' a function ''f'' : ''A'' \to R from some set ''A'' to the real numbers :''Search for:'' an element ''x''0 in ''A'' such that ''f''(''x''0) ≤ ''f''(''x'') for all ''x'' in ''A''. In continuous optimization, ''A'' is some subset of the Euclidean space R''n'', often spec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Optimization Programming Language
Optimization Programming Language (OPL) is an algebraic modeling language for mathematical optimization models, which makes the coding easier and shorter than with a general-purpose programming language. It is part of the CPLEX software package and therefore tailored for the IBM ILOG CPLEX and IBM ILOG CPLEX CP Optimizers. The original author of OPL is Pascal Van Hentenryck Pascal Van Hentenryck (born 8 March 1963) is the A. Russell Chandler III Chair and Professor of Industrial and Systems Engineering at Georgia Tech. He is credited with pioneering advances in constraint programming and stochastic optimization, bridg .... References {{Authority control Mathematical optimization software Algebraic modeling languages ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
AMPL
AMPL (A Mathematical Programming Language) is an algebraic modeling language to describe and solve high-complexity problems for large-scale mathematical computing (i.e., large-scale optimization and scheduling-type problems). It was developed by Robert Fourer, David Gay, and Brian Kernighan at Bell Laboratories. AMPL supports dozens of solvers, both open source and commercial software, including CBC, CPLEX, FortMP, MINOS, IPOPT, SNOPT, KNITRO, and LGO. Problems are passed to solvers as nl files. AMPL is used by more than 100 corporate clients, and by government agencies and academic institutions. One advantage of AMPL is the similarity of its syntax to the mathematical notation of optimization problems. This allows for a very concise and readable definition of problems in the domain of optimization. Many modern solvers available on the NEOS Server (formerly hosted at the Argonne National Laboratory, currently hosted at the University of Wisconsin, Madison) accept AMPL input. Ac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linear Programming
Linear programming (LP), also called linear optimization, is a method to achieve the best outcome (such as maximum profit or lowest cost) in a mathematical model whose requirements are represented by linear function#As a polynomial function, linear relationships. Linear programming is a special case of mathematical programming (also known as mathematical optimization). More formally, linear programming is a technique for the mathematical optimization, optimization of a linear objective function, subject to linear equality and linear inequality Constraint (mathematics), constraints. Its feasible region is a convex polytope, which is a set defined as the intersection (mathematics), intersection of finitely many Half-space (geometry), half spaces, each of which is defined by a linear inequality. Its objective function is a real number, real-valued affine function, affine (linear) function defined on this polyhedron. A linear programming algorithm finds a point in the polytope where ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
OptimJ
OptimJ is an extension for Java with language support for writing optimization models and abstractions for bulk data processing. The extensions and the proprietary product implementing the extensions were developed by Ateji which went out of business in September 2011. OptimJ aims at providing a clear and concise algebraic notation for optimization modeling, removing compatibility barriers between optimization modeling and application programming tools, and bringing software engineering techniques such as object-orientation and modern IDE support to optimization experts. OptimJ models are directly compatible with Java source code, existing Java libraries such as database access, Excel connection or graphical interfaces. OptimJ is compatible with development tools such as Eclipse, CVS, JUnit or JavaDoc. OptimJ is available free with the following solvers: lp_solve, glpk, LP or MPS file formats and also supports the following commercial solvers: MOSEK, IBM ILOG CPLEX Optimization S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quadratic Programming
Quadratic programming (QP) is the process of solving certain mathematical optimization problems involving quadratic functions. Specifically, one seeks to optimize (minimize or maximize) a multivariate quadratic function subject to linear constraints on the variables. Quadratic programming is a type of nonlinear programming. "Programming" in this context refers to a formal procedure for solving mathematical problems. This usage dates to the 1940s and is not specifically tied to the more recent notion of "computer programming." To avoid confusion, some practitioners prefer the term "optimization" — e.g., "quadratic optimization." Problem formulation The quadratic programming problem with variables and constraints can be formulated as follows. Given: * a real-valued, -dimensional vector , * an -dimensional real symmetric matrix , * an -dimensional real matrix , and * an -dimensional real vector , the objective of quadratic programming is to find an -dimensional vector , that wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SCIP (optimization Software)
The Zuse Institute Berlin (abbreviated ZIB, or ''Konrad-Zuse-Zentrum für Informationstechnik Berlin'') is a research institute for applied mathematics and computer science on the campus of Freie Universität Berlin in Dahlem, Berlin, Germany. The ZIB was founded by law as a statutory establishment and as a non-university research institute of the State of Berlin in 1984. In close interdisciplinary cooperation with the Berlin universities and scientific institutions Zuse Institute implements research and development in the field of information technology with a particular focus on application-oriented algorithmic mathematics and practical computer science. ZIB also provides high-performance computer capacity as an accompanying service as part of the ''Network of high performance computers in Northern Germany'' (Norddeutscher Verbund von Hoch- und Höchstleistungsrechnern (HLRN)). Konrad Zuse, born in Berlin in 1910, is the namesake of the ZIB. SCIP (optimization software) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
AIMMS
AIMMS (acronym for Advanced Interactive Multidimensional Modeling System) is a prescriptive analytics software company with offices in the Netherlands, United States, China and Singapore. It has two main product offerings that provide modeling and optimization capabilities across a variety of industries. The AIMMS Prescriptive Analytics Platform allows advanced users to develop optimization-based applications and deploy them to business users. AIMMS SC Navigator, launched in 2017, is built on the AIMMS Prescriptive Analytics Platform and provides configurable Apps for supply chain teams. SC Navigator provides supply chain analytics to non-advanced users. History AIMMS B.V. was founded in 1989 by mathematician Johannes Bisschop under the name of Paragon Decision Technology. His vision was to make optimization more approachable by building models rather than programming. In Bisschop’s view, modeling was able to build the bridge between the people who had problems and the people ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
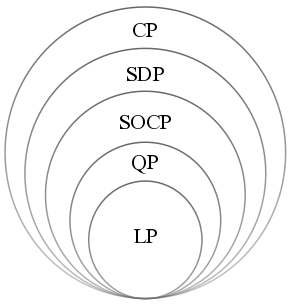
Second-order Cone Programming
A second-order cone program (SOCP) is a convex optimization problem of the form :minimize \ f^T x \ :subject to ::\lVert A_i x + b_i \rVert_2 \leq c_i^T x + d_i,\quad i = 1,\dots,m ::Fx = g \ where the problem parameters are f \in \mathbb^n, \ A_i \in \mathbb^, \ b_i \in \mathbb^, \ c_i \in \mathbb^n, \ d_i \in \mathbb, \ F \in \mathbb^, and g \in \mathbb^p. x\in\mathbb^n is the optimization variable. \lVert x \rVert_2 is the Euclidean norm and ^T indicates transpose. The "second-order cone" in SOCP arises from the constraints, which are equivalent to requiring the affine function (A x + b, c^T x + d) to lie in the second-order cone in \mathbb^. SOCPs can be solved by interior point methods and in general, can be solved more efficiently than semidefinite programming (SDP) problems. Some engineering applications of SOCP include filter design, antenna array weight design, truss design, and grasping force optimization in robotics. Applications in quantitative finance include p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Integer Programming
An integer programming problem is a mathematical optimization or Constraint satisfaction problem, feasibility program in which some or all of the variables are restricted to be integers. In many settings the term refers to integer linear programming (ILP), in which the objective function and the constraints (other than the integer constraints) are Linear function (calculus), linear. Integer programming is NP-complete. In particular, the special case of 0-1 integer linear programming, in which unknowns are binary, and only the restrictions must be satisfied, is one of Karp's 21 NP-complete problems. If some decision variables are not discrete, the problem is known as a mixed-integer programming problem. Canonical and standard form for ILPs In integer linear programming, the ''canonical form'' is distinct from the ''standard form''. An integer linear program in canonical form is expressed thus (note that it is the \mathbf vector which is to be decided): : \begin & \text && \math ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |