|
CD68
CD68 ( Cluster of Differentiation 68) is a protein highly expressed by cells in the monocyte lineage (e.g., monocytic phagocytes, osteoclasts), by circulating macrophages, and by tissue macrophages (e.g., Kupffer cells, microglia). Structure and function Human CD68 is a Type I transmembrane glycoprotein, heavily glycosylated in its extracellular domain, with a molecular weight of 110 kD. Its primary sequence consists of 354 amino acids with predicted molecular weight of 37.4 kD if it were not glycosylated. The human CD68 protein is encoded by the "CD68" gene which maps to Chromosome 17. Other names or aliases for this gene in humans and other animals include: CD68 Molecule, CD68 Antigen, GP110, Macrosialin, Scavenger Receptor Class D, Member 1, SCARD1, and LAMP4. The mouse equivalent is known as "macrosialin". CD68 is functionally and evolutionarily related to other gene/protein family members, including: * the hematopoietic mucin-like family of molecules that includes leuko ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
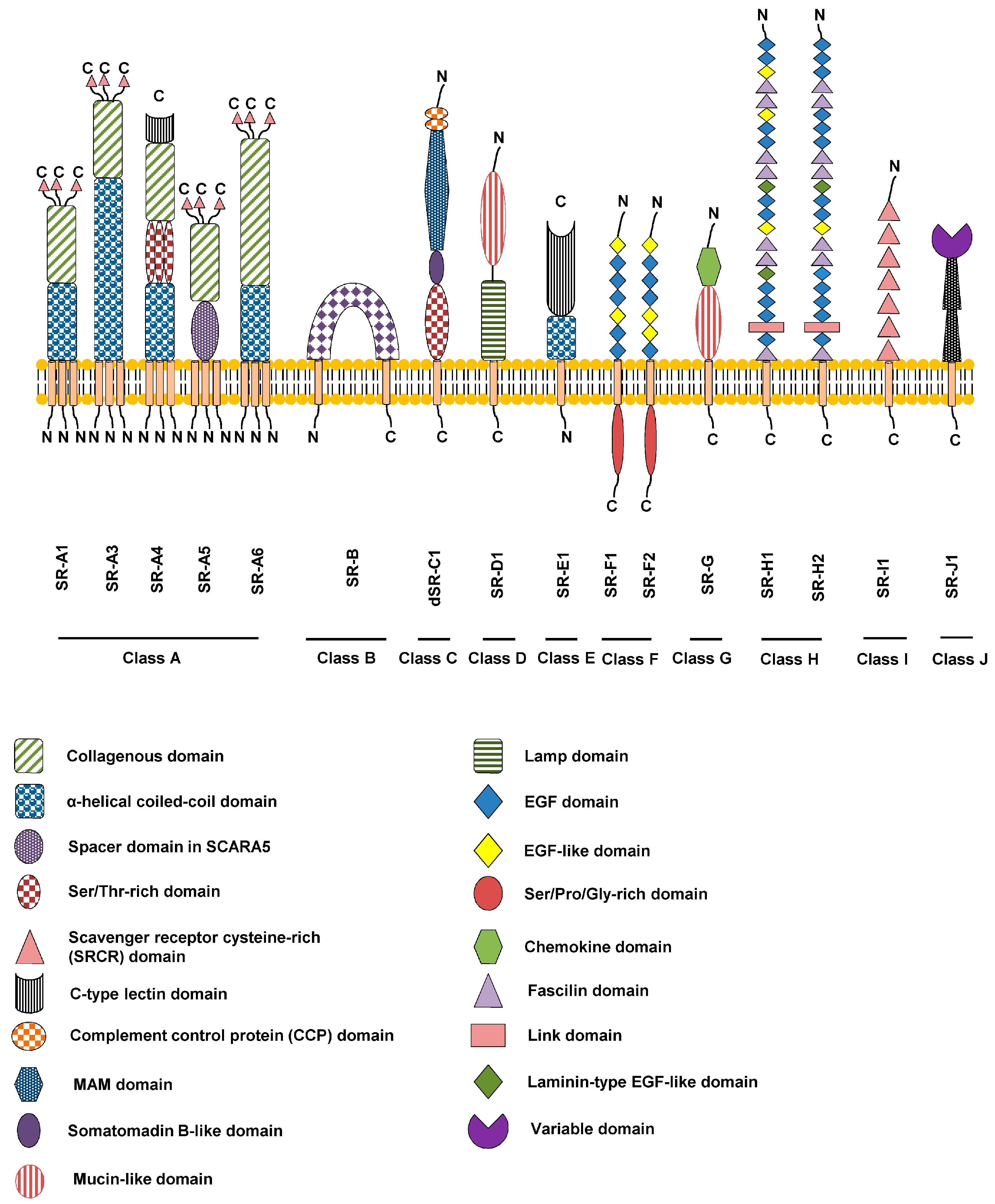
Scavenger Receptor (immunology)
Scavenger receptors are a large and diverse superfamily of cell surface receptors. Its properties were first recorded in 1970 by Drs. Brown and Goldstein, with the defining property being the ability to bind and remove modified low density lipoproteins (LDL). Today scavenger receptors are known to be involved in a wide range of processes, such as: homeostasis, apoptosis, inflammatory diseases and pathogen clearance. Scavenger receptors are mainly found on myeloid cells and other cells that bind to numerous ligands, primarily endogenous and modified host-molecules together with pathogen-associated molecular patterns(PAMPs), and remove them. The Kupffer cells in the liver are particularly rich in scavenger receptors, includes SR-A I, SR-A II, and MARCO. Function The scavenger receptor superfamily is defined by its ability to recognize and bind a broad range of common ligands. These ligands include: polyanionic ligands including lipoproteins, apoptotic cells, cholesterol este ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scavenger Receptor (immunology)
Scavenger receptors are a large and diverse superfamily of cell surface receptors. Its properties were first recorded in 1970 by Drs. Brown and Goldstein, with the defining property being the ability to bind and remove modified low density lipoproteins (LDL). Today scavenger receptors are known to be involved in a wide range of processes, such as: homeostasis, apoptosis, inflammatory diseases and pathogen clearance. Scavenger receptors are mainly found on myeloid cells and other cells that bind to numerous ligands, primarily endogenous and modified host-molecules together with pathogen-associated molecular patterns(PAMPs), and remove them. The Kupffer cells in the liver are particularly rich in scavenger receptors, includes SR-A I, SR-A II, and MARCO. Function The scavenger receptor superfamily is defined by its ability to recognize and bind a broad range of common ligands. These ligands include: polyanionic ligands including lipoproteins, apoptotic cells, cholesterol este ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Macrophage
Macrophages (abbreviated as M φ, MΦ or MP) ( el, large eaters, from Greek ''μακρός'' (') = large, ''φαγεῖν'' (') = to eat) are a type of white blood cell of the immune system that engulfs and digests pathogens, such as cancer cells, microbes, cellular debris, and foreign substances, which do not have proteins that are specific to healthy body cells on their surface. The process is called phagocytosis, which acts to defend the host against infection and injury. These large phagocytes are found in essentially all tissues, where they patrol for potential pathogens by amoeboid movement. They take various forms (with various names) throughout the body (e.g., histiocytes, Kupffer cells, alveolar macrophages, microglia, and others), but all are part of the mononuclear phagocyte system. Besides phagocytosis, they play a critical role in nonspecific defense ( innate immunity) and also help initiate specific defense mechanisms (adaptive immunity) by recruiting othe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Giant Cell
A giant cell (also known as multinucleated giant cell, or multinucleate giant cell) is a mass formed by the union of several distinct cells (usually histiocytes), often forming a granuloma. Although there is typically a focus on the pathological aspects of multinucleate giant cells (MGCs), they also play many important physiological roles. Osteoclasts specifically are invaluable to healthy physiological functions and are key players in the skeletal system. Osteoclasts are frequently classified and discussed separately from other MGCs which are more closely linked with human pathologies. Non-osteoclast MGCs can arise in response to an infection, such as from tuberculosis, herpes, or HIV, or foreign body. These MGCs are cells of monocyte or macrophage lineage fused together. Similar to their monocyte precursors, they are able to phagocytose foreign materials. However, their large size and extensive membrane ruffling make them better equipped to clear up larger particles. They ut ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Histiocytes
A histiocyte is a vertebrate cell that is part of the mononuclear phagocyte system (also known as the reticuloendothelial system or lymphoreticular system). The mononuclear phagocytic system is part of the organism's immune system. The histiocyte is a tissue macrophage or a dendritic cell (histio, diminutive of histo, meaning ''tissue'', and cyte, meaning ''cell''). Part of their job is to clear out neutrophils once they've reached the end of their lifespan. Development Histiocytes are derived from the bone marrow by multiplication from a stem cell. The derived cells migrate from the bone marrow to the blood as monocytes. They circulate through the body and enter various organs, where they undergo differentiation into histiocytes, which are part of the mononuclear phagocytic system (MPS). However, the term ''histiocyte'' has been used for multiple purposes in the past, and some cells called "histocytes" do not appear to derive from monocytic-macrophage lines. The term Hi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Macrophage Activation
Macrophages (abbreviated as M φ, MΦ or MP) ( el, large eaters, from Greek ''μακρός'' (') = large, ''φαγεῖν'' (') = to eat) are a type of white blood cell of the immune system that engulfs and digests pathogens, such as cancer cells, microbes, cellular debris, and foreign substances, which do not have proteins that are specific to healthy body cells on their surface. The process is called phagocytosis, which acts to defend the host against infection and injury. These large phagocytes are found in essentially all tissues, where they patrol for potential pathogens by amoeboid movement. They take various forms (with various names) throughout the body (e.g., histiocytes, Kupffer cells, alveolar macrophages, microglia, and others), but all are part of the mononuclear phagocyte system. Besides phagocytosis, they play a critical role in nonspecific defense (innate immunity) and also help initiate specific defense mechanisms (adaptive immunity) by recruiting other immune ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lysosome-associated Membrane Glycoprotein
Lysosome-associated membrane glycoproteins (LAMPs) are integral membrane proteins, specific to lysosomes, and whose exact biological function is not yet clear. Structurally, the lamp proteins consist of two internally homologous lysosome-luminal domains separated by a proline-rich hinge region; at the C-terminal extremity there is a transmembrane region (TM) followed by a very short cytoplasmic tail (C). In each of the duplicated domains, there are two conserved disulfide bonds. This structure is schematically represented in the figure below. +-----+ +-----+ +-----+ +-----+ , , , , , , , , +--------------------------++Hinge++--------------------------++TM++C+ In mammals, there are two closely related types of lamp: LAMP1 and LAMP2. CD69 (also called gp110 or macrosialin) is a heavily glycosylated integral membrane protein whose structure consists of a mucin-like domain followed by a pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bovine
Bovines (subfamily Bovinae) comprise a diverse group of 10 genera of medium to large-sized ungulates, including cattle, bison, African buffalo, water buffalos, and the four-horned and spiral-horned antelopes. The evolutionary relationship between the members of the group is still debated, and their classification into loose tribes rather than formal subgroups reflects this uncertainty. General characteristics include cloven hooves and usually at least one of the sexes of a species having true horns. The largest extant bovine is the gaur. In many countries, bovid milk and meat is used as food by humans. Cattle are kept as livestock almost everywhere except in parts of India and Nepal, where they are considered sacred by most Hindus. Bovids are used as draft animals and as riding animals. Small breeds of domestic bovid, such as the Miniature Zebu, are kept as pets. Bovid leather is durable and flexible and is used to produce a wide range of goods including clothing and bags. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monoclonal Antibody
A monoclonal antibody (mAb, more rarely called moAb) is an antibody produced from a cell Lineage made by cloning a unique white blood cell. All subsequent antibodies derived this way trace back to a unique parent cell. Monoclonal antibodies can have monovalent affinity, binding only to the same epitope (the part of an antigen that is recognized by the antibody). In contrast, polyclonal antibodies bind to multiple epitopes and are usually made by several different antibody-secreting plasma cell lineages. Bispecific monoclonal antibodies can also be engineered, by increasing the therapeutic targets of one monoclonal antibody to two epitopes. It is possible to produce monoclonal antibodies that specifically bind to virtually any suitable substance; they can then serve to detect or purify it. This capability has become an investigative tool in biochemistry, molecular biology, and medicine. Monoclonal antibodies are being used on a clinical level for both the diagnosis and thera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gaucher's Disease
Gaucher's disease or Gaucher disease () (GD) is a genetic disorder in which glucocerebroside (a sphingolipid, also known as glucosylceramide) accumulates in cells and certain organs. The disorder is characterized by bruising, fatigue, anemia, low blood platelet count and enlargement of the liver and spleen, and is caused by a hereditary deficiency of the enzyme glucocerebrosidase (also known as glucosylceramidase), which acts on glucocerebroside. When the enzyme is defective, glucocerebroside accumulates, particularly in white blood cells and especially in macrophages ( mononuclear leukocytes, which is often a target for intracellular parasites). Glucocerebroside can collect in the spleen, liver, kidneys, lungs, brain, and bone marrow. Manifestations may include enlarged spleen and liver, liver malfunction, skeletal disorders or bone lesions that may be painful, severe neurological complications, swelling of lymph nodes and (occasionally) adjacent joints, distended abdomen, a br ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lymphoma
Lymphoma is a group of blood and lymph tumors that develop from lymphocytes (a type of white blood cell). In current usage the name usually refers to just the cancerous versions rather than all such tumours. Signs and symptoms may include enlarged lymph nodes, fever, drenching sweats, unintended weight loss, itching, and constantly feeling tired. The enlarged lymph nodes are usually painless. The sweats are most common at night. Many subtypes of lymphomas are known. The two main categories of lymphomas are the non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL) (90% of cases) and Hodgkin lymphoma (HL) (10%). The World Health Organization (WHO) includes two other categories as types of lymphoma – multiple myeloma and immunoproliferative diseases. Lymphomas and leukemias are a part of the broader group of tumors of the hematopoietic and lymphoid tissues. Risk factors for Hodgkin lymphoma include infection with Epstein–Barr virus and a history of the disease in the family. Risk factors for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malignant Histiocytosis
Malignant histiocytosis is a rare hereditary disease found in the Bernese Mountain Dog and humans, characterized by histiocytic infiltration of the lungs and lymph nodes. The liver, spleen, and central nervous system can also be affected. Histiocytes are a component of the immune system that proliferate abnormally in this disease. In addition to its importance in veterinary medicine, the condition is also important in human pathology. Histiocytic disorders A histiocyte is a differentiated tissue cell that has its origin in the bone marrow. The source for histiocytes is the monocyte/macrophage line. Monocytes (found in the blood) and macrophages (found in tissue) are responsible for phagocytosis (ingestion) of foreign material in the body. Langerhans cells are dendritic cells found in the skin and function by internalizing antigens (foreign particles) and presenting them to T cells. They arise from monocytes. Histiocytic disorders refer to diseases that are caused by abnorma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |