|
CD57
3-beta-glucuronosyltransferase 1 (B3GAT1) is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''B3GAT1'' gene, whose enzymatic activity creates the CD57 epitope on other cell surface proteins. In immunology, the CD57 antigen (CD stands for cluster of differentiation) is also known as HNK1 (human natural killer-1) or LEU7. It is expressed as a carbohydrate epitope that contains a residue in several adhesion molecules of the nervous system. Function The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the glucuronyltransferase gene family. These enzymes exhibit strict acceptor specificity, recognizing nonreducing terminal sugars and their anomeric linkages. This gene product functions as the key enzyme in a glucuronyl transfer reaction during the biosynthesis of the carbohydrate epitope HNK-1 (human natural killer-1, also known as CD57 and LEU7). Alternate transcriptional splice variants have been characterized. Immunohistochemistry In anatomical pathology, CD57 (immunostaining) is simila ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Large Granular Lymphocytic Leukemia
Large granular lymphocytic (LGL) leukemia is a chronic lymphoproliferative disorder that exhibits an unexplained, chronic (> 6 months) elevation in large granular lymphocytes (LGLs) in the peripheral blood. It is divided in two main categories: T-cell LGL leukemia (T-LGLL) and natural-killer (NK)-cell LGL leukemia (NK-LGLL). As the name suggests, ''T-cell large granular lymphocyte leukemia'' is characterized by involvement of cytotoxic-T cells). In a study based in the US, the average age of diagnosis was 66.5 years whereas in a French study the median age at diagnosis was 59 years (with an age range of 12–87 years old). In the French study, only 26% of patients were younger than 50 years which suggests that this disorder is associated with older age at diagnosis. Due to lack of presenting symptoms, the disorder is likely to be underdiagnosed in the general population. Signs and symptoms This disease is known for an indolent clinical course and incidental discovery. The most co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neuron Specific Enolase
Gamma-enolase, also known as enolase 2 (ENO2) or neuron specific enolase (NSE), is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''ENO2'' gene. Gamma-enolase is a phosphopyruvate hydratase. Gamma-enolase is one of the three enolase isoenzymes found in mammals. This isoenzyme, a homodimer, is found in mature neurons and cells of neuronal origin. A switch from alpha enolase to gamma enolase occurs in neural tissue during development in rats and primates. Interactive pathway map Utility Detection of NSE with antibodies can be used to identify neuronal cells and cells with neuroendocrine differentiation. NSE is produced by small-cell carcinomas, which are neuroendocrine Neuroendocrine cells are cells that receive neuronal input (through neurotransmitters released by nerve cells or neurosecretory cells) and, as a consequence of this input, release messenger molecules ( hormones) into the blood. In this way they b ... in origin. NSE is therefore a useful tumor marker for distinguish ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Natural Killer Cell
Natural killer cells, also known as NK cells or large granular lymphocytes (LGL), are a type of cytotoxic lymphocyte critical to the innate immune system that belong to the rapidly expanding family of known innate lymphoid cells (ILC) and represent 5–20% of all circulating lymphocytes in humans. The role of NK cells is analogous to that of cytotoxic T cells in the vertebrate adaptive immune response. NK cells provide rapid responses to virus-infected cell and other intracellular pathogens acting at around 3 days after infection, and respond to tumor formation. Typically, immune cells detect the major histocompatibility complex (MHC) presented on infected cell surfaces, triggering cytokine release, causing the death of the infected cell by lysis or apoptosis. NK cells are unique, however, as they have the ability to recognize and kill stressed cells in the absence of antibodies and MHC, allowing for a much faster immune reaction. They were named "natural killers" because ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
T Cell
A T cell is a type of lymphocyte. T cells are one of the important white blood cells of the immune system and play a central role in the adaptive immune response. T cells can be distinguished from other lymphocytes by the presence of a T-cell receptor (TCR) on their cell surface. T cells are born from hematopoietic stem cells, found in the bone marrow. Developing T cells then migrate to the thymus gland to develop (or mature). T cells derive their name from the thymus. After migration to the thymus, the precursor cells mature into several distinct types of T cells. T cell differentiation also continues after they have left the thymus. Groups of specific, differentiated T cell subtypes have a variety of important functions in controlling and shaping the immune response. One of these functions is immune-mediated cell death, and it is carried out by two major subtypes: CD8+ "killer" and CD4+ "helper" T cells. (These are named for the presence of the cell surface proteins CD8 or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chromogranin
Granin (chromogranin and secretogranin) is a protein family of regulated secretory proteins ubiquitously found in the cores of amine and peptide hormone and neurotransmitter dense-core secretory vesicles. Function Granins (chromogranins or secretogranins) are acidic proteins and are present in the secretory granules of a wide variety of endocrine and neuro-endocrine cells. The exact function(s) of these proteins is not yet settled but there is evidence that granins function as pro-hormones, giving rise to an array of peptide fragments for which autocrine, paracrine, and endocrine activities have been demonstrated in vitro and in vivo. The intracellular biochemistry of granins includes binding of Ca2+, ATP and catecholamines (epinephrine, norepinephrine) within the hormone storage vesicle core. There is also evidence that CgA, and perhaps other granins, regulate the biogenesis of dense-core secretory vesicles and hormone sequestration in neuroendocrine cells. Structure Apa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
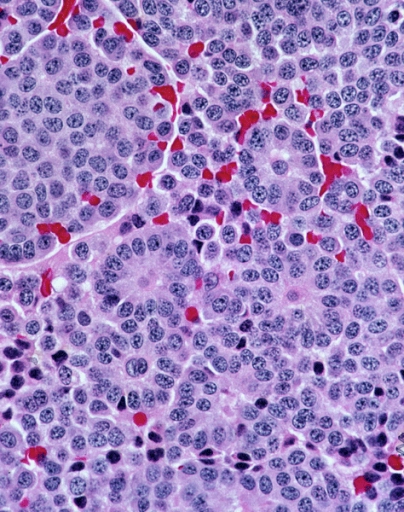
Carcinoid
A carcinoid (also carcinoid tumor) is a slow-growing type of neuroendocrine tumor originating in the cells of the neuroendocrine system. In some cases, metastasis may occur. Carcinoid tumors of the midgut (jejunum, ileum, appendix, and cecum) are associated with carcinoid syndrome. Carcinoid tumors are the most common malignant tumor of the appendix, but they are most commonly associated with the small intestine, and they can also be found in the rectum and stomach. They are known to grow in the liver, but this finding is usually a manifestation of metastatic disease from a primary carcinoid occurring elsewhere in the body. They have a very slow growth rate compared to most malignant tumors. The median age at diagnosis for all patients with neuroendocrine tumors is 63 years. Signs and symptoms While most carcinoids are asymptomatic through the natural life and are discovered only upon surgery for unrelated reasons (so-called ''coincidental carcinoids''), all carcinoids are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thyroid Neoplasm
Thyroid neoplasm is a neoplasm or tumor of the thyroid. It can be a benign tumor such as thyroid adenoma,Chapter 20 in: 8th edition. or it can be a malignant neoplasm (thyroid cancer), such as papillary thyroid cancer, papillary, follicular thyroid cancer, follicular, medullary thyroid cancer, medullary or anaplastic thyroid cancer.Hu MI, Vassilopoulou-Sellin R, Lustig R, Lamont JP"Thyroid and Parathyroid Cancers"in Pazdur R, Wagman LD, Camphausen KA, Hoskins WJ (EdsCancer Management: A Multidisciplinary Approach 11 ed. 2008. Most patients are 25 to 65 years of age when first diagnosed; women are more affected than men.Al-Zaher N, Al-Salam S, El Teraifi H. Thyroid carcinoma in the United Arab Emirates: perspectives and experience of a tertiary care hospital. Hematol Oncol Stem Cell Ther 2008;1:14-21"Hematology/Oncology and Stem Cell Therapy"/ref> The estimated number of new cases of thyroid cancer in the United States in 2010 is 44,670 compared to only 1,690 deaths.National Cancer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
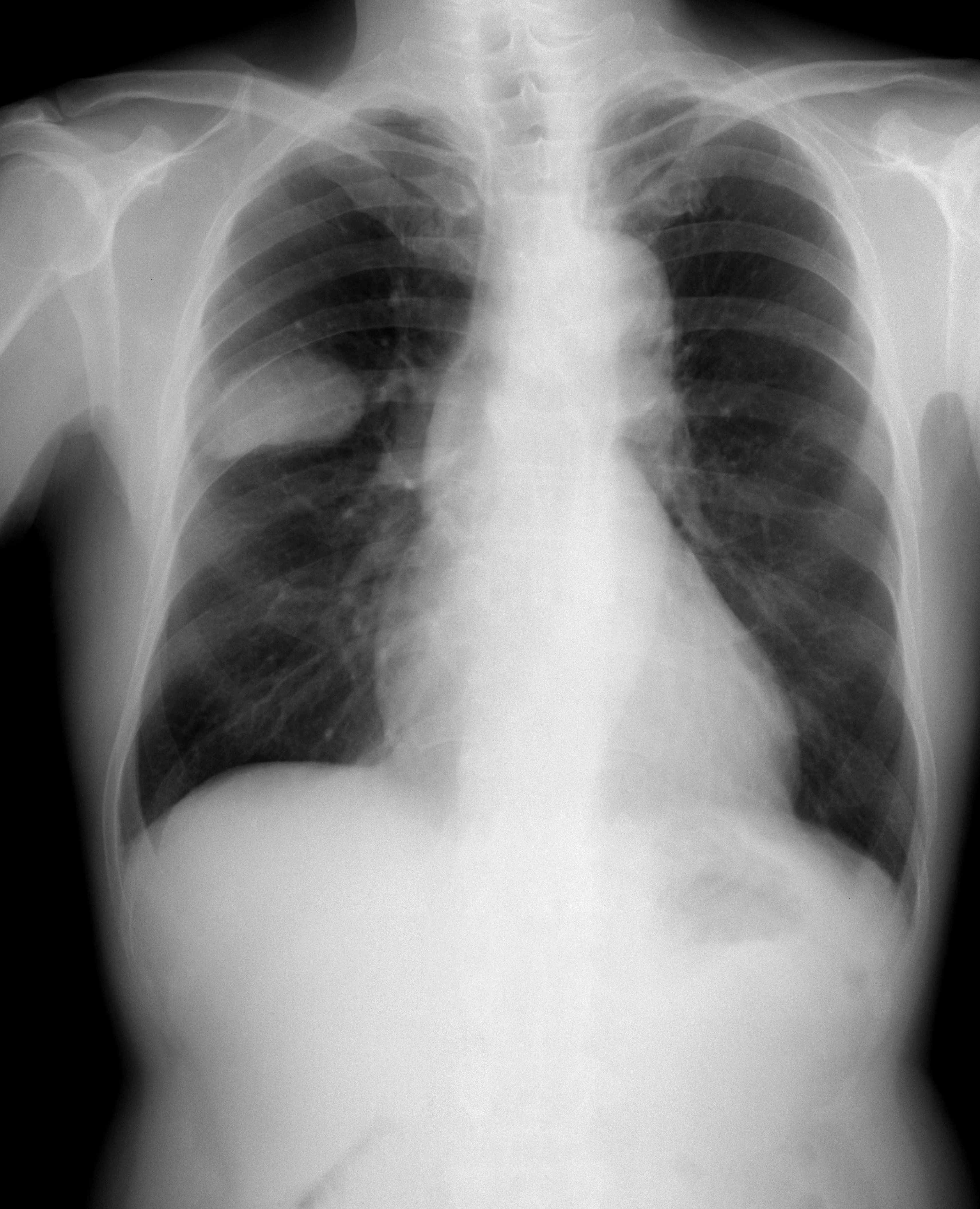
Small-cell Carcinoma
Small-cell carcinoma is a type of highly malignant cancer that most commonly arises within the lung, although it can occasionally arise in other body sites, such as the cervix, prostate, and gastrointestinal tract. Compared to non-small cell carcinoma, small cell carcinoma has a shorter doubling time, higher growth fraction, and earlier development of metastases. Extensive stage small cell lung cancer is classified as a rare disorder. Ten-year relative survival rate is 3.5%; however, women have a higher survival rate, 4.3%, and men lower, 2.8%. Survival can be higher or lower based on a combination of factors including stage, age, gender and race. Types of SCLC Small-cell lung carcinoma has long been divided into two clinicopathological stages, termed ''limited stage'' (LS) and ''extensive stage'' (ES). The stage is generally determined by the presence or absence of metastases, whether or not the tumor appears limited to the thorax, and whether or not the entire tumor burden wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neoplasm
A neoplasm () is a type of abnormal and excessive growth of tissue. The process that occurs to form or produce a neoplasm is called neoplasia. The growth of a neoplasm is uncoordinated with that of the normal surrounding tissue, and persists in growing abnormally, even if the original trigger is removed. This abnormal growth usually forms a mass, when it may be called a tumor. ICD-10 classifies neoplasms into four main groups: benign neoplasms, in situ neoplasms, malignant neoplasms, and neoplasms of uncertain or unknown behavior. Malignant neoplasms are also simply known as cancers and are the focus of oncology. Prior to the abnormal growth of tissue, as neoplasia, cells often undergo an abnormal pattern of growth, such as metaplasia or dysplasia. However, metaplasia or dysplasia does not always progress to neoplasia and can occur in other conditions as well. The word is from Ancient Greek 'new' and 'formation, creation'. Types A neoplasm can be benign, potentially ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
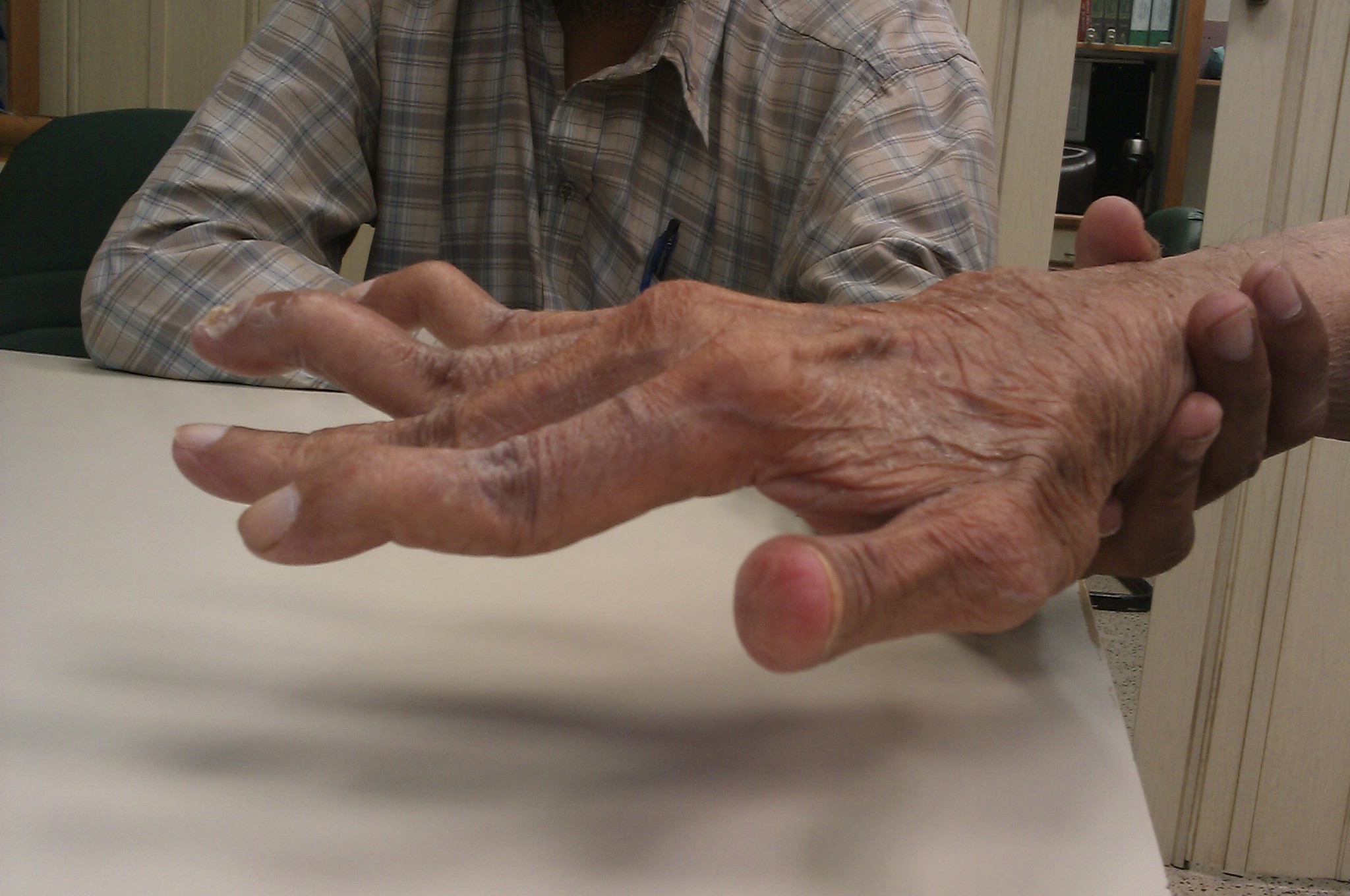
Felty's Syndrome
Felty's syndrome (FS), also called Felty syndrome, is rare autoimmune disease characterized by the triad of rheumatoid arthritis, enlargement of the spleen and low neutrophil count. The condition is more common in those aged 50–70 years, specifically more prevalent in females than males, and more so in Caucasians than those of African descent. It is a deforming disease that causes many complications for the individual. Signs and symptoms The symptoms of Felty's syndrome are similar to those of rheumatoid arthritis. Affected individuals have painful, stiff, and swollen joints, most commonly in the joints of the hands, feet, and arms. In some affected individuals, Felty's syndrome may develop during a period when the symptoms and physical findings associated with rheumatoid arthritis have subsided or are not present; in this case, Felty's syndrome may remain undiagnosed. In more rare instances, the development of Felty's syndrome may precede the development of the symptoms and ph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rheumatoid Arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a long-term autoimmune disorder that primarily affects joints. It typically results in warm, swollen, and painful joints. Pain and stiffness often worsen following rest. Most commonly, the wrist and hands are involved, with the same joints typically involved on both sides of the body. The disease may also affect other parts of the body, including skin, eyes, lungs, heart, nerves and blood. This may result in a low red blood cell count, inflammation around the lungs, and inflammation around the heart. Fever and low energy may also be present. Often, symptoms come on gradually over weeks to months. While the cause of rheumatoid arthritis is not clear, it is believed to involve a combination of genetic and environmental factors. The underlying mechanism involves the body's immune system attacking the joints. This results in inflammation and thickening of the joint capsule. It also affects the underlying bone and cartilage. The diagnosis is made mos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lymph Node
A lymph node, or lymph gland, is a kidney-shaped organ of the lymphatic system and the adaptive immune system. A large number of lymph nodes are linked throughout the body by the lymphatic vessels. They are major sites of lymphocytes that include B and T cells. Lymph nodes are important for the proper functioning of the immune system, acting as filters for foreign particles including cancer cells, but have no detoxification function. In the lymphatic system a lymph node is a secondary lymphoid organ. A lymph node is enclosed in a fibrous capsule and is made up of an outer cortex and an inner medulla. Lymph nodes become inflamed or enlarged in various diseases, which may range from trivial throat infections to life-threatening cancers. The condition of lymph nodes is very important in cancer staging, which decides the treatment to be used and determines the prognosis. Lymphadenopathy refers to glands that are enlarged or swollen. When inflamed or enlarged, lymph nodes can be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)