|
Washington, Tyne And Wear
Washington is a town in the City of Sunderland, Sunderland district, in Tyne and Wear, England. Historically part of County Durham, it is the ancestral settlement of the local Washington family, from which the first President of the United States George Washington descended. It has a population of 67,085. It is located between Chester-le-Street, Gateshead and South Tyneside. Washington was designated a New towns in the United Kingdom, new town in 1964. It became part of Tyne and Wear in 1974. The town has expanded dramatically since its designation; new villages were created and areas were reassigned from Chester-le-Street, to offer housing and employment to those moving from adjoining areas and further afield. At the United Kingdom Census 2011, 2011 census, Washington had a population of 67,085, compared to 53,388 in 2001. History Toponymy Early references appear around 1096 in Old English as Wasindone. The etymological origin is disputed and there are several proposed theor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
City Of Sunderland
Sunderland () is a port city and metropolitan borough in Tyne and Wear, England. It is a port at the mouth of the River Wear on the North Sea, approximately south-east of Newcastle upon Tyne. It is the most populous settlement in the Wearside conurbation and the second most populous settlement in North East England after Newcastle. Sunderland was once known as 'the largest shipbuilding town in the world' and once made a quarter of all of the world's ships from its famous yards, which date back to 1346 on the River Wear. The centre of the modern city is an amalgamation of three settlements founded in the Anglo-Saxon era: Monkwearmouth, on the north bank of the Wear, and Sunderland and Bishopwearmouth on the south bank. Monkwearmouth contains St Peter's Church, which was founded in 674 and formed part of Monkwearmouth–Jarrow Abbey, a significant centre of learning in the seventh and eighth centuries. Sunderland was a fishing settlement and later a port, being granted a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Germanic Languages
The Germanic languages are a branch of the Indo-European languages, Indo-European language family spoken natively by a population of about 515 million people mainly in Europe, North America, Oceania, and Southern Africa. The most widely spoken Germanic language, English language, English, is also the world's most List of languages by total number of speakers, widely spoken language with an estimated 2 billion speakers. All Germanic languages are derived from Proto-Germanic language, Proto-Germanic, spoken in Iron Age Scandinavia, History of Germany#Iron Age, Iron Age Northern Germany and along the North Sea and Baltic coasts. The West Germanic languages include the three most widely spoken Germanic languages: English language, English with around 360–400 million native speakers; German language, German, with over 100 million native speakers; and Dutch language, Dutch, with 24 million native speakers. Other West Germanic languages include Afrikaans, an offshoot of Dutch origi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William De Hertburn
Margaret of Huntingdon (1145 – 1201) was a Scottish princess and Duchess of Brittany. She was the sister of Scottish kings Malcolm IV and William I, wife of Conan IV, Duke of Brittany, and the mother of Constance, Duchess of Brittany. Her second husband was Humphrey de Bohun, hereditary Constable of England. Following her second marriage, Margaret styled herself as the Countess of Hereford. Life Margaret's parents were Henry of Scotland, Earl of Huntingdon and Northumbria, and Ada de Warenne. She has traditionally been considered the second-eldest daughter, younger than Ada, but it is possible that Margaret was the eldest since she married before Ada and was named after their paternal great-grandmother Saint Margaret (while Ada was named after their maternal great-grandmother Adelaide of Vermandois). Through her father, Margaret was the granddaughter of King David I of Scotland and Queen Maud, 2nd Countess of Huntingdon. In 1160, Margaret became Duchess of Brittany and C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Washington Old Hall (geograph 5906778)
Washington Old Hall is a historic manor house in Washington, Tyne and Wear, England. It lies in the centre of Washington, being surrounded by other villages. The building was the ancestral home of the family of George Washington (1732–1799), the first president of the United States. History William de Hertburne (originally William Bayard), an ancestor of George Washington, assumed tenancy of the Wessyngtonlands from the Bishop of Durham in the late 12th century. Soon after, he changed his name to William de Wessyngton (later Washington). In the early 15th century Sir William Mallory married Dionysia Tempest, the last Wessyngton heir at the Hall. Dionysia was daughter of Sir William Tempest and his cousin, Eleanor Wessyngton. In 1613, Sir John Mallory (a descendant of Sir William Mallory and Dionysia Tempest) and Anna Eure, shareholders in the Virginia Company, moved south to Sulgrave Manor in Northamptonshire, and the manor was sold to the Bishop of Durham. The Hall continu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
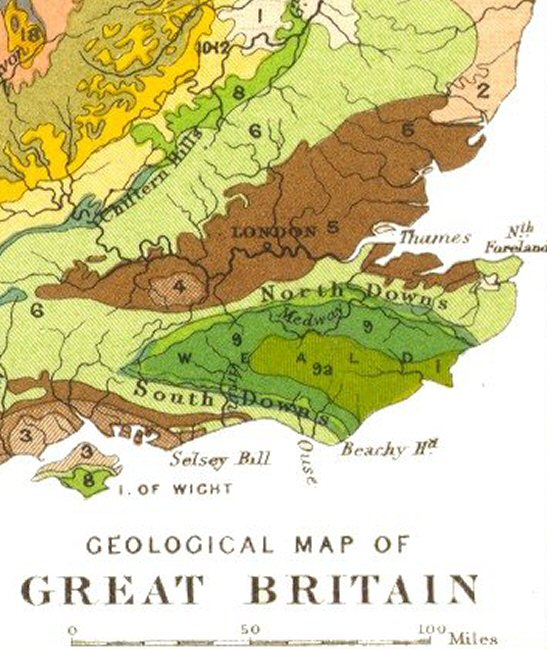
South Downs
The South Downs are a range of chalk hills in the south-eastern coastal counties of England that extends for about across the south-eastern coastal counties of England from the Itchen valley of Hampshire in the west to Beachy Head, in the Eastbourne Downland Estate, East Sussex, in the east. The Downs are bounded on the northern side by a steep escarpment, from whose crest there are extensive views northwards across the Weald. The South Downs National Park forms a much larger area than the chalk range of the South Downs, and includes large parts of the Weald. The national park is the UK's most visited, attracting an estimated 39 million visitor-days annually. The South Downs are characterised by rolling chalk downland with close-cropped turf and dry valleys, and are recognised as one of the most important chalk landscapes in England. The range is one of the four main areas of chalk downland in southern England. The South Downs are relatively less populated compared to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North Downs
The North Downs are a ridge of chalk hills in south east England that stretch from Farnham in Surrey to the White Cliffs of Dover in Kent. Much of the North Downs comprises two Area of Outstanding Natural Beauty, Areas of Outstanding Natural Beauty (AONBs): the Surrey Hills AONB, Surrey Hills and the Kent Downs AONB, Kent Downs. The North Downs Way National Trail runs along the North Downs from Farnham to Dover. The highest point in the North Downs is Botley Hill, Surrey ( above sea level). The ''County Top'' of Kent is Betsom's Hill ( above sea level), which is less than 1 km from Westerham Heights, Bromley, the highest point in Greater London at an elevation of . Etymology 'Downs' is from Old English ''dun'', meaning, amongst other things, "hill". The word acquired the sense of "elevated rolling grassland" around the 14th century. The name contains "North" to distinguish them from a similar range of hills – the South Downs – which runs roughly parallel to them but s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Washington Old Hall
Washington Old Hall is a historic manor house in Washington, Tyne and Wear, England. It lies in the centre of Washington, being surrounded by other villages. The building was the ancestral home of the family of George Washington (1732–1799), the first president of the United States. History William de Hertburne (originally William Bayard), an ancestor of George Washington, assumed tenancy of the Wessyngtonlands from the Bishop of Durham in the late 12th century. Soon after, he changed his name to William de Wessyngton (later Washington). In the early 15th century Sir William Mallory married Dionysia Tempest, the last Wessyngton heir at the Hall. Dionysia was daughter of Sir William Tempest and his cousin, Eleanor Wessyngton. In 1613, Sir John Mallory (a descendant of Sir William Mallory and Dionysia Tempest) and Anna Eure, shareholders in the Virginia Company, moved south to Sulgrave Manor in Northamptonshire, and the manor was sold to the Bishop of Durham. The Hall continu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
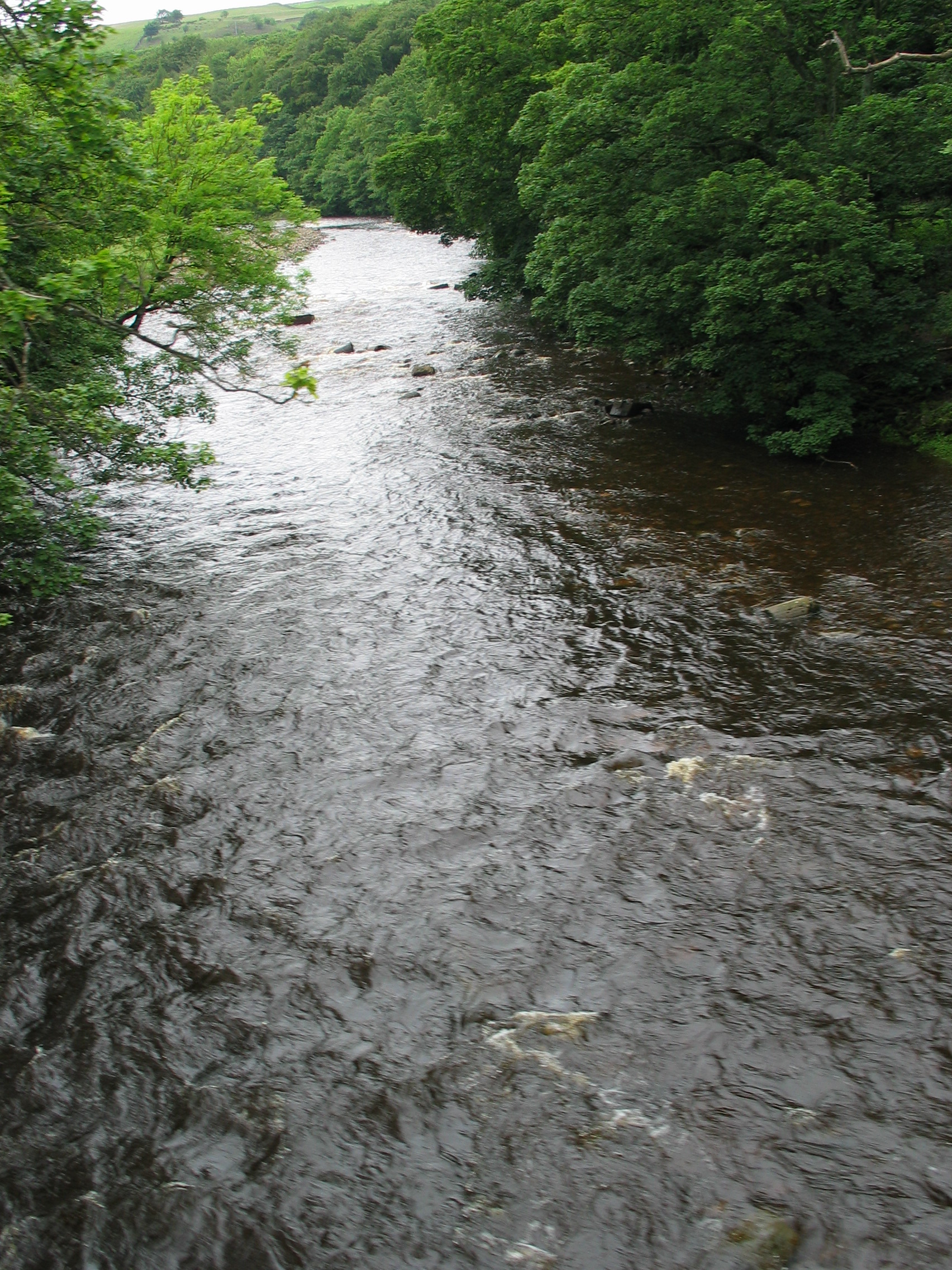
River Wear
The River Wear (, ) in Northern England rises in the Pennines and flows eastwards, mostly through County Durham, to the North Sea in the City of Sunderland. At long, it is one of the region's longest rivers. The Wear wends in a steep valley through the cathedral city of Durham and gives its name to Weardale in its upper reach and Wearside by its mouth. Etymology The origin behind the hydronym ''Wear'' is uncertain but is generally understood to be Celtic. The ''River Vedra'' on the Roman Map of Britain may very well be the River Wear. The name may be derived from Brittonic ''*wejr'' (<''*wẹ:drā''), which meant "a bend" (cf. Welsh ''-gwair-''). An alternative but very problematic etymology might involve ''*wẹ:d-r-'', from a lengthened form of the |
Noun
In grammar, a noun is a word that represents a concrete or abstract thing, like living creatures, places, actions, qualities, states of existence, and ideas. A noun may serve as an Object (grammar), object or Subject (grammar), subject within a phrase, clause, or sentence.Example nouns for: * Living creatures (including people, alive, dead, or imaginary): ''mushrooms, dogs, Afro-Caribbeans, rosebushes, Mandela, bacteria, Klingons'', etc. * Physical objects: ''hammers, pencils, Earth, guitars, atoms, stones, boots, shadows'', etc. * Places: ''closets, temples, rivers, Antarctica, houses, Uluru, utopia'', etc. * Actions of individuals or groups: ''swimming, exercises, cough, explosions, flight, electrification, embezzlement'', etc. * Physical qualities: ''colors, lengths, porosity, weights, roundness, symmetry, solidity,'' etc. * Mental or bodily states: ''jealousy, sleep, joy, headache, confusion'', etc. In linguistics, nouns constitute a lexical category (part of speech) defined ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Verb
A verb is a word that generally conveys an action (''bring'', ''read'', ''walk'', ''run'', ''learn''), an occurrence (''happen'', ''become''), or a state of being (''be'', ''exist'', ''stand''). In the usual description of English, the basic form, with or without the particle ''to'', is the infinitive. In many languages, verbs are inflected (modified in form) to encode tense, aspect, mood, and voice. A verb may also agree with the person, gender or number of some of its arguments, such as its subject, or object. In English, three tenses exist: present, to indicate that an action is being carried out; past, to indicate that an action has been done; and future, to indicate that an action will be done, expressed with the auxiliary verb ''will'' or ''shall''. For example: * Lucy ''will go'' to school. ''(action, future)'' * Barack Obama ''became'' the President of the United States in 2009. ''(occurrence, past)'' * Mike Trout ''is'' a center fielder. ''(state of bein ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
-ington
This article lists a number of common generic forms in place names in the British Isles, their meanings and some examples of their use. The study of place names is called toponymy; for a more detailed examination of this subject in relation to British and Irish place names, refer to Toponymy in the United Kingdom and Ireland. Key to languages: Bry: Brythonic; C: Cumbric; K: Cornish; I: Irish; L: Latin; ME: Middle English; NF: Norman French; OE: Old English (Anglo-Saxon); ON: Old Norse; P: Pictish; S: Scots; SG: Scots Gaelic; W: Welsh See also * English Place-Name Society * Germanic toponymy * Place name origins * Place names in Ireland * Placenames Database of Ireland * Scottish toponymy * Toponymy in the United Kingdom and Ireland * Toponymy of England * Welsh toponymy References External links * * {{DEFAULTSORT:Place Names, Generic Forms English toponymy Ireland geography-related lists Irish toponymy Lists of United Kingdom placename etymology United Kingdo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Icelandic Language
Icelandic ( ; , ) is a North Germanic languages, North Germanic language from the Indo-European languages, Indo-European language family spoken by about 314,000 people, the vast majority of whom live in Iceland, where it is the national language. Since it is a West Scandinavian languages, West Scandinavian language, it is most closely related to Faroese language, Faroese, western Norwegian dialects, and the extinct language Norn language, Norn. It is not mutually intelligible with the continental Scandinavian languages (Danish language, Danish, Norwegian language, Norwegian, and Swedish language, Swedish) and is more distinct from the most widely spoken Germanic languages, English language, English and German language, German. The written forms of Icelandic and Faroese are very similar, but their spoken forms are not Mutual intelligibility, mutually intelligible. The language is more Linguistic conservatism, conservative than most other Germanic languages. While most of them hav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |