|
Vympel NPO Products
Directorate "V" of the FSB Special Purpose Center, often referred to as Spetsgruppa "V" Vympel ( pennant in Russian, originated from German , and having the same meaning), but also known as KGB Directorate "V", Vega Group, is a stand-alone sub-unit of Russia's special forces within the Russian Special Forces Center of the Federal Security Service (FSB). Vympel is the sister unit of Spetsgruppa "A" (Alpha Group), an FSB unit. Origins KUOS As most of the training in the KGB academy concentrated on plainclothes operational work focused on espionage and counter-espionage, in 1955 the First Chief Directorate of the service established the Development Courses for Officer Personnel ( (), Latinized abbreviation KUOS) – a training cadre with the purpose of training general duty KGB officers in irregular warfare and combat tactics for clandestine operations overseas or as a stay-behind cadre and backbone for the formation of partisan units in case of a foreign invasion. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flag Of The Russian Federal Security Service
A flag is a piece of fabric (most often rectangular) with distinctive colours and design. It is used as a symbol, a signalling device, or for decoration. The term ''flag'' is also used to refer to the graphic design employed, and flags have evolved into a general tool for rudimentary signalling and identification, especially in environments where communication is challenging (such as the maritime environment, where semaphore is used). Many flags fall into groups of similar designs called flag families. The study of flags is known as "vexillology" from the Latin , meaning "flag" or "banner". National flags are patriotic symbols with widely varied interpretations that often include strong military associations because of their original and ongoing use for that purpose. Flags are also used in messaging, advertising, or for decorative purposes. Some military units are called "flags" after their use of flags. A ''flag'' (Arabic: ) is equivalent to a brigade in Arab countries. In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Long-range Penetration
A long-range penetration patrol, group, or force is a special operations unit capable of operating long distances behind enemy lines far away from direct contact with friendly forces as opposed to a Long Range Reconnaissance Patrol, a small group primarily engaged in scouting missions. History Though the concept of long range penetration is as old as war itself, in the modern era it is recognized as starting with Major Ralph Alger Bagnold with his 1940 Long Range Desert Group ( LRDG) in the Western Desert. The LRDG carried out operations of reconnaissance and sabotage far behind the enemy's lines in the Libyan Desert. Bagnold was an experienced desert explorer who had his LRDG trained in desert driving, navigation through using the sun and stars as well as a compass, and knowing their territory. They were supplied by all the equipment that their trucks could carry. In 1942, several British Special Operations Executive (SOE) personnel who had escaped from Singapore to Australi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
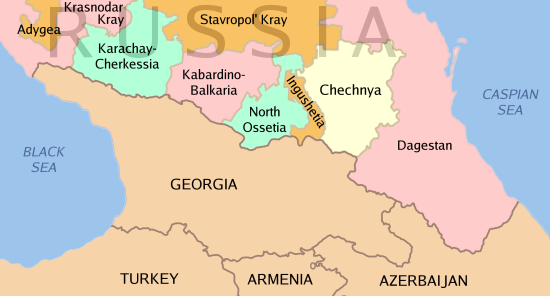
Insurgency In The North Caucasus
History and background In late 1999, Russia's Premier, Vladimir Putin, ordered military, police and security forces to enter the breakaway region of Chechnya. By early 2000, these forces occupied most of the region. High levels of fighting continued for several more years and resulted in thousands of Russian and Chechen casualties and hundreds of thousands of displaced persons. In 2005, Chechen rebel leader, Abdul-Halim Sadulayev, decreed the formation of a Caucasian Front (militant group), Caucasus Front against Russia, among Islamic believers in the North Caucasus, in an attempt to widen Chechnya's conflict with Russia. After his death, his successor, Dokka Umarov, declared continuing jihad to establish an Islamic fundamentalist Caucasus Emirate in the North Caucasus and beyond. Russia's pacification policy in Chechnya has involved setting up a pro-Moscow regional government and transferring more local security duties to this government. An important factor in Russia's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beslan School Hostage Crisis
The Beslan school siege, also referred to as the Beslan school hostage crisis or the Beslan massacre, was an Islamic terrorist attack that started on 1 September 2004. It lasted three days, and involved the imprisonment of more than 1,100 people as hostages, including 777 children, ending with the deaths of 334 people, 186 of them children, as well as 31 of the attackers. It is considered the deadliest school shooting in history. The crisis began when a group of armed terrorists occupied School Number One (SNO) in the town of Beslan, North Ossetia (an autonomous republic in the North Caucasus region of Russia), on 1 September 2004. The hostage-takers were members of the Riyad-us Saliheen, sent by the Chechen warlord Shamil Basayev, who demanded Russia withdraw from and recognize the independence of Chechnya. On the third day of the standoff, Russian security forces stormed the building. The event had security and political repercussions in Russia, leading to a series of feder ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moscow Theatre Hostage Crisis
The Moscow theater hostage crisis, also known as the 2002 Nord-Ost siege, was the seizure of the crowded Dubrovka Theater in Moscow by Chechen terrorists on 23 October 2002, resulting in the taking of 912 hostages. The attackers, led by Movsar Barayev, claimed allegiance to the Islamist separatist movement in Chechnya. They demanded the withdrawal of Russian forces from Chechnya and an end to the Second Chechen War. The crisis was resolved when Russian security services released sleeping gas into the building, and subsequently stormed it, killing all 40 hostage takers. 132 hostages died, largely due to the effects of the gas. Due to the layout of the theater, special forces would have had to fight through of corridor and advance up a well-defended staircase before they could reach the hall in which the hostages were held. The attackers had numerous explosives, with the most powerful in the center of the auditorium. Spetsnaz operators from Federal Security Service (FSB) Alph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second Chechen War
Names The Second Chechen War is also known as the Second Chechen Campaign () or the Second Russian Invasion of Chechnya from the Chechens, Chechen insurgents' point of view.Федеральный закон № 5-ФЗ от 12 января 1995 (в редакции от 27 ноября 2002) "О ветеранах" Historical basis of the conflict Russian Empire Chechnya is an area in the North Caucasus, Northern Caucasus which has constantly fought against foreign rule, including the Ottoman Turks in the 15th century. The Russian Terek Cossacks, Terek Cossack Host was established in lowland Chechnya in 1577 by free Cossacks who were resettled from the Volga to the Terek River. In 1783, the Russian Empire and the Georgia (country), Georgian Kingdom of Kartli-Kakheti signed the Treaty of Georgievsk, under which Kartli-Kakheti became a Russian protectorate. To secure communications with Georgia (country), Georgia and other regions of the Transcaucasia, the Russian Empire ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
First Chechen War
The First Chechen War, also referred to as the First Russo-Chechen War, was a struggle for independence waged by the Chechen Republic of Ichkeria against the invading Russia, Russian Federation from 1994 to 1996. After a mutually agreed on treaty and terms, the Russians withdrew until they invaded again three years later, in the Second Chechen War of 1999–2000. During the dissolution of the Soviet Union in late 1991, Chechnya came under the control of a secessionist regime led by Dzhokhar Dudayev. Russian president Boris Yeltsin supported anti-Dudayev militias until 1994, when he launched a military operation to "establish constitutional order in Chechnya". Thousands of Chechen civilians were killed in aerial bombings and urban warfare before Battle of Grozny (1994–1995), Grozny was captured in March 1995, but a Russian victory was denied as efforts to establish control over the remaining lowlands and mountainous regions of Chechnya were met with fierce resistance and frequent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1993 Russian Constitutional Crisis
In September and October 1993, a constitutional crisis arose in the Russian Federation from a conflict between the then Russian president Boris Yeltsin and the country's parliament. Yeltsin performed a self-coup, dissolving parliament and instituting a presidential rule by decree system. The crisis ended with Yeltsin using military force to attack Moscow's House of Soviets and arrest the lawmakers. In Russia, the events are known as the "October Coup" () or "Black October" (). With the dissolution of the Soviet Union in December 1991, the Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic turned into an independent country, the Russian Federation. The Soviet-era 1978 Russian constitution remained in effect, though it had been amended in April 1991 to install a president independent of the parliament. Boris Yeltsin, elected president in July 1991, began assuming increasing powers, leading to a political standoff with Russia's parliament, which in 1993 was composed of the Congress o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1991 Soviet Coup D'état Attempt
The 1991 Soviet coup attempt, also known as the August Coup, was a failed attempt by hardliners of the Communist Party of the Soviet Union (CPSU) to Coup d'état, forcibly seize control of the country from Mikhail Gorbachev, who was President of the Soviet Union, Soviet President and General Secretary of the CPSU at the time. The coup leaders consisted of top military and civilian officials, including Vice President Gennady Yanayev, who together formed the State Committee on the State of Emergency (). They opposed Gorbachev's Perestroika, reform program, were angry at the Revolutions of 1989, loss of control over Eastern European states and fearful of the New Union Treaty, which was on the verge of being signed by the Soviet Union (USSR). The treaty was to decentralize much of the Government of the Soviet Union, central Soviet government's power and distribute it among its Republics of the Soviet Union, fifteen republics; Boris Yeltsin's demand for more autonomy to the republics ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soviet–Afghan War
The Soviet–Afghan War took place in the Democratic Republic of Afghanistan from December 1979 to February 1989. Marking the beginning of the 46-year-long Afghan conflict, it saw the Soviet Union and the Armed Forces of the Democratic Republic of Afghanistan, Afghan military fight against the rebelling Afghan mujahideen, aided by Pakistan. While they were backed by various countries and organizations, the majority of the mujahideen's support came from Pakistan, the United States (as part of Operation Cyclone), the United Kingdom, China, Iran, and the Arab states of the Persian Gulf, in addition to a large influx of foreign fighters known as the Afghan Arabs. American and British involvement on the side of the mujahideen escalated the Cold War, ending a short period of relaxed Soviet Union–United States relations. Combat took place throughout the 1980s, mostly in the Afghan countryside, as most of the country's cities remained under Soviet control. The conflict resulted in the de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moscow
Moscow is the Capital city, capital and List of cities and towns in Russia by population, largest city of Russia, standing on the Moskva (river), Moskva River in Central Russia. It has a population estimated at over 13 million residents within the city limits, over 19.1 million residents in the urban area, and over 21.5 million residents in Moscow metropolitan area, its metropolitan area. The city covers an area of , while the urban area covers , and the metropolitan area covers over . Moscow is among the world's List of largest cities, largest cities, being the List of European cities by population within city limits, most populous city entirely in Europe, the largest List of urban areas in Europe, urban and List of metropolitan areas in Europe, metropolitan area in Europe, and the largest city by land area on the European continent. First documented in 1147, Moscow became the capital of the Grand Principality of Moscow, which led the unification of the Russian lan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Special Reconnaissance
Special reconnaissance (SR) is conducted by small units, such as a recon team, made up of highly trained military personnel, usually from special forces units and/or military intelligence organizations. Special reconnaissance teams operate behind enemy lines, avoiding direct combat and detection by the enemy. As a role, SR is distinct from commando operations, but both are often carried out by the same units. The SR role frequently includes covert direction of airstrikes and indirect fire, in areas deep behind enemy lines, placement of remotely monitored sensors, and preparations for other special forces. Like other special forces, SR units may also carry out direct action and unconventional warfare, including guerrilla operations. In intelligence terms, SR is a human intelligence (HUMINT) collection discipline. Its operational control is likely to be inside a compartmented cell of the HUMINT, or possibly the operations, staff functions. Since such personnel are trained for intell ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |