|
Telomeres
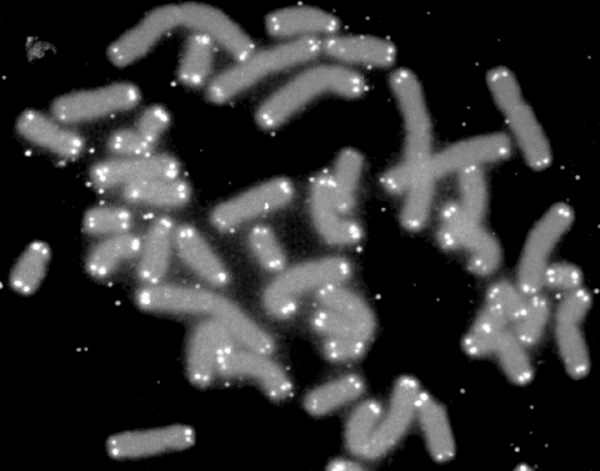
A telomere (; ) is a region of repetitive nucleotide sequences associated with specialized proteins at the ends of linear chromosomes (see Sequences). Telomeres are a widespread genetic feature most commonly found in eukaryotes. In most, if not all species possessing them, they protect the terminal regions of chromosomal DNA from progressive degradation and ensure the integrity of linear chromosomes by preventing DNA repair systems from mistaking the very ends of the DNA strand for a double-strand break. Discovery The existence of a special structure at the ends of chromosomes was independently proposed in 1938 by Hermann Joseph Muller, studying the fruit fly ''Drosophila melanogaster'', and in 1939 by Barbara McClintock, working with maize. Muller observed that the ends of irradiated fruit fly chromosomes did not present alterations such as deletions or inversions. He hypothesized the presence of a protective cap, which he coined "telomeres", from the Greek ''telos'' (end) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Telomere Caps
A telomere (; ) is a region of repetitive nucleotide sequences associated with specialized proteins at the ends of linear chromosomes (see Sequences). Telomeres are a widespread genetic feature most commonly found in eukaryotes. In most, if not all species possessing them, they protect the terminal regions of chromosomal DNA from progressive degradation and ensure the integrity of linear chromosomes by preventing DNA repair systems from mistaking the very ends of the DNA strand for a double-strand break. Discovery The existence of a special structure at the ends of chromosomes was independently proposed in 1938 by Hermann Joseph Muller, studying the fruit fly ''Drosophila melanogaster'', and in 1939 by Barbara McClintock, working with maize. Muller observed that the ends of irradiated fruit fly chromosomes did not present alterations such as deletions or inversions. He hypothesized the presence of a protective cap, which he coined "telomeres", from the Greek ''telos'' (end ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Telomerase
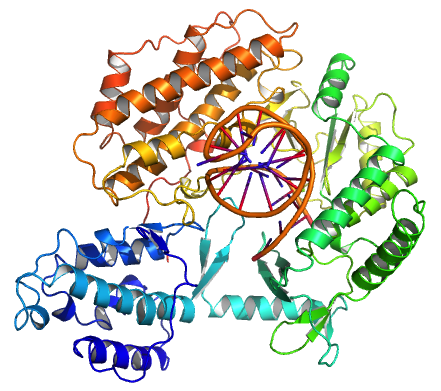
Telomerase, also called terminal transferase, is a ribonucleoprotein that adds a species-dependent telomere repeat sequence to the 3' end of telomeres. A telomere is a region of repetitive sequences at each end of the chromosomes of most eukaryotes. Telomeres protect the end of the chromosome from DNA damage or from fusion with neighbouring chromosomes. The fruit fly ''Drosophila melanogaster'' lacks telomerase, but instead uses retrotransposons to maintain telomeres. Telomerase is a reverse transcriptase enzyme that carries its own RNA molecule (e.g., with the sequence 3′- CCC AA UCCC-5′ in '' Trypanosoma brucei'') which is used as a template when it elongates telomeres. Telomerase is active in gametes and most cancer cells, but is normally absent in most somatic cells. History The existence of a compensatory mechanism for telomere shortening was first found by Soviet biologist Alexey Olovnikov in 1973, who also suggested the telomere hypothesis of aging and the telo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elizabeth Blackburn
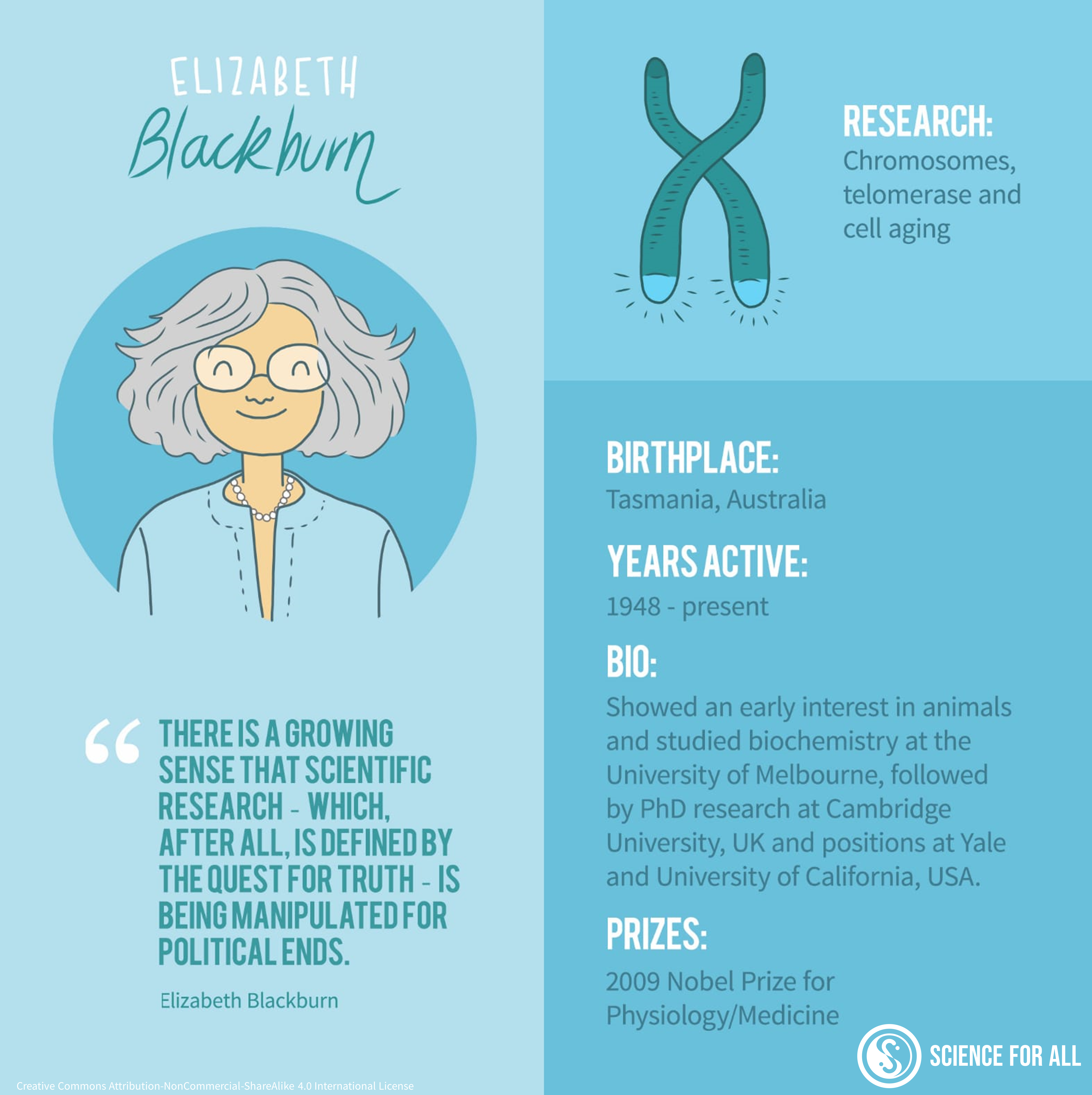
Elizabeth Helen Blackburn (born 26 November 1948) is an Australian-American Nobel laureate who is the former president of the Salk Institute for Biological Studies. In 1984, Blackburn co-discovered telomerase, the enzyme that replenishes the telomere, with Carol W. Greider. For this work, she was awarded the 2009 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine, sharing it with Carol W. Greider and Jack W. Szostak, becoming the first Australian woman Nobel laureate. She also worked in medical ethics, and was controversially dismissed from the Bush administration's President's Council on Bioethics. 170 scientists signed an open letter to the president in her support, maintaining that she was fired because of political opposition to her advice. Early life and education Elizabeth Helen Blackburn, the second of seven children, was born in Hobart, Tasmania, on 26 November 1948, with both her parents being family physicians. Her family moved to the city of Launceston when she was fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carol Greider
Carolyn Widney Greider (born April 15, 1961) is an American molecular biologist and Nobel laureate. She is a Distinguished Professor of Molecular, Cell, and Developmental Biology at the University of California, Santa Cruz. Greider discovered the enzyme telomerase in 1984, while she was a graduate student of Elizabeth Blackburn at the University of California, Berkeley. Greider pioneered research on the structure of telomeres, the ends of the chromosomes. She was awarded the 2009 Nobel Prize for Physiology or Medicine, along with Blackburn and Jack W. Szostak, for their discovery that telomeres are protected from progressive shortening by the enzyme telomerase. Early life and education Greider was born in San Diego, California. Her father, Kenneth Greider, was a physics professor. Her family moved from San Diego to Davis, California, where she spent many of her early years and graduated from Davis Senior High School in 1979. She graduated from the College of Creative Studies ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |