|
Telecommunications Engineering
Telecommunications engineering is a subfield of electronics engineering which seeks to design and devise systems of communication at a distance. The work ranges from basic circuit design to strategic mass developments. A telecommunication engineer is responsible for designing and overseeing the installation of telecommunications equipment and facilities, such as complex electronic switching system, and other plain old telephone service facilities, optical fiber cabling, IP networks, and microwave transmission systems. Telecommunications engineering also overlaps with broadcast engineering. Telecommunication is a diverse field of engineering connected to electronic, civil and systems engineering. Ultimately, telecom engineers are responsible for providing high-speed data transmission services. They use a variety of equipment and transport media to design the telecom network infrastructure; the most common media used by wired telecommunications today are twisted pair, co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
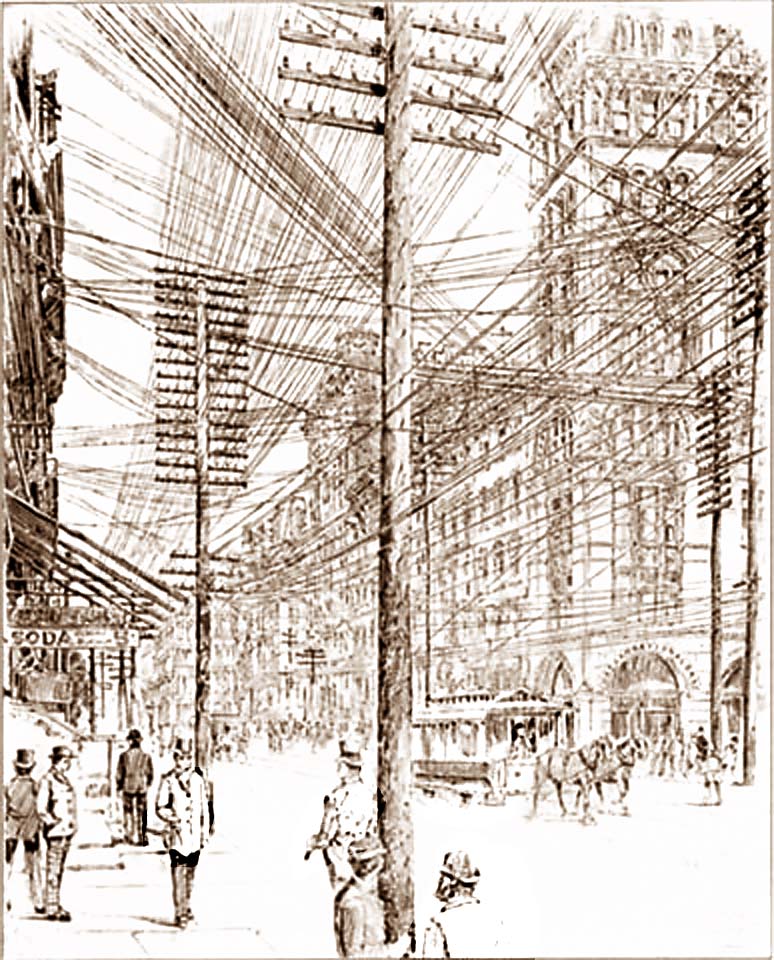
The Telephone Service Carries On, London, January 1942 D6437
''The'' is a grammatical Article (grammar), article in English language, English, denoting nouns that are already or about to be mentioned, under discussion, implied or otherwise presumed familiar to listeners, readers, or speakers. It is the definite article in English. ''The'' is the Most common words in English, most frequently used word in the English language; studies and analyses of texts have found it to account for seven percent of all printed English-language words. It is derived from gendered articles in Old English which combined in Middle English and now has a single form used with nouns of any gender. The word can be used with both singular and plural nouns, and with a noun that starts with any letter. This is different from many other languages, which have different forms of the definite article for different genders or numbers. Pronunciation In most dialects, "the" is pronounced as (with the voiced dental fricative followed by a schwa) when followed by a con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coaxial Cable
Coaxial cable, or coax (pronounced ), is a type of electrical cable consisting of an inner Electrical conductor, conductor surrounded by a concentric conducting Electromagnetic shielding, shield, with the two separated by a dielectric (Insulator (electricity), insulating material); many coaxial cables also have a protective outer sheath or jacket. The term ''coaxial'' refers to the inner conductor and the outer shield sharing a geometric axis. Coaxial cable is a type of transmission line, used to carry high-frequency Signal, electrical signals with low losses. It is used in such applications as telephone trunk lines, Internet access, broadband internet networking cables, high-speed computer bus (computing), data buses, cable television signals, and connecting Transmitter, radio transmitters and Radio receiver, receivers to their Antenna (radio), antennas. It differs from other shielded cables because the dimensions of the cable and connectors are controlled to give a precise, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
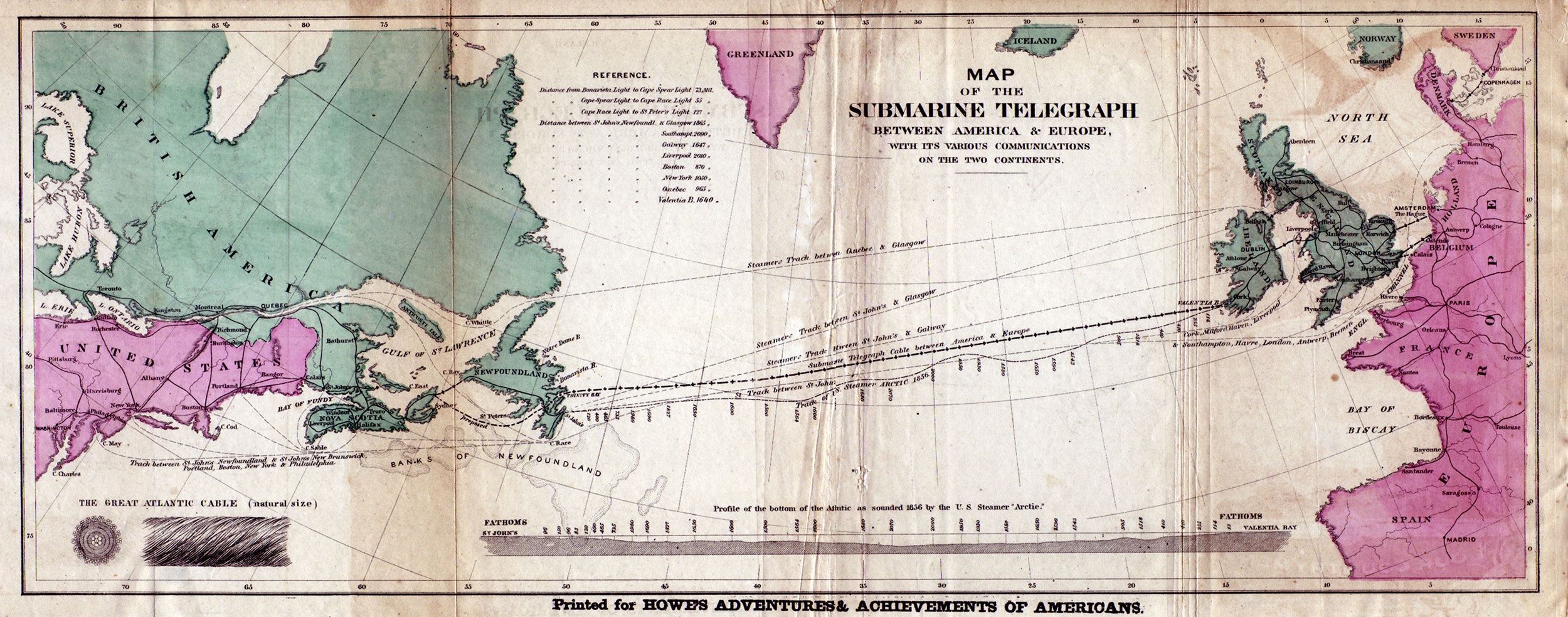
Victorian Internet
''The Victorian Internet: The Remarkable Story of the Telegraph and the Nineteenth Century's On-Line Pioneers'' is a 1998 book by Tom Standage. The book was first published in September 1998 through Walker & Company and discusses the development and uses of the electric telegraph during the second half of the 19th century and some of the similarities the telegraph shared with the Internet of the late 20th century. The central thesis of the book argues that of these two technologies, it was the telegraph that was the more significant, since the ability to communicate globally at all in real-time was a qualitative shift, while according to Standage the change brought on by the modern Internet was merely a quantitative shift. Contents The book describes to general readers how some of the uses of telegraph in commercial, soldier, and social communication were, in a sense, analogous to modern uses of the internet. A few rather unusual stories are related, about couples who fell in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transatlantic Telegraph Cable
Transatlantic telegraph cables were undersea cables running under the Atlantic Ocean for telegraph communications. Telegraphy is a largely obsolete form of communication, and the cables have long since been decommissioned, but telephone and data are still carried on other transatlantic telecommunications cables. The Atlantic Telegraph Company led by Cyrus West Field constructed the first transatlantic telegraph cable. The project began in 1854 with the first cable laid from Valentia Island off the west coast of Ireland to Bay of Bulls, Trinity Bay, Newfoundland. The first communications occurred on August 16, 1858, but the line speed was poor. The first official telegram to pass between two continents that day was a letter of congratulations from Queen Victoria of the United Kingdom to President of the United States James Buchanan. Signal quality declined rapidly, slowing transmission to an almost unusable speed. The cable was destroyed after three weeks when Wildman ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baltimore
Baltimore is the most populous city in the U.S. state of Maryland. With a population of 585,708 at the 2020 census and estimated at 568,271 in 2024, it is the 30th-most populous U.S. city. The Baltimore metropolitan area is the 20th-largest metropolitan area in the country at 2.84 million residents. The city is also part of the Washington–Baltimore combined statistical area, which had a population of 9.97 million in 2020. Baltimore was designated as an independent city by the Constitution of Maryland in 1851. Though not located under the jurisdiction of any county in the state, it forms part of the central Maryland region together with the surrounding county that shares its name. The land that is present-day Baltimore was used as hunting ground by Paleo-Indians. In the early 1600s, the Susquehannock began to hunt there. People from the Province of Maryland established the Port of Baltimore in 1706 to support the tobacco trade with Europe and established the Town ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alfred Vail
Alfred Lewis Vail (September 25, 1807 – January 18, 1859) was an American machinist and inventor. Along with Samuel Morse, Vail was central in developing and commercializing American electrical telegraphy between 1837 and 1844. Vail and Morse were the first two telegraph operators on Morse's first experimental line between Washington, D.C., and Baltimore, and Vail took charge of building and managing several early telegraph lines between 1845 and 1848. He was also responsible for several technical innovations of Morse's system, particularly the first sending key, which Vail invented, and improved recording registers and relay magnets. Vail left the telegraph industry in 1848 because he believed that the managers of Morse's lines did not fully value his contributions. His last assignment, superintendent of the Washington and New Orleans Telegraph Company, paid him only $900 a year, leading Vail to write to Morse, Early life Vail's parents were Bethiah Youngs (1778–184 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Samuel Morse
Samuel Finley Breese Morse (April 27, 1791 – April 2, 1872) was an American inventor and painter. After establishing his reputation as a portrait painter, Morse, in his middle age, contributed to the invention of a Electrical telegraph#Morse system, single-wire telegraph system based on European telegraphs. He was a co-developer of Morse code in 1837 and helped to develop the commercial use of telegraphy. Personal life Samuel F. B. Morse was born in Charlestown, Boston, Massachusetts, the first child of the pastor Jedidiah Morse, who was also a geographer, and his wife Elizabeth Ann Finley Breese. His father was a great preacher of the Calvinism, Calvinist faith and supporter of the Federalist Party. He thought it helped preserve Puritan traditions (strict observance of Christian Sabbath, Sabbath, among other things), and believed in the Federalist support of an alliance with Britain and a strong central government. Morse strongly believed in education within a Federalist f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alexander Graham Bell's Big Box Telephone, 1876, One Of The First Commercially Available Telephones - National Museum Of American History - DSC06223
Alexander () is a male name of Greek origin. The most prominent bearer of the name is Alexander the Great, the king of the Ancient Greek kingdom of Macedonia who created one of the largest empires in ancient history. Variants listed here are Aleksandar, Aleksander, Oleksandr, Oleksander, Aleksandr, and Alekzandr. Related names and diminutives include Iskandar, Alec, Alek, Alex, Alexsander, Alexandre, Aleks, Aleksa, Aleksandre, Alejandro, Alessandro, Alasdair, Sasha, Sandy, Sandro, Sikandar, Skander, Sander and Xander; feminine forms include Alexandra, Alexandria, and Sasha. Etymology The name ''Alexander'' originates from the (; 'defending men' or 'protector of men'). It is a compound of the verb (; 'to ward off, avert, defend') and the noun (, genitive: , ; meaning 'man'). The earliest attested form of the name, is the Mycenaean Greek feminine anthroponym , , (/Alexandra/), written in the Linear B syllabic script. Alaksandu, alternatively called ''Alakasan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Public Switched Telephone Network
The public switched telephone network (PSTN) is the aggregate of the world's telephone networks that are operated by national, regional, or local telephony operators. It provides infrastructure and services for public telephony. The PSTN consists of telephone lines, fiber-optic cables, microwave transmission links, cellular networks, communications satellites, and undersea telephone cables interconnected by switching centers, such as central offices, network tandems, and international gateways, which allow telephone users to communicate with each other. Originally a network of fixed-line analog telephone systems, the PSTN is now predominantly digital in its core network and includes terrestrial cellular, satellite, and landline systems. These interconnected networks enable global communication, allowing calls to be made to and from nearly any telephone worldwide. Many of these networks are progressively transitioning to Internet Protocol to carry their telephony traffi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Broadband
In telecommunications, broadband or high speed is the wide-bandwidth (signal processing), bandwidth data transmission that exploits signals at a wide spread of frequencies or several different simultaneous frequencies, and is used in fast Internet access. The transmission medium can be coaxial cable, optical fiber, wireless Internet (radio), twisted pair cable, or satellite broadband, satellite. Originally used to mean 'using a wide-spread frequency' and for services that were analog at the lowest level, nowadays in the context of Internet access, 'broadband' is often used to mean any high-speed Internet access that is seemingly always 'on' and is faster than Dial-up Internet access, dial-up access over traditional plain old telephone service, analog or ISDN public switched telephone network, PSTN services. The ideal telecommunication network has the following characteristics: ''broadband'', ''multi-media'', ''multi-point'', ''multi-rate'' and economical implementation for a di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wi-Fi
Wi-Fi () is a family of wireless network protocols based on the IEEE 802.11 family of standards, which are commonly used for Wireless LAN, local area networking of devices and Internet access, allowing nearby digital devices to exchange data by radio waves. These are the most widely used computer networks, used globally in small office/home office, home and small office networks to link devices and to provide Internet access with wireless routers and wireless access points in public places such as coffee shops, restaurants, hotels, libraries, and airports. ''Wi-Fi'' is a trademark of the Wi-Fi Alliance, which restricts the use of the term "''Wi-Fi Certified''" to products that successfully complete Interoperability Solutions for European Public Administrations, interoperability certification testing. Non-compliant hardware is simply referred to as WLAN, and it may or may not work with "''Wi-Fi Certified''" devices. the Wi-Fi Alliance consisted of more than 800 companies from ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |