|
Southland, New Zealand
Southland ( mi, Murihiku) is New Zealand's southernmost region. It consists mainly of the southwestern portion of the South Island and Stewart Island/Rakiura. It includes Southland District, Gore District and the city of Invercargill. The region covers over 3.1 million hectares and spans over 3,400 km of coast. History The earliest inhabitants of Murihiku (meaning "the last joint of the tail") were Māori of the Waitaha iwi, followed later by Kāti Māmoe and Kāi Tahu. Waitaha sailed on the Uruao waka, whose captain Rakaihautū named sites and carved out lakes throughout the area. The Takitimu Mountains were formed by the overturned Kāi Tahu waka Tākitimu. Descendants created networks of customary food gathering sites, travelling seasonally as needed, to support permanent and semi-permanent settlements in coastal and inland regions. In later years, the coastline was a scene of early extended contact between Māori and Europeans, in this case sealers, whalers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kāti Māmoe
Kāti Māmoe (also spelled Ngāti Māmoe but not by the tribe themselves) is a historic Māori iwi. Originally from the Hastings area, they moved in the 16th century to the South Island which at the time was already occupied by the Waitaha. A century later, the Ngāti Māmoe were largely subsequently absorbed via marriage and conquest by the Ngāi Tahu, who migrated south in turn. There is no distinct Ngāti Māmoe organisation today but many Ngāi Tahu have Ngāti Māmoe links in their whakapapa. In the far south of the island especially, "... southern Māori still think of themselves as Ngai Tahu-Ngati Mamoe, a synthesis of the two tribal groups ...." According to Edward Shortland, Kāti Māmoe's historical hapū included Kāti Rakai and Kāti Hinekato. History Early history Kāti Māmoe's descent is traced from the ancestor Hotumāmoe, said to be a descendant of Toi, a great-great-great grandson of Rākaihautū. Hotumāmoe is said to have lived in the Heretaunga District. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Māori Language
Māori (), or ('the Māori language'), also known as ('the language'), is an Eastern Polynesian language spoken by the Māori people, the indigenous population of mainland New Zealand. Closely related to Cook Islands Māori, Tuamotuan, and Tahitian, it gained recognition as one of New Zealand's official languages in 1987. The number of speakers of the language has declined sharply since 1945, but a Māori-language revitalisation effort has slowed the decline. The 2018 New Zealand census reported that about 186,000 people, or 4.0% of the New Zealand population, could hold a conversation in Māori about everyday things. , 55% of Māori adults reported some knowledge of the language; of these, 64% use Māori at home and around 50,000 people can speak the language "very well" or "well". The Māori language did not have an indigenous writing system. Missionaries arriving from about 1814, such as Thomas Kendall, learned to speak Māori, and introduced the Latin alphabet. In 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Waka (canoe)
Waka () are Māori watercraft, usually canoes ranging in size from small, unornamented canoes (''waka tīwai'') used for fishing and river travel to large, decorated war canoes (''waka taua'') up to long. The earliest remains of a canoe in New Zealand were found near the Anaweka estuary in a remote part of the Tasman District and radiocarbon-dated to about 1400. The canoe was constructed in New Zealand, but was a sophisticated canoe, compatible with the style of other Polynesian voyaging canoes at that time. Since the 1970s about eight large double-hulled canoes of about 20 metres have been constructed for oceanic voyaging to other parts of the Pacific. They are made of a blend of modern and traditional materials, incorporating features from ancient Melanesia, as well as Polynesia. Waka taua (war canoes) ''Waka taua'' (in Māori, ''waka'' means "canoe" and ''taua'' means "army" or "war party") are large canoes manned by up to 80 paddlers and are up to in length. Large waka, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Otago
Otago (, ; mi, Ōtākou ) is a region of New Zealand located in the southern half of the South Island administered by the Otago Regional Council. It has an area of approximately , making it the country's second largest local government region. Its population was The name "Otago" is the local southern Māori dialect pronunciation of "Ōtākou", the name of the Māori village near the entrance to Otago Harbour. The exact meaning of the term is disputed, with common translations being "isolated village" and "place of red earth", the latter referring to the reddish-ochre clay which is common in the area around Dunedin. "Otago" is also the old name of the European settlement on the harbour, established by the Weller Brothers in 1831, which lies close to Otakou. The upper harbour later became the focus of the Otago Association, an offshoot of the Free Church of Scotland, notable for its adoption of the principle that ordinary people, not the landowner, should choose the ministe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
James Alexander Robertson Menzies
James Alexander Robertson Menzies (21 February 1821 – 18 August 1888) was the first superintendent of the Southland Province in New Zealand from 3 August 1861 to November 1864, during its breakaway from Otago Province (1861 to 1870). He continued serving on the Provincial Council after his superintendency ended. During Menzies' tenure as superintendent, two railways projects were undertaken, a railway to link Invercargill to the port at Bluff and a wooden railway to Winton. The former is now known as the Bluff Branch, while the latter was upgraded to the standards of a normal railway and extended to ultimately form the Kingston Branch. Menzies served on the Legislative Council for 30 years, from 1858 until his death in 1888, and promoted the interests of Southland. See also * Southland, New Zealand Southland ( mi, Murihiku) is New Zealand's southernmost region. It consists mainly of the southwestern portion of the South Island and Stewart Island/Rakiura. It includ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Free Church Of Scotland (1843–1900)
The Free Church of Scotland is a Scottish denomination which was formed in 1843 by a large withdrawal from the established Church of Scotland in a schism known as the Disruption of 1843. In 1900, the vast majority of the Free Church of Scotland joined with the United Presbyterian Church of Scotland to form the United Free Church of Scotland (which itself mostly re-united with the Church of Scotland in 1929). In 1904, the House of Lords judged that the constitutional minority that did not enter the 1900 union were entitled to the whole of the church's patrimony, the Free Church of Scotland acquiesced in the division of those assets, between itself and those who had entered the union, by a Royal Commission in 1905. Despite the late founding date, Free Church of Scotland leadership claims an unbroken succession of leaders going all the way back to the Apostles. Origins The Free Church was formed by Evangelicals who broke from the Establishment of the Church of Scotland in 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Church Of Scotland
The Church of Scotland ( sco, The Kirk o Scotland; gd, Eaglais na h-Alba) is the national church in Scotland. The Church of Scotland was principally shaped by John Knox, in the Scottish Reformation, Reformation of 1560, when it split from the Catholic Church and established itself as a church in the reformed tradition. The church is Calvinist Presbyterian, having no head of faith or leadership group and believing that God invited the church's adherents to worship Jesus. The annual meeting of its general assembly is chaired by the Moderator of the General Assembly of the Church of Scotland. The Church of Scotland celebrates two sacraments, Baptism and the Lord's Supper in Reformed theology, Lord's Supper, as well as five other Rite (Christianity), rites, such as Confirmation and Christian views on marriage, Matrimony. The church adheres to the Bible and the Westminster Confession of Faith, and is a member of the World Communion of Reformed Churches. History Presbyterian tra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schism (religion)
A schism ( , , or, less commonly, ) is a division between people, usually belonging to an organization, movement, or religious denomination. The word is most frequently applied to a split in what had previously been a single religious body, such as the Great East–West Schism or the Western Schism. It is also used of a split within a non-religious organization or movement or, more broadly, of a separation between two or more people, be it brothers, friends, lovers, etc. A schismatic is a person who creates or incites schism in an organization or who is a member of a splinter group. Schismatic as an adjective means pertaining to a schism or schisms, or to those ideas, policies, etc. that are thought to lead towards or promote schism. In religion, the charge of schism is distinguished from that of heresy, since the offence of schism concerns not differences of belief or doctrine but promotion of, or the state of division, especially among groups with differing pastoral jurisdict ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scottish People
The Scots ( sco, Scots Fowk; gd, Albannaich) are an ethnic group and nation native to Scotland. Historically, they emerged in the early Middle Ages from an amalgamation of two Celtic-speaking peoples, the Picts and Gaels, who founded the Kingdom of Scotland (or ''Alba'') in the 9th century. In the following two centuries, the Celtic-speaking Cumbrians of Strathclyde and the Germanic-speaking Angles of north Northumbria became part of Scotland. In the High Middle Ages, during the 12th-century Davidian Revolution, small numbers of Norman nobles migrated to the Lowlands. In the 13th century, the Norse-Gaels of the Western Isles became part of Scotland, followed by the Norse of the Northern Isles in the 15th century. In modern usage, "Scottish people" or "Scots" refers to anyone whose linguistic, cultural, family ancestral or genetic origins are from Scotland. The Latin word ''Scoti'' originally referred to the Gaels, but came to describe all inhabitants of Scotland. Cons ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Walter Mantell
Walter Baldock Durrant Mantell (11 March 1820 – 7 September 1895) was a 19th-century New Zealand naturalist, politician, and land purchase commissioner. He was a founder and first secretary of the New Zealand Institute, and a collector of moa remains. Early life Mantell was born in Lewes, Sussex, England, the son of geologists Gideon Mantell and Mary Ann Mantell (née Woodhouse). He arrived in Wellington on the ''Oriental'' in 1840. In 1848, Mantell was appointed to the office of commissioner for extinguishing native titles in the South Island. After his father committed suicide in 1852, much of his collection of fossils was inherited by Walter and consequently transported to New Zealand. Mantell left New Zealand as he did not feel right about trying to convince the indigenous Māori people to undersell their land and returned to England in 1856, where he met Geraldine Jewsbury, a woman eight years his senior. When in New Zealand, the Maori people called Mantell "Matara". Je ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Treaty Of Waitangi
The Treaty of Waitangi ( mi, Te Tiriti o Waitangi) is a document of central importance to the history, to the political constitution of the state, and to the national mythos of New Zealand. It has played a major role in the treatment of the Māori population in New Zealand, by successive governments and the wider population, a role that has been especially prominent from the late 20th century. The treaty document is an agreement, not a treaty as recognised in international law and it has no independent legal status, being legally effective only to the extent it is recognised in various statutes. It was first signed on 6 February 1840 by Captain William Hobson as consul for the British Crown and by Māori chiefs () from the North Island of New Zealand. The treaty was written at a time when the New Zealand Company, acting on behalf of large numbers of settlers and would-be settlers, were establishing a colony in New Zealand, and when some Māori leaders had petitioned the Briti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tūhawaiki
Tūhawaiki ( – 10 October 1844) — often known as ''Hone Tūhawaiki'', ''John Tūhawaiki'' or ''Jack Tūhawaiki'', or by his nickname of "Bloody Jack" — became a paramount chief of the Ngāi Tahu Māori iwi in the southern part of the South Island of New Zealand, and was based predominantly on Ruapuke Island. He gained his nickname from early interactions with Foveaux Strait whalers on account of his red coats bought off soldiers in Australia that he and his whailing crew wore. Born at Inch Clutha in South Otago in the early years of the 19th century, he gained prominence in about 1833 when a war-party led by him defeated the Ngāti Toa chief Te Rauparaha at Lake Grassmere. The Ngāti Toa leader escaped with his life only through luck. Four years later, a war-party led by Tūhawaiki and Taiaroa inflicted severe damage on Ngāti Toa troops in a number of raids. Around the same time, Tūhawaiki became Ngāi Tahu chief upon the death of his uncle, Te Whakataupuka. He gaine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

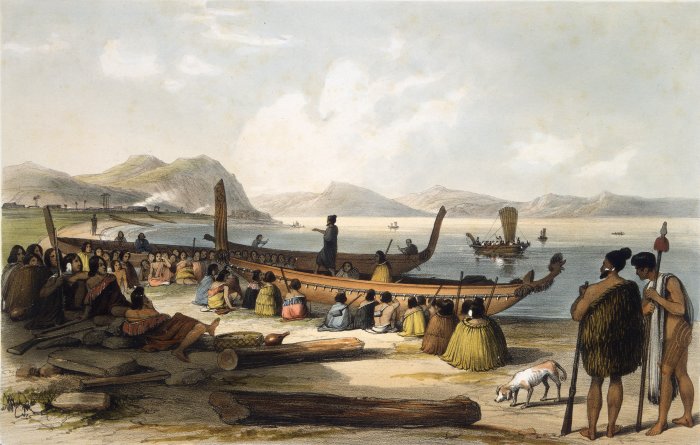
.jpg)



