|
Sindhi Culture
The Culture of Sindhi ( sd, سنڌ جي ثقافت) has its roots in the Indus Valley civilization. Sindh has been shaped by the largely desert region, the natural resources it had available, and continuous foreign influence. The Indus River, Indus or Sindhu River that passes through the land, and the Arabian Sea (that defines its borders) also supported the seafaring traditions among the local people. The local climate also reflects why the Sindhis have the Sindhi language, language, folklore, traditions, customs and lifestyle that are so different from the neighboring regions. The Sindhi culture is also practiced by the Sindhi diaspora. History The roots of Sindhi culture go back to the distant past. Archaeological research during 19th and 20th centuries showed the roots of social life, religion and culture of the people of the Sindh: their agricultural practices, traditional arts and crafts, customs and tradition and other parts of social life, going back to a mature Indus val ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Location Map Pakistan Sindh
In geography, location or place are used to denote a region (point, line, or area) on Earth's surface or elsewhere. The term ''location'' generally implies a higher degree of certainty than ''place'', the latter often indicating an entity with an ambiguous boundary, relying more on human or social attributes of place identity and sense of place than on geometry. Types Locality A locality, settlement, or populated place is likely to have a well-defined name but a boundary that is not well defined varies by context. London, for instance, has a legal boundary, but this is unlikely to completely match with general usage. An area within a town, such as Covent Garden in London, also almost always has some ambiguity as to its extent. In geography, location is considered to be more precise than "place". Relative location A relative location, or situation, is described as a displacement from another site. An example is "3 miles northwest of Seattle". Absolute location An absolute locatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
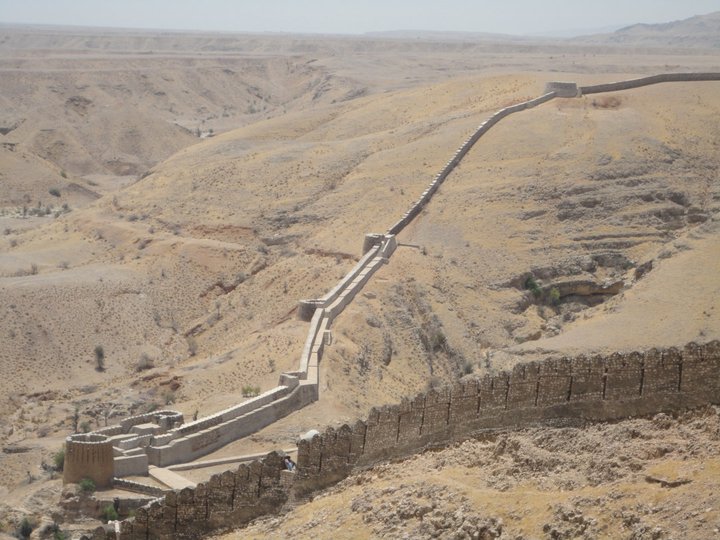
Ranikot Fort 07a
Ranikot Fort ( sd, راڻي ڪوٽ) (also known as Rannikot) is a historical Talpur fort near Sann, Jamshoro District, Sindh. in Pakistan .Ranikot Fort is also known as The Great Wall of Sindh and is believed to be the world's largest fort, with a circumference of approximately . The fort's ramparts have been compared to the Great Wall of China. The site was nominated in 1993 by the Pakistan National Commission for UNESCO world heritage status, and has since been on the tentative list of UNESCO World Heritage Sites. The fort is listed as a historical site under the Antiquities Act, 1975 and its subsequent amendments, and is provided protection. Location Ranikot Fort is to the north of Hyderabad on the indus highway (N55). There is also an easy access of about an hour's journey from Karachi to Sann on the Indus Highway. A diversion road, starting a little distance away from Sann, the nearest town, leads to the fort along a rugged road and reaches the eastern gate of the fort, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sindhi Sufi Singers
Sindhi may refer to: *something from, or related to Sindh, a province of Pakistan * Sindhi people, an ethnic group from the Sindh region * Sindhi language, the Indo-Aryan language spoken by them People with the name * Sarkash Sindhi (1940–2012), poet of Sindhi language * Ubaidullah Sindhi (1872–1944), political activist * Ahmad Bakhsh Sindhi (1917–2000), a leader of the Indian National Congress * Abu Raja Sindhi, Arabic scholar * Abu Mashar Sindhi, scholar of Hadith literature See also * * Sindi (other) * Sindi people, an ancient Scythian people * Sinti, a Romani people of Central Europe * Red Sindhi Red Sindhi cattle are the most popular of all Zebu dairy breeds. The breed originated in the Sindh province of Pakistan, they are widely kept for milk production across Pakistan, India, Bangladesh, Sri Lanka, and other countries. They have be ..., a breed of cattle {{Disambiguation Language and nationality disambiguation pages ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sindhi Literature
Sindhi literature ( sd, سنڌي ادب), is the composition of oral and written scripts and texts in the Sindhi language in the form of prose: (romantic tales, and epic stores) and poetry: (Ghazal, Wai and Nazm). The Sindhi language of the province of Sindh in Pakistan is considered to be the one of the oldest languages of Ancient India, due to the influence on the language of Indus Valley inhabitants. Sindhi literature has developed over a thousand years. According to the historians, Nabi Bux Baloch, Rasool Bux Palijo, and GM Syed, Sindhi had a great influence on the Hindi language in pre-Islamic times. Nevertheless, after the advent of Islam in eighth century, Arabic language and Persian language influenced the inhabitants of the area and were the official language of territory through different periods. Shah Abdul Latif Bhittai, Shah Abdul Karim Bulri, Shaikh Ayaz and Ustad Bukhari are important poets writing in Sindhi. History Early Period (712-1030) Before Arabs, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medicine
Medicine is the science and practice of caring for a patient, managing the diagnosis, prognosis, prevention, treatment, palliation of their injury or disease, and promoting their health. Medicine encompasses a variety of health care practices evolved to maintain and restore health by the prevention and treatment of illness. Contemporary medicine applies biomedical sciences, biomedical research, genetics, and medical technology to diagnose, treat, and prevent injury and disease, typically through pharmaceuticals or surgery, but also through therapies as diverse as psychotherapy, external splints and traction, medical devices, biologics, and ionizing radiation, amongst others. Medicine has been practiced since prehistoric times, and for most of this time it was an art (an area of skill and knowledge), frequently having connections to the religious and philosophical beliefs of local culture. For example, a medicine man would apply herbs and say prayers for healing, o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Astronomy
Astronomy () is a natural science that studies astronomical object, celestial objects and phenomena. It uses mathematics, physics, and chemistry in order to explain their origin and chronology of the Universe, evolution. Objects of interest include planets, natural satellite, moons, stars, nebulae, galaxy, galaxies, and comets. Relevant phenomena include supernova explosions, gamma ray bursts, quasars, blazars, pulsars, and cosmic microwave background radiation. More generally, astronomy studies everything that originates beyond atmosphere of Earth, Earth's atmosphere. Cosmology is a branch of astronomy that studies the universe as a whole. Astronomy is one of the oldest natural sciences. The early civilizations in recorded history made methodical observations of the night sky. These include the Babylonian astronomy, Babylonians, Greek astronomy, Greeks, Indian astronomy, Indians, Egyptian astronomy, Egyptians, Chinese astronomy, Chinese, Maya civilization, Maya, and many anc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baghdad
Baghdad (; ar, بَغْدَاد , ) is the capital of Iraq and the second-largest city in the Arab world after Cairo. It is located on the Tigris near the ruins of the ancient city of Babylon and the Sassanid Persian capital of Ctesiphon. In 762 CE, Baghdad was chosen as the capital of the Abbasid Caliphate, and became its most notable major development project. Within a short time, the city evolved into a significant cultural, commercial, and intellectual center of the Muslim world. This, in addition to housing several key academic institutions, including the House of Wisdom, as well as a multiethnic and multi-religious environment, garnered it a worldwide reputation as the "Center of Learning". Baghdad was the largest city in the world for much of the Abbasid era during the Islamic Golden Age, peaking at a population of more than a million. The city was largely destroyed at the hands of the Mongol Empire in 1258, resulting in a decline that would linger through many c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caliphs
A caliphate or khilāfah ( ar, خِلَافَة, ) is an institution or public office under the leadership of an Islamic steward with the title of caliph (; ar, خَلِيفَة , ), a person considered a political-religious successor to the Islamic prophet Muhammad and a leader of the entire Muslim world (ummah). Historically, the caliphates were polities based on Islam which developed into multi-ethnic trans-national empires. During the medieval period, three major caliphates succeeded each other: the Rashidun Caliphate (632–661), the Umayyad Caliphate (661–750), and the Abbasid Caliphate (750–1258). In the fourth major caliphate, the Ottoman Caliphate, the rulers of the Ottoman Empire claimed caliphal authority from 1517. Throughout the history of Islam, a few other Muslim states, almost all hereditary monarchies such as the Mamluk Sultanate (Cairo) and Ayyubid Caliphate, have claimed to be caliphates. The first caliphate, the Rashidun Caliphate, was established in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quran
The Quran (, ; Standard Arabic: , Classical Arabic, Quranic Arabic: , , 'the recitation'), also romanized Qur'an or Koran, is the central religious text of Islam, believed by Muslims to be a revelation in Islam, revelation from God in Islam, God. It is organized in 114 surah, chapters (pl.: , sing.: ), which consist of āyah, verses (pl.: , sing.: , construct case, cons.: ). In addition to its religious significance, it is widely regarded as the finest work in Arabic literature, and has significantly influenced the Arabic language. Muslims believe that the Quran was orally revealed by God to the Khatam an-Nabiyyin, final prophet, Muhammad in Islam, Muhammad, through the archangel Gabriel incrementally over a period of some 23 years, beginning in the month of Ramadan, when Muhammad was 40; and concluding in 632, the year of his death. Muslims regard the Quran as Muhammad's most important miracle; a proof of his prophethood; and the culmination of a series of divine message ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arab
The Arabs (singular: Arab; singular ar, عَرَبِيٌّ, DIN 31635: , , plural ar, عَرَب, DIN 31635: , Arabic pronunciation: ), also known as the Arab people, are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in Western Asia, North Africa, the Horn of Africa, and the western Indian Ocean islands (including the Comoros). An Arab diaspora is also present around the world in significant numbers, most notably in the Americas, Western Europe, Turkey, Indonesia, and Iran. In modern usage, the term "Arab" tends to refer to those who both carry that ethnic identity and speak Arabic as their native language. This contrasts with the narrower traditional definition, which refers to the descendants of the tribes of Arabia. The religion of Islam was developed in Arabia, and Classical Arabic serves as the language of Islamic literature. 93 percent of Arabs are Muslims (the remainder consisted mostly of Arab Christians), while Arab Muslims are only 20 percent of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sindhi Literature
Sindhi literature ( sd, سنڌي ادب), is the composition of oral and written scripts and texts in the Sindhi language in the form of prose: (romantic tales, and epic stores) and poetry: (Ghazal, Wai and Nazm). The Sindhi language of the province of Sindh in Pakistan is considered to be the one of the oldest languages of Ancient India, due to the influence on the language of Indus Valley inhabitants. Sindhi literature has developed over a thousand years. According to the historians, Nabi Bux Baloch, Rasool Bux Palijo, and GM Syed, Sindhi had a great influence on the Hindi language in pre-Islamic times. Nevertheless, after the advent of Islam in eighth century, Arabic language and Persian language influenced the inhabitants of the area and were the official language of territory through different periods. Shah Abdul Latif Bhittai, Shah Abdul Karim Bulri, Shaikh Ayaz and Ustad Bukhari are important poets writing in Sindhi. History Early Period (712-1030) Before Arabs, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prose
Prose is a form of written or spoken language that follows the natural flow of speech, uses a language's ordinary grammatical structures, or follows the conventions of formal academic writing. It differs from most traditional poetry, where the form consists of verse (writing in lines) based on rhythmic metre or rhyme. The word "prose" first appears in English in the 14th century. It is derived from the Old French ''prose'', which in turn originates in the Latin expression ''prosa oratio'' (literally, straightforward or direct speech). Works of philosophy, history, economics, etc., journalism, and most fiction (an exception is the verse novel), are examples of works written in prose. Developments in twentieth century literature, including free verse, concrete poetry, and prose poetry, have led to the idea of poetry and prose as two ends on a spectrum rather than firmly distinct from each other. The British poet T. S. Eliot noted, whereas "the distinction between verse and pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |