|
Sesquioxides
A sesquioxide is an oxide of an element (or radical), where the ratio between the number of atoms of that element and the number of atoms of oxygen is 2:3. For example, aluminium oxide and phosphorus(III) oxide are sesquioxides. Many sesquioxides contain a metal in the +3 oxidation state and the oxide ion , e.g., aluminium oxide , lanthanum(III) oxide and iron(III) oxide . Sesquioxides of iron and aluminium are found in soil. The alkali metal sesquioxides are exceptions because they contain both peroxide and superoxide ions, e.g., rubidium sesquioxide is formulated . Sesquioxides of metalloids and nonmetals are exceptions too, e.g. boron trioxide , dinitrogen trioxide and phosphorus(III) oxide . Many transition metal oxides crystallize in the corundum structure type, with space group Rc. Sesquioxides of rare earth elements crystalize into one or more of three crystal structures: hexagonal (type A, space group Pm1), monoclinic (type B, space group C2/m), or body-cente ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
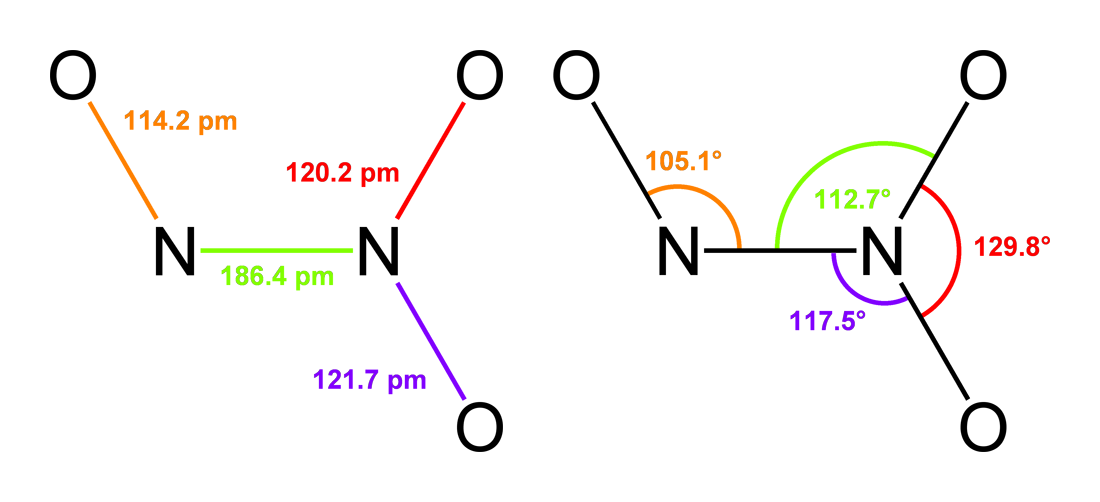
N2O3
Dinitrogen trioxide is the chemical compound with the formula N2O3. It is one of the simple nitrogen oxides. It forms upon mixing equal parts of nitric oxide and nitrogen dioxide and cooling the mixture below −21 °C (−6 °F): :NO + NO2 N2O3 Dinitrogen trioxide is only isolable at low temperatures, i.e. in the liquid and solid phases. In liquid and solid states, it has a deep blue color. At higher temperatures the equilibrium favors the constituent gases, with ''K''diss = 193 kPa (25 °C). This compound is sometimes called "nitrogen trioxide", but this name properly refers to another compound, the (uncharged) nitrate radical . Structure and bonding Typically, N–N bonds are similar in length to that in hydrazine (145 pm). Dinitrogen trioxide, however, has an unusually long N–N bond at 186 pm. Some other nitrogen oxides also possess long N–N bonds, including dinitrogen tetroxide (175 pm). The N2O3 molecule is planar and exhibits Cs symmetry. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iron(III) Oxide
Iron(III) oxide or ferric oxide is the inorganic compound with the formula Fe2O3. It is one of the three main oxides of iron, the other two being iron(II) oxide (FeO), which is rare; and iron(II,III) oxide (Fe3O4), which also occurs naturally as the mineral magnetite. As the mineral known as hematite, Fe2O3 is the main source of iron for the steel industry. Fe2O3 is readily attacked by acids. Iron(III) oxide is often called rust, and to some extent this label is useful, because rust shares several properties and has a similar composition; however, in chemistry, rust is considered an ill-defined material, described as Hydrous ferric oxide. Structure Fe2O3 can be obtained in various polymorphs. In the main one, α, iron adopts octahedral coordination geometry. That is, each Fe center is bound to six oxygen ligands. In the γ polymorph, some of the Fe sit on tetrahedral sites, with four oxygen ligands. Alpha phase α-Fe2O3 has the rhombohedral, corundum (α-Al2O3) structure and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boron Trioxide
Boron trioxide or diboron trioxide is the oxide of boron with the formula . It is a colorless transparent solid, almost always glassy (amorphous), which can be crystallized only with great difficulty. It is also called boric oxide or boria. It has many important industrial applications, chiefly in ceramics as a flux for glazes and enamels and in the production of glasses. Structure Boron trioxide has three known forms, one amorphous and two crystalline. Amorphous form The amorphous form (g-) is by far the most common. It is thought to be composed of boroxol rings which are six-membered rings composed of alternating 3-coordinate boron and 2-coordinate oxygen. Because of the difficulty of building disordered models at the correct density with many boroxol rings, this view was initially controversial, but such models have recently been constructed and exhibit properties in excellent agreement with experiment. It is now recognized, from experimental and theoretical studies, that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dinitrogen Trioxide
Dinitrogen trioxide is the chemical compound with the formula N2O3. It is one of the simple nitrogen oxides. It forms upon mixing equal parts of nitric oxide and nitrogen dioxide and cooling the mixture below −21 °C (−6 °F): :NO + NO2 N2O3 Dinitrogen trioxide is only isolable at low temperatures, i.e. in the liquid and solid phases. In liquid and solid states, it has a deep blue color. At higher temperatures the equilibrium favors the constituent gases, with ''K''diss = 193 kPa (25 °C). This compound is sometimes called "nitrogen trioxide", but this name properly refers to another compound, the (uncharged) nitrate radical . Structure and bonding Typically, N–N bonds are similar in length to that in hydrazine (145 pm). Dinitrogen trioxide, however, has an unusually long N–N bond at 186 pm. Some other nitrogen oxides also possess long N–N bonds, including dinitrogen tetroxide (175 pm). The N2O3 molecule is planar and exhibits Cs symmet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soil
Soil, also commonly referred to as earth or dirt, is a mixture of organic matter, minerals, gases, liquids, and organisms that together support life. Some scientific definitions distinguish ''dirt'' from ''soil'' by restricting the former term specifically to displaced soil. Soil consists of a solid phase of minerals and organic matter (the soil matrix), as well as a porous phase that holds gases (the soil atmosphere) and water (the soil solution). Accordingly, soil is a three-state system of solids, liquids, and gases. Soil is a product of several factors: the influence of climate, relief (elevation, orientation, and slope of terrain), organisms, and the soil's parent materials (original minerals) interacting over time. It continually undergoes development by way of numerous physical, chemical and biological processes, which include weathering with associated erosion. Given its complexity and strong internal connectedness, soil ecologists regard soil as an ecosystem. Most ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lanthanum(III) Oxide
Lanthanum(III) oxide, also known as lanthana, chemical formula , is an inorganic compound containing the rare earth element lanthanum and oxygen. It is used in some ferroelectric materials, as a component of optical materials, and is a feedstock for certain catalysts, among other uses. Properties Lanthanum oxide is a white solid that is insoluble in water, but dissolves in acidic solutions. absorbs moisture from air, converts to lanthanum hydroxide. Lanthanum oxide has p-type semiconducting properties and a band gap of approximately 5.8 eV. Its average room temperature resistivity is 10 kΩ·cm, which decreases with an increase in temperature. has the lowest lattice energy of the rare earth oxides, with very high dielectric constant, ε = 27. Structure At low temperatures, has an A- hexagonal crystal structure. The metal atoms are surrounded by a 7 coordinate group of atoms, the oxygen ions are in an octahedral shape around the metal atom and there is one oxygen ion above ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
B2O3
Boron trioxide or diboron trioxide is the oxide of boron with the formula . It is a colorless transparent solid, almost always glassy (amorphous), which can be crystallized only with great difficulty. It is also called boric oxide or boria. It has many important industrial applications, chiefly in ceramics as a flux for glazes and enamels and in the production of glasses. Structure Boron trioxide has three known forms, one amorphous and two crystalline. Amorphous form The amorphous form (g-) is by far the most common. It is thought to be composed of boroxol rings which are six-membered rings composed of alternating 3-coordinate boron and 2-coordinate oxygen. Because of the difficulty of building disordered models at the correct density with many boroxol rings, this view was initially controversial, but such models have recently been constructed and exhibit properties in excellent agreement with experiment. It is now recognized, from experimental and theoretical studies, that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phosphorus(III) Oxide
Phosphorus trioxide is the chemical compound with the molecular formula P4O6. Although the molecular formula suggests the name tetraphosphorus hexaoxide, the name phosphorus trioxide preceded the knowledge of the compound's molecular structure, and its usage continues today. This colorless solid is structurally related to adamantane. It is formally the anhydride of phosphorous acid, H3PO3, but cannot be obtained by the dehydration of the acid. A white solid that melts at room temperature, it is waxy, crystalline and highly toxic, with garlic odour. Preparation It is obtained by the combustion of phosphorus in a limited supply of air at low temperatures. :P4 + 3 O2 → P4O6 By-products include red phosphorus suboxide. Chemical properties Phosphorus trioxide reacts with water to form phosphorous acid, reflecting the fact that it is the anhydride of that acid. : P4O6 + 6 H2O → 4 H3PO3 It reacts with hydrogen chloride to form H3PO3 and phosphorus trichloride. : P4O6 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rubidium Sesquioxide
Rubidium sesquioxide is a chemical compound with the formula or . In terms of oxidation states, Rubidium in this compound has a nominal charge of +1, and the oxygen is a mixed peroxide () and superoxide () for a structural formula of . It has been studied theoretically as an example of a strongly correlated material. The compound was predicted to be a rare example of a ferromagnetic compound that is magnetic due to a p-block element, and a half-metal that was conducting in the minority spin band. However, while the material does have exotic magnetic behavior, experimental results instead showed an electrically insulating magnetically frustrated system. also displays a Verwey transition where charge ordering appears at 290 K. Rubidium sesquioxide can be prepared by reacting the peroxide and the superoxide : : It is initially discovered in 1907, and more thoroughly characterized in 1939. The compound crystallizes in a body-centered cubic form with the same crystal structure ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scrabble
''Scrabble'' is a word game in which two to four players score points by placing tiles, each bearing a single letter, onto a game board divided into a 15×15 grid of squares. The tiles must form words that, in crossword fashion, read left to right in rows or downward in columns and are included in a standard dictionary or lexicon. The name ''Scrabble'' is a trademark of Mattel in most of the world, except in the United States and Canada, where it is a trademark of Hasbro, under the brands of both of its subsidiaries, Milton Bradley and Parker Brothers. The game is sold in 121 countries and is available in more than 30 languages; approximately 150 million sets have been sold worldwide, and roughly one-third of American and half of British homes have a ''Scrabble'' set. There are approximately 4,000 ''Scrabble'' clubs around the world. Game details The game is played by two to four players on a square game board imprinted with a 15×15 grid of cells (individually known as " ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rare Earth Elements
The rare-earth elements (REE), also called the rare-earth metals or (in context) rare-earth oxides or sometimes the lanthanides (yttrium and scandium are usually included as rare earths), are a set of 17 nearly-indistinguishable lustrous silvery-white soft heavy metals. Compounds containing rare earths have diverse applications in electrical and electronic components, lasers, glass, magnetic materials, and industrial processes. Scandium and yttrium are considered rare-earth elements because they tend to occur in the same ore deposits as the lanthanides and exhibit similar chemical properties, but have different electronic and magnetic properties. These metals tarnish slowly in air at room temperature and react slowly with cold water to form hydroxides, liberating hydrogen. They react with steam to form oxides, and at elevated temperature (400°C) ignite spontaneously. These elements and their compounds have no biological function other than in several specialized enzymes, su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nonmetals
In chemistry, a nonmetal is a chemical element that generally lacks a predominance of metallic properties; they range from colorless gases (like hydrogen) to shiny solids (like carbon, as graphite). The electrons in nonmetals behave differently from those in metals. With some exceptions, those in nonmetals are fixed in place, resulting in nonmetals usually being poor conductors of heat and electricity and brittle or crumbly when solid. The electrons in metals are generally free moving and this is why metals are good conductors and most are easily flattened into sheets and drawn into wires. Nonmetal atoms tend to attract electrons in chemical reactions and to form acidic compounds. Two nonmetals, hydrogen and helium, make up about 99% of ordinary matter in the observable universe by mass. Five nonmetallic elements, hydrogen, carbon, nitrogen, oxygen and silicon, largely make up the Earth's crust, atmosphere, oceans and biosphere. Most nonmetals have biological, technological ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |