|
Ruthenium Compounds
The transition metal ruthenium forms several compounds, with oxidation states of ruthenium ranging from 0 to +8, and −2. The properties of ruthenium and osmium compounds are often similar. The +2, +3, and +4 states are the most common. The most prevalent precursor is ruthenium trichloride, a red solid that is poorly defined chemically but versatile synthetically. Oxides and chalcogenides Ruthenium can be oxidized to ruthenium(IV) oxide (RuO2, oxidation state +4), which can, in turn, be oxidized by sodium metaperiodate to the volatile yellow tetrahedral ruthenium tetroxide, RuO4, an aggressive, strong oxidizing agent with structure and properties analogous to osmium tetroxide. RuO4 is mostly used as an intermediate in the purification of ruthenium from ores and radiowastes. Dipotassium ruthenate (K2RuO4, +6) and potassium perruthenate (KRuO4, +7) are also known. Unlike osmium tetroxide, ruthenium tetroxide is less stable, is strong enough as an oxidising agent to oxidise dilut ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transition Metal
In chemistry, a transition metal (or transition element) is a chemical element in the d-block of the periodic table (groups 3 to 12), though the elements of group 12 (and less often group 3) are sometimes excluded. They are the elements that can use d orbitals as valence orbitals to form chemical bonds. The lanthanide and actinide elements (the f-block) are called inner transition metals and are sometimes considered to be transition metals as well. Since they are metals, they are lustrous and have good electrical and thermal conductivity. Most (with the exception of group 11 and group 12) are hard and strong, and have high melting and boiling temperatures. They form compounds in any of two or more different oxidation states and bind to a variety of ligands to form coordination complexes that are often coloured. They form many useful alloys and are often employed as catalysts in elemental form or in compounds such as coordination complexes and oxides. Most are strongly param ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ruthenium Chloride Hydrate
Ruthenium is a chemical element with the symbol Ru and atomic number 44. It is a rare transition metal belonging to the platinum group of the periodic table. Like the other metals of the platinum group, ruthenium is inert to most other chemicals. Russian-born scientist of Baltic-German ancestry Karl Ernst Claus discovered the element in 1844 at Kazan State University and named ruthenium in honor of Russia. Ruthenium is usually found as a minor component of platinum ores; the annual production has risen from about 19 tonnes in 2009Summary. Ruthenium platinum.matthey.com, p. 9 (2009) to some 35.5 tonnes in 2017. Most ruthenium produced is used in wear-resistant electrical contacts and thick-film resistors. A minor application for ruthenium is in platinum |
Ruthenocene
Ruthenocene is an organoruthenium compound with the formula (C5H5)2Ru. This pale yellow, volatile solid is classified as a sandwich compound and more specifically, as a metallocene. Structure and bonding Ruthenocene consists of a ruthenium ion sandwiched in between two cyclopentadienyl rings. It features ruthenium centre bound symmetrically to the planes of two cyclopentadienyl rings. It is closely related to the isoelectronic ferrocene. In contrast to ferrocene, wherein the cyclopentadienyl rings are in a staggered conformation, those of ruthenocene crystallise with an eclipsed conformation. This difference is due to the larger ionic radius of ruthenium, which increases the distance between the cyclopentadienyl rings, decreasing steric interactions and allowing an eclipsed conformation to prevail. In solution, these rings rotate with a very low barrier. Preparation Ruthenocene was first synthesized in 1952 by Geoffrey Wilkinson, a Nobel laureate who had collaborated in assig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grubbs' Catalyst
Grubbs catalysts are a series of transition metal carbene complexes used as catalysts for olefin metathesis. They are named after Robert H. Grubbs, the chemist who supervised their synthesis. Several generations of the catalyst have been developed. Grubbs catalysts tolerate many functional groups in the alkene substrates, are air-tolerant, and are compatible with a wide range of solvents. For these reasons, Grubbs catalysts have become popular in synthetic organic chemistry. Grubbs, together with Richard R. Schrock and Yves Chauvin, won the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in recognition of their contributions to the development of olefin metathesis. First-generation catalyst In the 1960s, ruthenium trichloride was found to catalyze olefin metathesis. Processes were commercialized based on these discoveries. These ill-defined but highly active homogeneous catalysts remain in industrial use. The first well-defined ruthenium catalyst was reported in 1992. It was prepared from RuCl2(PPh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tris(bipyridine)ruthenium(II) Chloride
Tris(bipyridine)ruthenium(II) chloride is the chloride salt coordination complex with the formula u(bpy)3sup>2+ 2Cl−. This polypyridine complex is a red crystalline salt obtained as the hexahydrate, although all of the properties of interest are in the cation u(bpy)3sup>2+, which has received much attention because of its distinctive optical properties. The chlorides can be replaced with other anions, such as PF6−. Synthesis and structure left, 144px, Cis-Dichlorobis(bipyridine)ruthenium(II), ''cis''-Dichlorobis(bipyridine)ruthenium(II) is an intermediate in the synthesis of tris(bipyridine)ruthenium(II) chloride. This salt is prepared by treating an aqueous solution of ruthenium trichloride with 2,2'-bipyridine. In this conversion, Ru(III) is reduced to Ru(II), and hypophosphorous acid is typically added as a reducing agent. u(bpy)3sup>2+ is octahedral, containing a central low spin d6 Ru(II) ion and three bidentate bpy ligands. The Ru-N distances are 2.053(2), short ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Luminescence
Luminescence is spontaneous emission of light by a substance not resulting from heat; or "cold light". It is thus a form of cold-body radiation. It can be caused by chemical reactions, electrical energy, subatomic motions or stress on a crystal. This distinguishes luminescence from incandescence, which is light emitted by a substance as a result of heating. Historically, radioactivity was thought of as a form of "radio-luminescence", although it is today considered to be separate since it involves more than electromagnetic radiation. The dials, hands, scales, and signs of aviation and navigational instruments and markings are often coated with luminescent materials in a process known as "luminising". Types The following are types of luminescence: * Chemiluminescence, the emission of light as a result of a chemical reaction **Bioluminescence, a result of biochemical reactions in a living organism **Electrochemiluminescence, a result of an electrochemical reaction **Lyolumine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Terpyridine
Terpyridine (2,2';6',2"-terpyridine, often abbreviated to Terpy or Tpy) is a heterocyclic compound derived from pyridine. It is a white solid that is soluble in most organic solvents. The compound is mainly used as a ligand in coordination chemistry. Synthesis Terpyridine was first synthesized by G. Morgan and F. H. Burstall in 1932 by the oxidative coupling of pyridines. This method, however, proceeded in low yields. More efficient syntheses have since been described, mainly starting from 2-acetylpyridine. One method produces an enaminone by the reaction of 2-acetylpyridine with N,N-dimethylformamide dimethyl acetal. The base-catalyzed reaction of 2-acetylpyridine with carbon disulfide followed by alkylation with methyl iodide gives C5H4NCOCH=C(SMe)2. Condensation of this species with 2-acetylpyridine forms the related 1,5-diketone, which condenses with ammonium acetate to form a terpyridine. Treatment of this derivative with Raney nickel removes the thioether group. Other ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
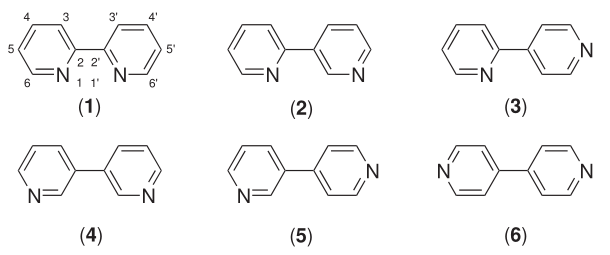
Bipyridine
Bipyridines also known as bipyridyls, dipyridyls, and dipyridines, are a family of chemical compounds with the formula (C5H4N)2, consisting of two pyridyl (C5H4N) rings. Pyridine is an aromatic nitrogen-containing heterocycle. Bipyridines are of significance in pesticides. Six isomers of bipyridine exist, but two are prominent: 2,2′-bipyridine is a popular ligand. 4,4'-Bipyridine is a precursor to the commercial herbicide paraquat. The bipyridines are all colourless solids, which are soluble in organic solvents and slightly soluble in water. 2,2′-Bipyridine 2,2′-Bipyridine (2,2′-bipy) is a chelating ligand that forms complexes with most transition metal ions that are of broad academic interest. Many of these complexes have distinctive optical properties, and some are of interest for analysis. Its complexes are used in studies of electron and energy transfer, supramolecular and materials chemistry, and catalysis. 2,2′-Bipyridine is used in the manufacture of diqua ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grubbs Catalyst Gen2
Grubbs may refer to: People * Grubbs (surname) In fiction * Grubbs Grady, a main character in ''The Demonata'' series of novels * Verla Grubbs, a character in the ''All My Children'' TV series Other uses * Grubbs catalyst, a series of transition metal carbene complexes used as catalysts for olefin metathesis * Grubbs's test for outliers, a statistical test used to detect outliers * Grubb's Tramway (Mowbray), a tramway in northern Tasmania * Grubb's Tramway (Zeehan), a tramway in western Tasmania * Grubbs, Arkansas * Grubbs Corner, West Virginia Grubbs Corner is an unincorporated community in Berkeley County, West Virginia West Virginia is a state in the Appalachian, Mid-Atlantic and Southeastern regions of the United States.The Census Bureau and the Association of American Geo ... * '' United States v. Grubbs'', a 2006 United States Supreme Court case See also * Grubb (other) {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tris(bipyridine)ruthenium(II)-chloride-powder
Tris, or tris(hydroxymethyl)aminomethane, or known during medical use as tromethamine or THAM, is an organic compound with the formula (HOCH2)3CNH2, one of the twenty Good's buffers. It is extensively used in biochemistry and molecular biology as a component of buffer solutions such as in TAE and TBE buffers, especially for solutions of nucleic acids. It contains a primary amine and thus undergoes the reactions associated with typical amines, e.g. condensations with aldehydes. Tris also complexes with metal ions in solution. In medicine, tromethamine is occasionally used as a drug, given in intensive care for its properties as a buffer for the treatment of severe metabolic acidosis in specific circumstances. Some medications are formulated as the "tromethamine salt" including Hemabate (carboprost as trometamol salt), and "ketorolac trometamol". Buffering features The conjugate acid of tris has a p''K''a of 8.07 at 25 °C, which implies that the buffer has an effective pH r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ruthenium Trichloride
Ruthenium(III) chloride is the chemical compound with the formula RuCl3. "Ruthenium(III) chloride" more commonly refers to the hydrate RuCl3·''x''H2O. Both the anhydrous and hydrated species are dark brown or black solids. The hydrate, with a varying proportion of water of crystallization, often approximating to a trihydrate, is a commonly used starting material in ruthenium chemistry. Preparation and properties Anhydrous ruthenium(III) chloride is usually prepared by heating powdered ruthenium metal with chlorine. In the original synthesis, the chlorination was conducted in the presence of carbon monoxide, the product being carried by the gas stream and crystallising upon cooling. Two allotropes of RuCl3 are known. The black α-form adopts the CrCl3-type structure with long Ru-Ru contacts of 346 pm. This allotrope has honeycomb layers of Ru3+ which are surrounded with an octahedral cage of Cl− anions. The ruthenium cations are magnetic residing in a low-spin J~1/2 ground st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iodine
Iodine is a chemical element with the symbol I and atomic number 53. The heaviest of the stable halogens, it exists as a semi-lustrous, non-metallic solid at standard conditions that melts to form a deep violet liquid at , and boils to a violet gas at . The element was discovered by the French chemist Bernard Courtois in 1811 and was named two years later by Joseph Louis Gay-Lussac, after the Ancient Greek 'violet-coloured'. Iodine occurs in many oxidation states, including iodide (I−), iodate (), and the various periodate anions. It is the least abundant of the stable halogens, being the sixty-first most abundant element. As the heaviest essential mineral nutrient, iodine is required for the synthesis of thyroid hormones. Iodine deficiency affects about two billion people and is the leading preventable cause of intellectual disabilities. The dominant producers of iodine today are Chile and Japan. Due to its high atomic number and ease of attachment to organic compound ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |