|
Preservatives
A preservative is a substance or a chemical that is added to products such as food products, beverages, pharmaceutical drugs, paints, biological samples, cosmetics, wood, and many other products to prevent decomposition by microbial growth or by undesirable chemical changes. In general, preservation is implemented in two modes, chemical and physical. Chemical preservation entails adding chemical compounds to the product. Physical preservation entails processes such as refrigeration or drying.Erich Lück and Gert-Wolfhard von Rymon Lipinski "Foods, 3. Food Additives" in ''Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry'', 2002, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim. Preservative food additives reduce the risk of foodborne infections, decrease microbial spoilage, and preserve fresh attributes and nutritional quality. Some physical techniques for food preservation include dehydration, UV-C radiation, freeze-drying, and refrigeration. Chemical preservation and physical preservation techniques are s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sorbic Acid
Sorbic acid, or 2,4-hexadienoic acid, is a natural organic compound used as a food preservative. It has the chemical formula and the structure . It is a colourless solid that is slightly soluble in water and sublimes readily. It was first isolated from the unripe berries of the ''Sorbus aucuparia'' ( rowan tree), hence its name. Production The traditional route to sorbic acid involves condensation of malonic acid and crotonaldehyde. It can also be prepared from isomeric hexadienoic acids, which are available via a nickel-catalyzed reaction of allyl chloride, acetylene, and carbon monoxide. The route used commercially, however, is from crotonaldehyde and ketene. An estimated 30,000 tons are produced annually. History Sorbic acid was isolated in 1859 by distillation of rowanberry oil by A. W. von Hofmann. This affords parasorbic acid, the lactone of sorbic acid, which he converted to sorbic acid by hydrolysis. Its antimicrobial activities were discovered in the late 1930 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Food Preservation
Food preservation includes processes that make food more resistant to microorganism growth and slow the oxidation of fats. This slows down the decomposition and rancidification process. Food preservation may also include processes that inhibit visual deterioration, such as the enzymatic browning reaction in apples after they are cut during food preparation. By preserving food, food waste can be reduced, which is an important way to decrease production costs and increase the efficiency of food systems, improve food security and nutrition and contribute towards environmental sustainability. For instance, it can reduce the environmental impact of food production. Many processes designed to preserve food involve more than one food preservation method. Preserving fruit by turning it into jam, for example, involves boiling (to reduce the fruit's moisture content and to kill bacteria, etc.), sugaring (to prevent their re-growth) and sealing within an airtight jar (to prevent re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Formaldehyde Releaser
A formaldehyde releaser, formaldehyde donor or formaldehyde-releasing preservative is a chemical compound that slowly releases formaldehyde. Formaldehyde-releasers are added to prevent microbial growth and extend shelf life. The intent of these compounds is that they release formaldehyde at levels that suppress microbial growth but sufficiently low to not threaten humans. The use of these chemicals in cosmetics has elicited controversy. Examples Many compounds have been formulated a formaldehyde-releasers. * Quaternium-15 (Dowicil 200; Dowicil 75; Dowicil 100; Dowco 184; Dowicide Q). It was used in low concentrations in cosmetics but has been banned in the EU since 2017 and a bill is under consideration in the US. * DMDM hydantoin * (ethylenedioxy)dimethanol (EDDM) *(Benzyloxy)methanol (BHF, benzylhemiformal) * 2,2',2''-(Hexahydro-1,3-5-triazine-1,3,5-triyl-)triethanol (HHT) * Tetramethylolacetylenediurea (TMAD) * 1,3-Bis(hydroxymethyl)-5,5-dimethylimidazolidine-2,4-dion ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isothiazolinone
Isothiazolinone (sometimes isothiazolone) is an organic compound with the formula (CH)2SN(H)CO. A white solid, it is structurally related to isothiazole. Isothiazolone itself is of limited interest, but several of its derivatives are widely used preservatives and antimicrobials. Synthesis Compared to many other simple heterocycles, the discovery of isothiazolinone is fairly recent, with reports first appearing in the 1960s. Isothiazolinones can be prepared on an industrial scale by the ring-closure of 3-mercaptopropanamides. These in turn are produced from acrylic acid via the 3-mercaptopropionic acid: : Ring-closure of the thiol-amide is typically effected by chlorination or oxidation of the 3-sulfanylpropanamide to the corresponding disulfide. : Many other routes have been developed, including addition of thiocyanate to propargyl amides. Mechanism of action The antimicrobial activity of isothiazolinones is attributed to their ability to inhibit life-sustaining enzymes, s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
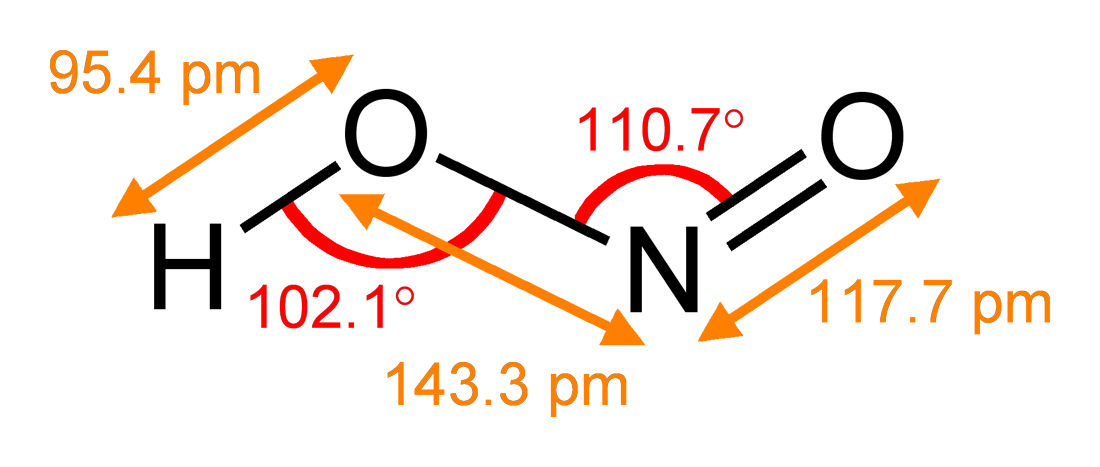
Nitrite
The nitrite ion has the chemical formula . Nitrite (mostly sodium nitrite) is widely used throughout chemical and pharmaceutical industries. The nitrite anion is a pervasive intermediate in the nitrogen cycle in nature. The name nitrite also refers to organic compounds having the –ONO group, which are esters of nitrous acid. Production Sodium nitrite is made industrially by passing a mixture of nitrogen oxides into aqueous sodium hydroxide or sodium carbonate solution: : The product is purified by recrystallization. Alkali metal nitrites are thermally stable up to and beyond their melting point (441 °C for KNO2). Ammonium nitrite can be made from dinitrogen trioxide, N2O3, which is formally the anhydride of nitrous acid: :2 NH3 + H2O + N2O3 → 2 NH4NO2 Structure The nitrite ion has a symmetrical structure (C2v symmetry), with both N–O bonds having equal length and a bond angle of about 115°. In valence bond theory, it is described as a resonance hybrid with equal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lactic Acid
Lactic acid is an organic acid. It has a molecular formula . It is white in the solid state and it is miscible with water. When in the dissolved state, it forms a colorless solution. Production includes both artificial synthesis as well as natural sources. Lactic acid is an alpha-hydroxy acid (AHA) due to the presence of a hydroxyl group adjacent to the carboxyl group. It is used as a synthetic intermediate in many organic synthesis industries and in various biochemical industries. The conjugate base of lactic acid is called lactate (or the lactate anion). The name of the derived acyl group is lactoyl. In solution, it can ionize by loss of a proton to produce the lactate ion . Compared to acetic acid, its p''K'' is 1 unit less, meaning lactic acid is ten times more acidic than acetic acid. This higher acidity is the consequence of the intramolecular hydrogen bonding between the α-hydroxyl and the carboxylate group. Lactic acid is chiral, consisting of two enantiomers. One ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sulfur Dioxide
Sulfur dioxide ( IUPAC-recommended spelling) or sulphur dioxide (traditional Commonwealth English) is the chemical compound with the formula . It is a toxic gas responsible for the odor of burnt matches. It is released naturally by volcanic activity and is produced as a by-product of copper extraction and the burning of sulfur- bearing fossil fuels. Structure and bonding SO2 is a bent molecule with ''C''2v symmetry point group. A valence bond theory approach considering just ''s'' and ''p'' orbitals would describe the bonding in terms of resonance between two resonance structures. The sulfur–oxygen bond has a bond order of 1.5. There is support for this simple approach that does not invoke ''d'' orbital participation. In terms of electron-counting formalism, the sulfur atom has an oxidation state of +4 and a formal charge of +1. Occurrence Sulfur dioxide is found on Earth and exists in very small concentrations and in the atmosphere at about 1 ppm. On other p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paraben
Parabens are a class of widely used preservatives in cosmetic and pharmaceutical products. Chemically, they are a series of parahydroxybenzoates or esters of parahydroxybenzoic acid (also known as 4-hydroxybenzoic acid). Parabens are effective preservatives in many types of formulas. These compounds, and their salts, are used primarily for their bactericidal and fungicidal properties. They are found in shampoos, commercial moisturizers, shaving gels, personal lubricants, topical/ parenteral pharmaceuticals, suntan products, makeup, and toothpaste. They are also used as food preservatives. Certain parabens have been linked to cancer. Mode of action Parabens are active against a broad spectrum of microorganisms. However, their antibacterial mode of action is not well understood. They are thought to act by disrupting membrane transport processes or by inhibiting synthesis of DNA and RNA or of some key enzymes, such as ATPases and phosphotransferases, in some bacterial sp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Food Additive
Food additives are substances added to food to preserve flavor or enhance taste, appearance, or other sensory qualities. Some additives have been used for centuries as part of an effort to preserve food, for example vinegar (pickling), salt (salting), smoke ( smoking), sugar ( crystallization), etc. This allows for longer-lasting foods such as bacon, sweets or wines. With the advent of processed foods in the second half of the twentieth century, many additives have been introduced, of both natural and artificial origin. Food additives also include substances that may be introduced to food indirectly (called "indirect additives") in the manufacturing process, through packaging, or during storage or transport. Numbering To regulate these additives and inform consumers, each additive is assigned a unique number called an "E number", which is used in Europe for all approved additives. This numbering scheme has now been adopted and extended by the ''Codex Alimentarius'' Commiss ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pickling
Pickling is the process of food preservation, preserving or extending the shelf life of food by either Anaerobic organism, anaerobic fermentation (food), fermentation in brine or immersion in vinegar. The pickling procedure typically affects the food's texture and flavor. The resulting food is called a ''pickle'', or, to prevent ambiguity, prefaced with ''pickled''. Foods that are pickled include vegetables, fruits, meats, fish, dairy and eggs. Pickling solutions that are typically highly acidic, with a pH of 4.6 or lower, and high in salt, prevent enzymes from working and micro-organisms from multiplying. Pickling can preserve Decomposition, perishable foods for months. Antimicrobial herbs and spices, such as mustard seed, garlic, cinnamon or cloves, are often added. If the food contains sufficient moisture, a pickling brine may be produced simply by adding dry salt. For example, sauerkraut and Korean kimchi are produced by salting the vegetables to draw out excess water. Natur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Juice
Juice is a drink made from the extraction or pressing of the natural liquid contained in fruit and vegetables. It can also refer to liquids that are flavored with concentrate or other biological food sources, such as meat or seafood, such as clam juice. Juice is commonly consumed as a beverage or used as an ingredient or flavoring in foods or other beverages, as for smoothies. Juice emerged as a popular beverage choice after the development of pasteurization methods enabled its preservation without using fermentation (which is used in wine production). The largest fruit juice consumers are New Zealand (nearly a cup, or 8 ounces, each day) and Colombia (more than three quarters of a cup each day). Fruit juice consumption on average increases with a country's income level. Etymology The word "juice" comes from Old French in about 1300; it developed from the Old French words "''jus, juis, jouis''", which mean "liquid obtained by boiling herbs". The "Old French ''jus'' " ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cheese
Cheese is a dairy product produced in wide ranges of flavors, textures, and forms by coagulation of the milk protein casein. It comprises proteins and fat from milk, usually the milk of cows, buffalo, goats, or sheep. During production, milk is usually acidified and the enzymes of either rennet or bacterial enzymes with similar activity are added to cause the casein to coagulate. The solid curds are then separated from the liquid whey and pressed into finished cheese. Some cheeses have aromatic molds on the rind, the outer layer, or throughout. Over a thousand types of cheese exist and are produced in various countries. Their styles, textures and flavors depend on the origin of the milk (including the animal's diet), whether they have been pasteurized, the butterfat content, the bacteria and mold, the processing, and how long they have been aged. Herbs, spices, or wood smoke may be used as flavoring agents. The yellow to red color of many cheeses is produc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.jpg)