|
Polatlı
Polatlı (formerly Ancient Greek: Γόρδιον, Górdion and Latin: Gordium) is a city and a district in Ankara Province in the Central Anatolia region of Turkey, 80 km west of the Turkish capital Ankara, on the road to Eskişehir. According to 2019 census, population of the district is 125,075 of which 98,605 live in the city of Polatlı. The district covers an area of 3,789 km2, and the average elevation is 850 m. Geography Polatlı is situated at the heart of the high Anatolian Plateau, a large steppe covered with grass. Far from the coast, it has a typical steppe climate. The winters are generally cold, the summers dry and dusty. The springs are the most humid times of the year. Polatlı is one of the most productive agricultural districts in Turkey and is best known for its cereal production, especially barley and wheat. Polatlı is one of Turkey's largest grain stores. Sugar beet, melon and onion are also grown. History Ancient settlement The ancient Phrygia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gordion
Gordion ( Phrygian: ; el, Γόρδιον, translit=Górdion; tr, Gordion or ; la, Gordium) was the capital city of ancient Phrygia. It was located at the site of modern Yassıhüyük, about southwest of Ankara (capital of Turkey), in the immediate vicinity of Polatlı district. Gordion's location at the confluence of the Sakarya and Porsuk rivers gave it a strategic location with control over fertile land. Gordion lies where the ancient road between Lydia and Assyria/Babylonia crossed the Sangarius river. Occupation at the site is attested from the Early Bronze Age (c. 2300 BCE) continuously until the 4th century CE and again in the 13th and 14th centuries CE. The Citadel Mound at Gordion is approximately 13.5 hectares in size, and at its height habitation extended beyond this in an area approximately 100 hectares in size. Gordion is the type site of Phrygian civilization, and its well-preserved destruction level of c. 800 BCE is a chronological linchpin in the region. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gordion Museum 0851
Gordion ( Phrygian: ; el, Γόρδιον, translit=Górdion; tr, Gordion or ; la, Gordium) was the capital city of ancient Phrygia. It was located at the site of modern Yassıhüyük, about southwest of Ankara (capital of Turkey), in the immediate vicinity of Polatlı district. Gordion's location at the confluence of the Sakarya and Porsuk rivers gave it a strategic location with control over fertile land. Gordion lies where the ancient road between Lydia and Assyria/ Babylonia crossed the Sangarius river. Occupation at the site is attested from the Early Bronze Age (c. 2300 BCE) continuously until the 4th century CE and again in the 13th and 14th centuries CE. The Citadel Mound at Gordion is approximately 13.5 hectares in size, and at its height habitation extended beyond this in an area approximately 100 hectares in size. Gordion is the type site of Phrygian civilization, and its well-preserved destruction level of c. 800 BCE is a chronological linchpin in the region ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phrygia
In classical antiquity, Phrygia ( ; grc, Φρυγία, ''Phrygía'' ) was a kingdom in the west central part of Anatolia, in what is now Asian Turkey, centered on the Sangarios River. After its conquest, it became a region of the great empires of the time. Stories of the heroic age of Greek mythology tell of several legendary Phrygian kings: * Gordias, whose Gordian Knot would later be cut by Alexander the Great * Midas, who turned whatever he touched to gold * Mygdon, who warred with the Amazons According to Homer's ''Iliad'', the Phrygians participated in the Trojan War as close allies of the Trojans, fighting against the Achaeans. Phrygian power reached its peak in the late 8th century BC under another, historical, king Midas, who dominated most of western and central Anatolia and rivaled Assyria and Urartu for power in eastern Anatolia. This later Midas was, however, also the last independent king of Phrygia before Cimmerians sacked the Phrygian capital, Go ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
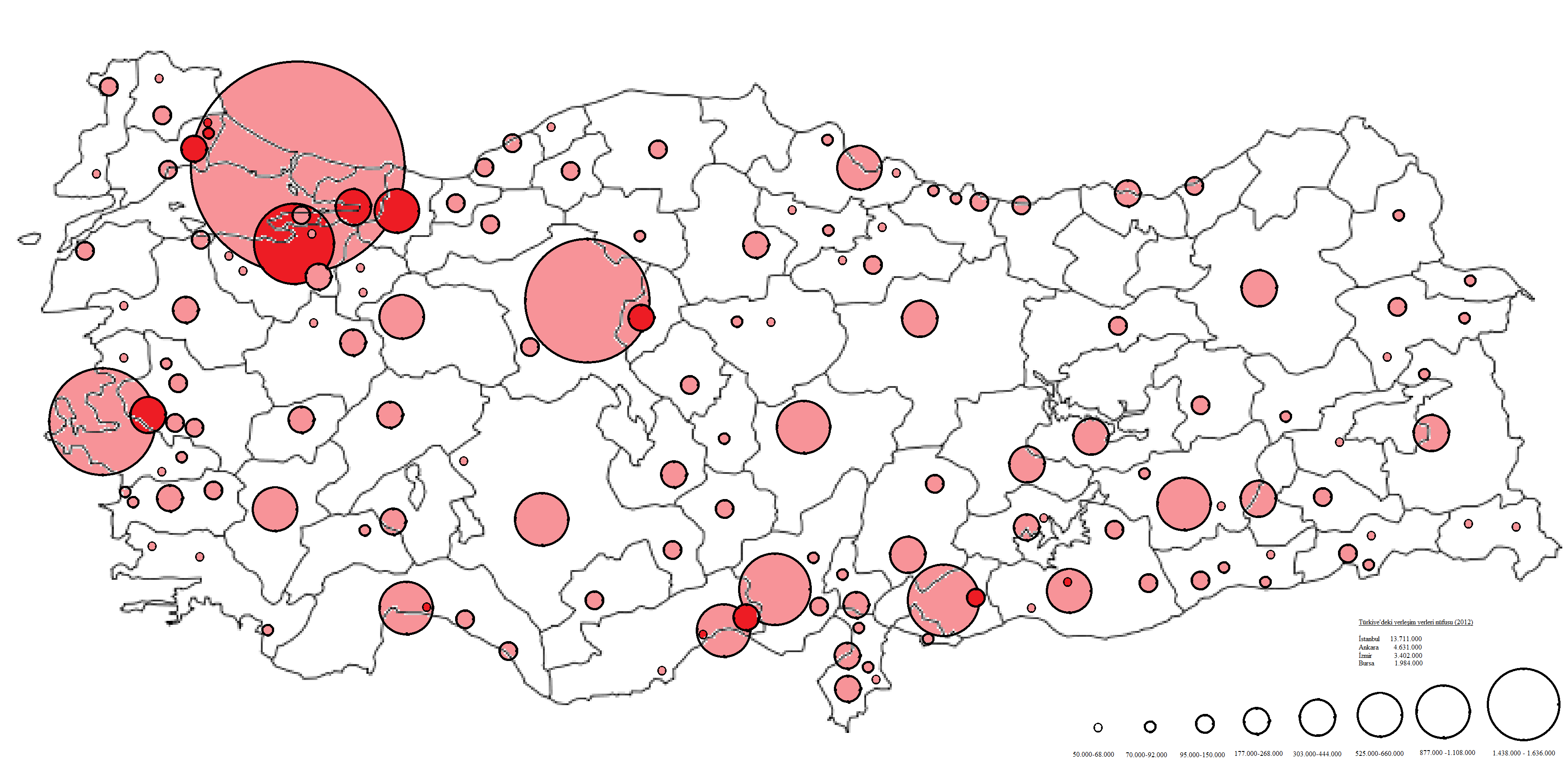
List Of Largest Cities And Towns In Turkey
This is a list of cities and towns in Turkey by population, which includes cities and towns that are provincial capitals or have a population of at least 7,000. The total population of Turkey is 84,680,273 according to the 2020 estimate, making it the 17th most populated country in the world. *Istanbul, Turkey's economic and cultural capital is the largest city with a population of 15.84 million in its metropolitan area as of 2021. *Ankara, the capital of Turkey and Turkey's second largest city has a population of 5.7 million in its metropolitan area as of 2021. * Izmir, Turkey's third largest city has a population of over 4.3 million in its metropolitan area as of 2019. *Bursa, Turkey's fourth largest city has a population of over 3.1 million in its metropolitan area as of 2021. *Antalya, Turkey's fifth-largest city has a population of 2.6 million in its metropolitan area as of 2019. Cities and towns with more than 7,000 inhabitants Cities and Towns with a population of over ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turkish Car Number Plates
Turkish vehicle registration plates are number plates found on Turkish vehicles. The plates use an indirect numbering system associated with the geographical info. In Turkey, number plates are made by authorized private workshops. Appearance Turkish number plate is rectangular in shape and made of aluminium. On the left, there is the country code "TR" in a 4×10 cm blue stripe like in EU countries (without the 12 golden stars). The text is in black characters on white background, and for official vehicles white on black. On all vehicles two plates have to be present, being one in front and the other in rear except motorcycles and tractors. The serial letters use the Turkish letters except Ç, Ş, İ, Ö, Ü and Ğ. Dimensions *150×240 mm in rear only for motorbikes, motorcycles and tractors with rubber wheels, *110×520 mm in front and rear for cars, 210×320 mm rear available for off-road vehicles, vans, trucks and busses. The size is 150×300 m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sakarya River
The Sakarya (Sakara River, tr, Sakarya Irmağı; gr, Σαγγάριος, translit=Sangarios; Latin: ''Sangarius'') is the third longest river in Turkey. It runs through the region known in ancient times as Phrygia. It was considered one of the principal rivers of Asia Minor (Anatolia) in classical antiquity, and is mentioned in the ''Iliad'' and in ''Theogony''. Its name appears in different forms as Sagraphos, Sangaris, or Sagaris. In ''Geographica'', Strabo wrote during classical antiquity that the river had its sources on Mount Adoreus, near the town of Sangia in Phrygia, not far from the border with Galatia, and flowed in a very tortuous course: first in an eastern, then toward the north, next the north-west and finally the north through Bithynia into the Euxine (Black Sea). Part of its course formed the boundary between Phrygia and Bithynia, which in early times was bounded on the east by the river. The Bithynian part of the river was navigable and was celebrated for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ankara Province
Ankara Province ( tr, , ) is a province of Turkey with the capital city Ankara. Demographics History The site of the modern city has been home to settlements by many historic Anatolian civilizations in antiquity and classical times, including Phrygians, Lydians, Persians and Alexander the Great, Romans, and Galatians. The city of Ankara became a fortified stronghold of the Byzantines; it fell to the Seljuk Turks and later the Ottoman Empire. It was finally chosen by Mustafa Kemal Atatürk and the Turkish National Movement as the site of the provisional government and the Turkish parliament in 1920, and in 1923 as the capital city of the newly established Republic of Turkey. Districts Ankara has 25 districts. Geography Ankara is mostly in the Central Anatolia region, and partly in the Black Sea region. Ankara has mountain forests to its north, and the dry plain of Konya to its south. The province is irrigated by the Kızılırmak and Sakarya River systems, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eastern European Summer Time
Eastern European Summer Time (EEST) is one of the names of the UTC+03:00 time zone, which is 3 hours ahead of Coordinated Universal Time. It is used as a summer daylight saving time in some European and Middle Eastern countries, which makes it the same as Arabia Standard Time, East Africa Time, and Moscow Time. During the winter periods, Eastern European Time ( UTC+02:00) is used. Since 1996, European Summer Time has been applied from the last Sunday in March to the last Sunday in October. Previously, the rules were not uniform across the European Union. Usage The following countries and territories use Eastern European Summer Time during the summer: * Belarus, Moscow Summer Time in years 1981–89, regular EEST from 1991-2011 * Bulgaria, regular EEST since 1979 * Cyprus, regular EEST since 1979 ( Northern Cyprus stopped using EEST in September 2016, but returned to EEST in March 2018) * Estonia, Moscow Summer Time in years 1981–88, regular EEST since 1989 * Finland, regu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sugar Beet
A sugar beet is a plant whose root contains a high concentration of sucrose and which is grown commercially for sugar production. In plant breeding, it is known as the Altissima cultivar group of the common beet (''Beta vulgaris''). Together with other beet cultivars, such as beetroot and chard, it belongs to the subspecies ''Beta vulgaris'' subsp. ''vulgaris.'' Its closest wild relative is the sea beet (''Beta vulgaris'' subsp. ''maritima''). Sugar beets are grown in climates that are too cold for sugar cane. The low sugar content of the beets makes growing them a marginal proposition unless prices are relatively high. In 2020, Russia, the United States, Germany, France and Turkey were the world's five largest sugar beet producers. In 2010–2011, Europe, and North America except Arctic territories failed to supply the overall domestic demand for sugar and were all net importers of sugar. The US harvested of sugar beets in 2008. In 2009, sugar beets accounted for 20% of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
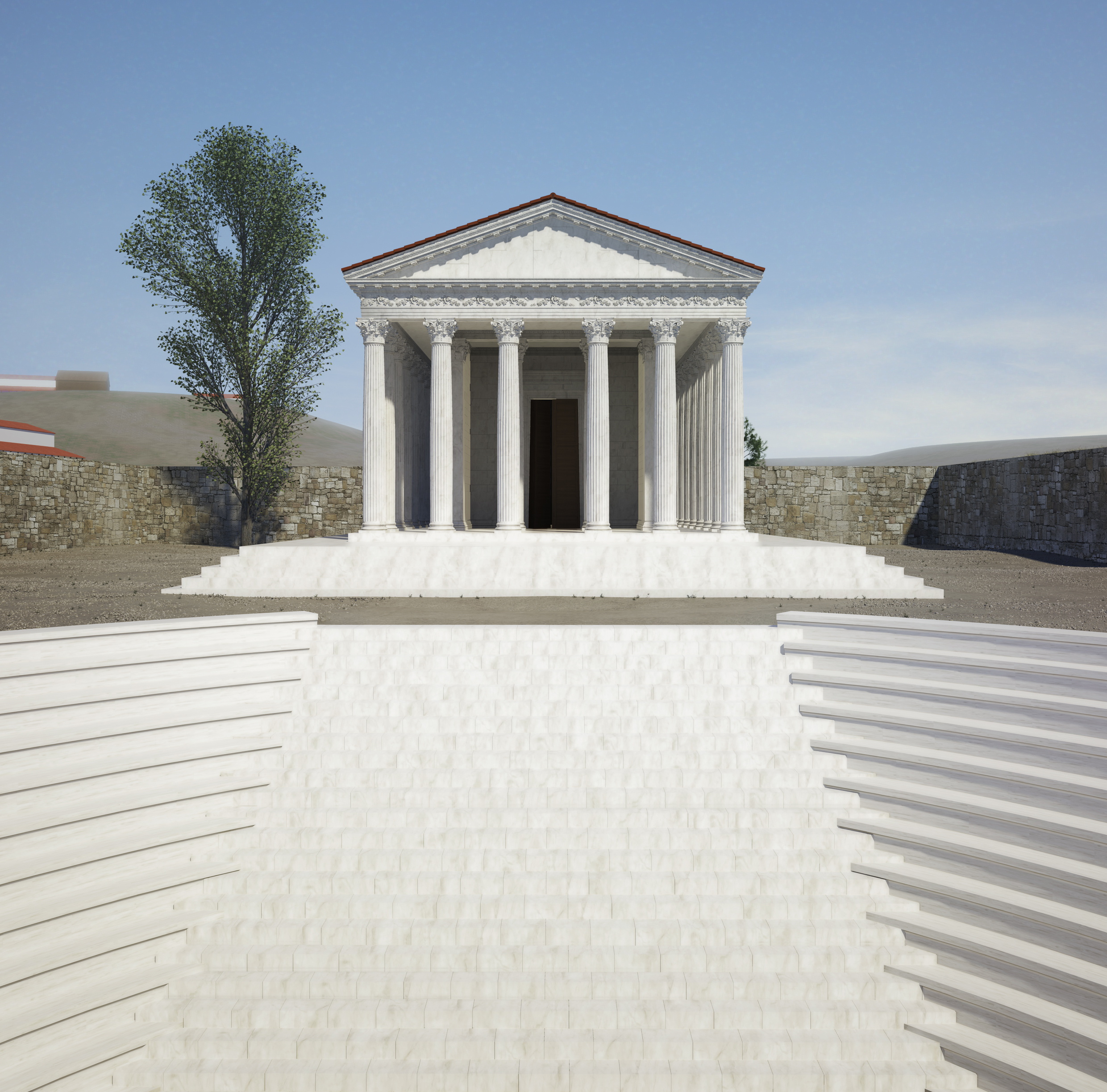
Pessinus
Pessinus ( el, Πεσσινούς or Πισσινούς) was an Ancient city and archbishopric in Asia Minor, a geographical area roughly covering modern Anatolia (Asian Turkey). The site of the city is now the modern Turkish village of Ballıhisar, in a tributary valley of the Sakarya River on the high Anatolian plateau at 950 m above sea level, 13 km from the small town of Sivrihisar. Pessinus remains a Catholic (formerly double) titular see. Description The temple area As yet, the temple area, which was excavated between 1967 and 1972, is the only well-studied area of Pessinus. It was studied thoroughly by M. Waelkens (current director of Sagalassos excavations) in the 1980s and between 2006 and 2012 by Verlinde (Ghent University), who built on the findings of the former to analyze and reconstruct the architecture of the Corinthian peripteral temple, of which only the massive foundations remain. Investigations led to several observations, such as the Tiberian da ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gordian Knot
The Gordian Knot is an Ancient Greek legend of Phrygian Gordium associated with Alexander the Great who is said to have cut the knot in 333 BC. It is often used as a metaphor for an intractable problem (untying an impossibly tangled knot) solved easily by finding an approach to the problem that renders the perceived constraints of the problem moot ("cutting the Gordian knot"): Legend The Phrygians were without a king, but an oracle at Telmissus (the ancient capital of Lycia) decreed that the next man to enter the city driving an ox-cart should become their king. A peasant farmer named Gordias drove into town on an ox-cart and was immediately declared king. Out of gratitude, his son Midas dedicated the ox-cart to the Phrygian god Sabazios (whom the Greeks identified with Zeus) and tied it to a post with an intricate knot of cornel bark (''Cornus mas''). The knot was later described by Roman historian Quintus Curtius Rufus as comprising "several knots all so tightly ent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alexander The Great
Alexander III of Macedon ( grc, wikt:Ἀλέξανδρος, Ἀλέξανδρος, Alexandros; 20/21 July 356 BC – 10/11 June 323 BC), commonly known as Alexander the Great, was a king of the Ancient Greece, ancient Greek kingdom of Macedonia (ancient kingdom), Macedon. He succeeded his father Philip II of Macedon, Philip II to the throne in 336 BC at the age of 20, and spent most of his ruling years conducting a lengthy military campaign throughout Western Asia and ancient Egypt, Egypt. By the age of thirty, he had created one of the List of largest empires, largest empires in history, stretching from Greece to northwestern Historical India, India. He was undefeated in battle and is widely considered to be one of history's greatest and most successful military commanders. Until the age of 16, Alexander was tutored by Aristotle. In 335 BC, shortly after his assumption of kingship over Macedon, he Alexander's Balkan campaign, campaigned in the Balkans and reasserted control ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |