 |
Pioneer Program
The Pioneer programs were two series of United States lunar and planetary space probes exploration. The first program, which ran from 1958 to 1960, unsuccessfully attempted to send spacecraft to orbit the Moon, successfully sent one spacecraft to fly by the Moon, and successfully sent one spacecraft to investigate interplanetary space between the orbits of Earth and Venus. The second program, which ran from 1965 to 1992, sent four spacecraft to measure interplanetary space weather, two to explore Jupiter and Saturn, and two to explore Venus. The two outer planet probes, ''Pioneer 10'' and ''Pioneer 11'', became the first two of five artificial objects to achieve the escape velocity that will allow them to leave the Solar System, and carried a golden plaque each depicting a man and a woman and information about the origin and the creators of the probes, in case any extraterrestrials find them someday. Naming Credit for naming the first probe has been attributed to Stephen A. Sal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
Air Force Ballistic Missile Division
Space Systems Command (SSC) is the United States Space Force's space development, acquisition, launch, and logistics field command. It is headquartered at Los Angeles Air Force Base, California and manages the United States' space launch ranges. Space Systems Command is the oldest military space organization in the United States Armed Forces, first established as the Western Development Division (WDD) on 1 April 1954 under Air Research and Development Command to manage the U.S. Air Force's ballistic missile program. It gained responsibility for spacecraft development in 1955 and was renamed the Air Force Ballistic Missile Division (AFBMD) in 1957. As part of Air Research and Development Command's transformation the Air Force Ballistic Missile Division's space and missile responsibilities were split, with the Space Systems Division (SSD) established in 1961. In 1967, the Space Systems Division was reorganized as the Space and Missile Systems Organization (SAMSO), absorbing th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
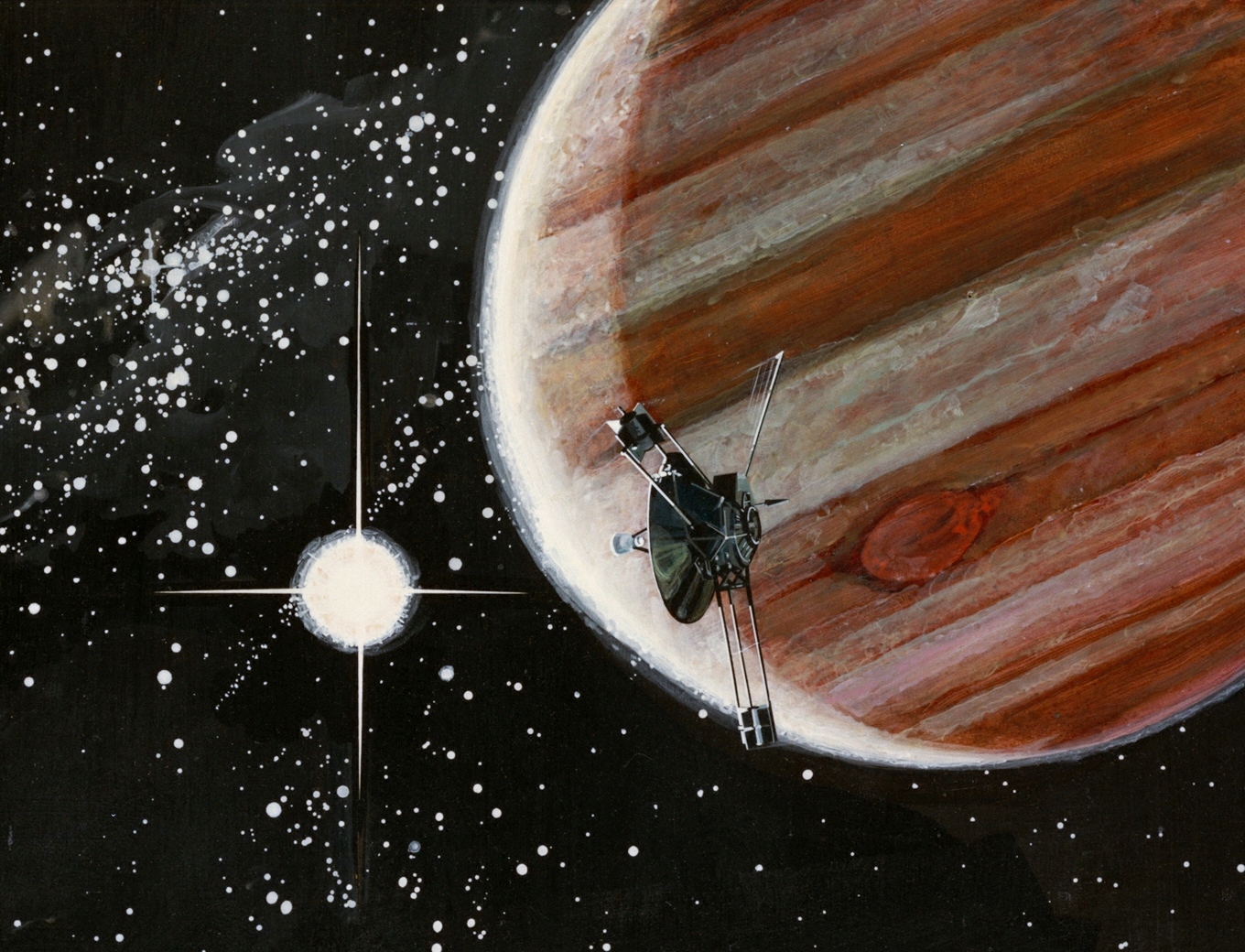 |
Pioneer 10
''Pioneer 10'' (originally designated Pioneer F) is an American space probe, launched in 1972 and weighing , that completed the first mission to the planet Jupiter. Thereafter, ''Pioneer 10'' became the first of five artificial objects to achieve the escape velocity needed to leave the Solar System. This space exploration project was conducted by the NASA Ames Research Center in California. The space probe was manufactured by TRW Inc. ''Pioneer 10'' was assembled around a hexagonal bus with a diameter parabolic dish high-gain antenna, and the spacecraft was spin stabilized around the axis of the antenna. Its electric power was supplied by four radioisotope thermoelectric generators that provided a combined 155 watts at launch. It was launched on March 3, 1972, at 01:49:00 UTC (March 2 local time), by an Atlas-Centaur expendable vehicle from Cape Canaveral, Florida. Between July 15, 1972, and February 15, 1973, it became the first spacecraft to traverse the asteroi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Pioneer P-1
Pioneer P-1 was a failed mission in the Pioneer program. The spacecraft was a 1-meter diameter sphere with a propulsion module, and was to carry a TV camera and magnetic field sensor. It was to be spin-stabilized Spin stabilization is the method of stabilizing a satellite or launch vehicle by means of spin, i.e. rotation along the longitudinal axis. The concept originates from ballistics, where the spin is commonly obtain by means of rifling. For most sate ... and was known as a 'paddlewheel' spacecraft. The spacecraft was intended for launch on an Atlas C-Able rocket, but this vehicle was destroyed on 24 September 1959 in an explosion on its launch pad during a pre-launch static firing. The P-1 spacecraft and an Able IV space engine were not present on the launch vehicle when it exploded, and were later used on the Pioneer P-3 mission. References External links Atlas-C Ableat Encyclopedia Astronautica Able IV information websiteSpace Technology Laboratories Documents ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Pioneer 2
Pioneer 2 (also known as Able 3) was the last of the three project Able space probes designed to probe lunar and cislunar space. The launch took place at 07:30:21 GMT on 8 November 1958. After Pioneer 1 had failed due to guidance system deficiencies, the guidance system was modified with a Doppler command system to ensure more accurate commands and minimize trajectory errors. Once again, the first and second stage portion of the flight was uneventful, but the third stage of the launch vehicle failed to ignite, making it impossible for Pioneer 2 to achieve orbital velocity. An attempt to fire the vernier engines on the probe was unsuccessful and the spacecraft attained a maximum altitude of before reentering Earth's atmosphere at 28.7° N, 1.9° E over NW Africa. A small amount of data was obtained during the short flight, including evidence that the equatorial region around Earth has higher flux and higher energy radiation than previously considered and that the micrometeorite ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
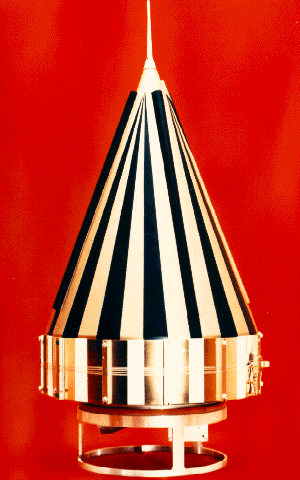
Pioneer 1
Pioneer 1 (also known as Able 2) was an American space probe, the first under the auspices of NASA, which was launched by a Thor-Able rocket on 11 October 1958. It was intended to orbit the Moon and make scientific measurements, but due to a guidance error failed to achieve lunar orbit and was ultimately destroyed upon reentering Earth's atmosphere. The flight, which lasted 43 hours and reached an apogee of 113,800 km (70,700 miles), was the second and most successful of the three Thor-Able space probes. Spacecraft design Pioneer 1 was fabricated by Space Technology Laboratories, a division of Ramo-Wooldridge Corp (later TRW Inc.), and consisted of a thin cylindrical midsection with a squat truncated cone on each side. The cylinder was in diameter and the height from the top of one cone to the top of the opposite cone was . Along the axis of the spacecraft and protruding from the end of the lower cone was an solid propellant injection rocket and rocket case, which f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Pioneer P-1 P-3 P-30 P-31
Pioneer commonly refers to a settler who migrates to previously uninhabited or sparsely inhabited land. In the United States pioneer commonly refers to an American pioneer, a person in American history who migrated west to join in settling and developing new areas. Pioneer, The Pioneer, or pioneering may also refer to: Companies and organizations *Pioneer Aerospace Corporation * Pioneer Chicken, an American fast-food restaurant chain * Pioneer Club Las Vegas, a casino in Las Vegas, Nevada, U.S. *Pioneer Corporation, a Japanese electronics manufacturer * Pioneer Energy, a Canadian gas station chain * Pioneer Entertainment, a Japanese anime company *Pioneer Hi-Bred, a U.S.-based agriculture company * Pioneer Hotel & Gambling Hall, Laughlin, Nevada, U.S. *Pioneer Instrument Company, an American aeronautical instrument manufacturer *Pioneer movement, a communist youth organization *Pioneer Natural Resources, an energy company in Texas, U.S. * Pioneer Pictures, a former American film ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
National Advisory Committee For Aeronautics
The National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA) was a United States federal agency founded on March 3, 1915, to undertake, promote, and institutionalize aeronautical research. On October 1, 1958, the agency was dissolved and its assets and personnel were transferred to the newly created National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA). NACA is an initialism, i.e., pronounced as individual letters, rather than as a whole word (as was NASA during the early years after being established). Among other advancements, NACA research and development produced the NACA duct, a type of air intake used in modern automotive applications, the NACA cowling, and several series of NACA airfoils, which are still used in aircraft manufacturing. During World War II, NACA was described as "The Force Behind Our Air Supremacy" due to its key role in producing working superchargers for high altitude bombers, and for producing the laminar wing profiles for the North American P-51 Mustang. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Moon
The Moon is Earth's only natural satellite. It is the fifth largest satellite in the Solar System and the largest and most massive relative to its parent planet, with a diameter about one-quarter that of Earth (comparable to the width of Australia). The Moon is a planetary-mass object with a differentiated rocky body, making it a satellite planet under the geophysical definitions of the term and larger than all known dwarf planets of the Solar System. It lacks any significant atmosphere, hydrosphere, or magnetic field. Its surface gravity is about one-sixth of Earth's at , with Jupiter's moon Io being the only satellite in the Solar System known to have a higher surface gravity and density. The Moon orbits Earth at an average distance of , or about 30 times Earth's diameter. Its gravitational influence is the main driver of Earth's tides and very slowly lengthens Earth's day. The Moon's orbit around Earth has a sidereal period of 27.3 days. During each s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
Extraterrestrial Life
Extraterrestrial life, colloquially referred to as alien life, is life that may occur outside Earth and which did not originate on Earth. No extraterrestrial life has yet been conclusively detected, although efforts are underway. Such life might range from simple forms like prokaryotes to intelligent beings, possibly bringing forth civilizations that might be far more advanced than humankind. The Drake equation speculates about the existence of sapient life elsewhere in the universe. The science of extraterrestrial life is known as astrobiology. Speculation about the possibility of inhabited "worlds" outside the planet Earth dates back to antiquity. Multiple early Christian writers discussed the idea of a "plurality of worlds" as proposed by earlier thinkers such as Democritus; Augustine references Epicurus's idea of innumerable worlds "throughout the boundless immensity of space" (originally expressed in his Letter to Herodotus) in '' The City of God''. In his first cent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Pioneer Plaque
The Pioneer plaques are a pair of gold-anodized aluminum plaques that were placed on board the 1972 ''Pioneer 10'' and 1973 ''Pioneer 11'' spacecraft, featuring a pictorial message, in case either ''Pioneer 10'' or ''11'' is intercepted by intelligent extraterrestrial life. The plaques show the nude figures of a human male and female along with several symbols that are designed to provide information about the origin of the spacecraft. The ''Pioneer 10'' and ''11'' spacecraft were the first human-built objects to achieve escape velocity from the Solar System. The plaques were attached to the spacecraft's antenna support struts in a position that would shield them from erosion by interstellar dust. History The original idea, that the Pioneer spacecraft should carry a message from mankind, was first mentioned by Eric Burgess when he visited the Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California, during the Mariner 9 mission. He approached Carl Sagan, who had lectured about com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
Solar System
The Solar System Capitalization of the name varies. The International Astronomical Union, the authoritative body regarding astronomical nomenclature, specifies capitalizing the names of all individual astronomical objects but uses mixed "Solar System" and "solar system" structures in theinaming guidelines document. The name is commonly rendered in lower case ('solar system'), as, for example, in the ''Oxford English Dictionary'' an''Merriam-Webster's 11th Collegiate Dictionary''. is the gravitationally bound system of the Sun and the objects that orbit it. It formed 4.6 billion years ago from the gravitational collapse of a giant interstellar molecular cloud. The vast majority (99.86%) of the system's mass is in the Sun, with most of the remaining mass contained in the planet Jupiter. The four inner system planets—Mercury, Venus, Earth and Mars—are terrestrial planets, being composed primarily of rock and metal. The four giant planets of the outer system a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |