|
Pig Landraces
The pig (''Sus domesticus''), often called swine, hog, or domestic pig when distinguishing from other members of the genus '' Sus'', is an omnivorous, domesticated, even-toed, hoofed mammal. It is variously considered a subspecies of ''Sus scrofa'' (the wild boar or Eurasian boar) or a distinct species. The pig's head-plus-body length ranges from , and adult pigs typically weigh between , with well-fed individuals even exceeding this range. The size and weight of hogs largely depends on their breed. Compared to other artiodactyls, a pig's head is relatively long and pointed. Most even-toed ungulates are herbivorous, but pigs are omnivores, like their wild relative. Pigs grunt and make snorting sounds. When used as livestock, pigs are farmed primarily for the production of meat, called pork. A group of pigs is called a ''passel'', a ''team'', or a ''sounder''. The animal's bones, hide, and bristles are also used in products. Pigs, especially miniature breeds, are kept as pets ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sus (genus)
''Sus'' is the genus of wild and domestic pigs, within the even-toed ungulate family Suidae. ''Sus'' include domestic pigs (''Sus domesticus'') and their ancestor, the common Eurasian wild boar (''Sus scrofa''), along with other species. ''Sus'' species, like all suids, are native to the Eurasian and African continents, ranging from Europe to the Pacific islands. Suids other than the pig are the babirusa of Indonesia, the pygmy hog of South Asia, the warthogs of Africa, and other pig genera from Africa. The suids are a sister clade to peccaries. Juvenile pigs are known as piglets. Pigs are highly social and intelligent animals. With around 1 billion of this species alive at any time, the domestic pig is among the most populous large mammals in the world. Pigs are omnivores and can consume a wide range of food. Pigs are biologically similar to humans and are thus frequently used for human medical research. Etymology The '' Online Etymology Dictionary'' provides anecdotal ev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
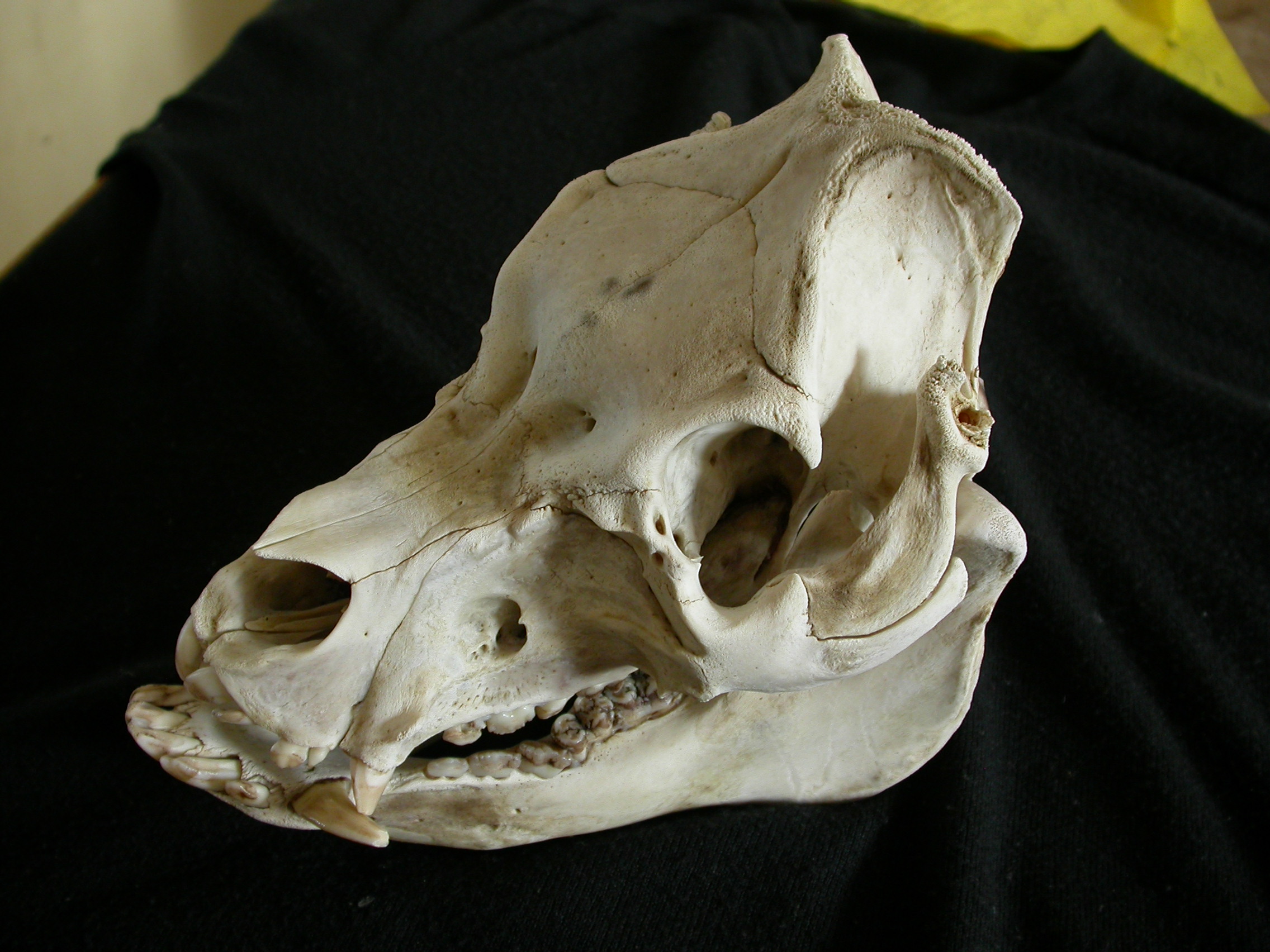
Domestic Pig Skull
Domestic may refer to: In the home * Anything relating to the human home or family ** A domestic animal, one that has undergone domestication ** A domestic appliance, or home appliance ** A domestic partnership ** Domestic science, sometimes called family and consumer science ** Domestic violence ** A domestic worker In the state * Domestic affairs, matters relating to the internal government of a Sovereign state * Domestic airport * Domestic flight * Domestic policy, the internal policy of a state Other * Domestic, Indiana, an unincorporated community in Wells County * ''Domestikos'' ( en, the Domestic), a Byzantine title ** Domestic of the Schools, commander-in-chief of the Byzantine army in the 9th-11th centuries * ''Domestic'' (film), a 2012 Romanian comedy film See also * Domestic discipline (other) * Housekeeper (other) Housekeeper may refer to: * Housekeeper (domestic worker), a person heading up domestic maintenance * "House Keeper" (song), 1996 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mucous Membrane
A mucous membrane or mucosa is a membrane that lines various cavities in the body of an organism and covers the surface of internal organs. It consists of one or more layers of epithelial cells overlying a layer of loose connective tissue. It is mostly of endodermal origin and is continuous with the skin at body openings such as the eyes, eyelids, ears, inside the nose, inside the mouth, lips, the genital areas, the urethral opening and the anus. Some mucous membranes secrete mucus, a thick protective fluid. The function of the membrane is to stop pathogens and dirt from entering the body and to prevent bodily tissues from becoming dehydrated. Structure The mucosa is composed of one or more layers of epithelial cells that secrete mucus, and an underlying lamina propria of loose connective tissue. The type of cells and type of mucus secreted vary from organ to organ and each can differ along a given tract. Mucous membranes line the digestive, respiratory and reproductive trac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eccrine Sweat Gland
Eccrine sweat glands (; from Greek ''ekkrinein'' 'secrete'; sometimes called merocrine glands) are the major sweat glands of the human body, found in virtually all skin, with the highest density in palm and soles, then on the head, but much less on the torso and the extremities. In other mammals, they are relatively sparse, being found mainly on hairless areas such as foot pads. They reach their peak of development in humans, where they may number 200–400/cm2 of skin surface.Bolognia, J., Jorizzo, J., & Schaffer, J. (2012). Dermatology (3rd ed., pp. 539-544). hiladelphia Elsevier Saunders. They produce a clear, odorless substance, sweat, consisting primarily of water. These are present from birth. Their secretory part is present deep inside the dermis. Eccrine glands are composed of an intraepidermal spiral duct, the "acrosyringium"; a dermal duct, consisting of a straight and coiled portion; and a secretory tubule, coiled deep in the dermis or hypodermis. The eccrine gland op ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apocrine Sweat Gland
An apocrine sweat gland (; from Greek ''apo'' 'away' and ''krinein'' 'to separate') is composed of a coiled secretory portion located at the junction of the dermis and subcutaneous fat, from which a straight portion inserts and secretes into the infundibular portion of the hair follicle. In humans, apocrine sweat glands are found only in certain locations of the body: the axillae (armpits), areola and nipples of the breast, ear canal, eyelids, wings of the nostril, perineal region, and some parts of the external genitalia. Modified apocrine glands include the ciliary glands in the eyelids; the ceruminous glands, which produce ear wax; and the mammary glands, which produce milk. The rest of the body is covered by eccrine sweat glands. Most non-primate mammals, however, have apocrine sweat glands over the greater part of their body. Domestic animals such as dogs and cats have apocrine glands at each hair follicle and even in their urinary system, but eccrine glands only in f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mangalitsa
The Mangalica (also Mangalitsa or Mangalitza) is a Hungarian breed of domestic pig. It was developed in the mid-19th century by crossbreeding breeds from the nearby Romanian Salonta (Hungarian: ''Nagyszalonta'', colloquially ''Szalonta'') and Hungarian Bakony with the European wild boar and the Serbian Šumadija breed. The Mangalica pig grows a thick, curly coat of hair. The only other pig breed noted for having a long coat is the extinct Lincolnshire Curly Coat pig of England. History The blonde Mangalica variety was developed from older, hardy types of Hungarian pig (Bakonyi and Szalontai) crossed with the European wild boar and a Serbian breed (and later others like Alföldi) in Austria-Hungary (1833). That year, Prince of Serbia Miloš Obrenović sent 12 pigs of the autochthonous Serbian ''Šumadinka'' breed, ten sows and two boars. Pigs originally grown at the Prince's Topčider farm near Belgrade were used to create the Syrmian black lasa breed, also known as t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
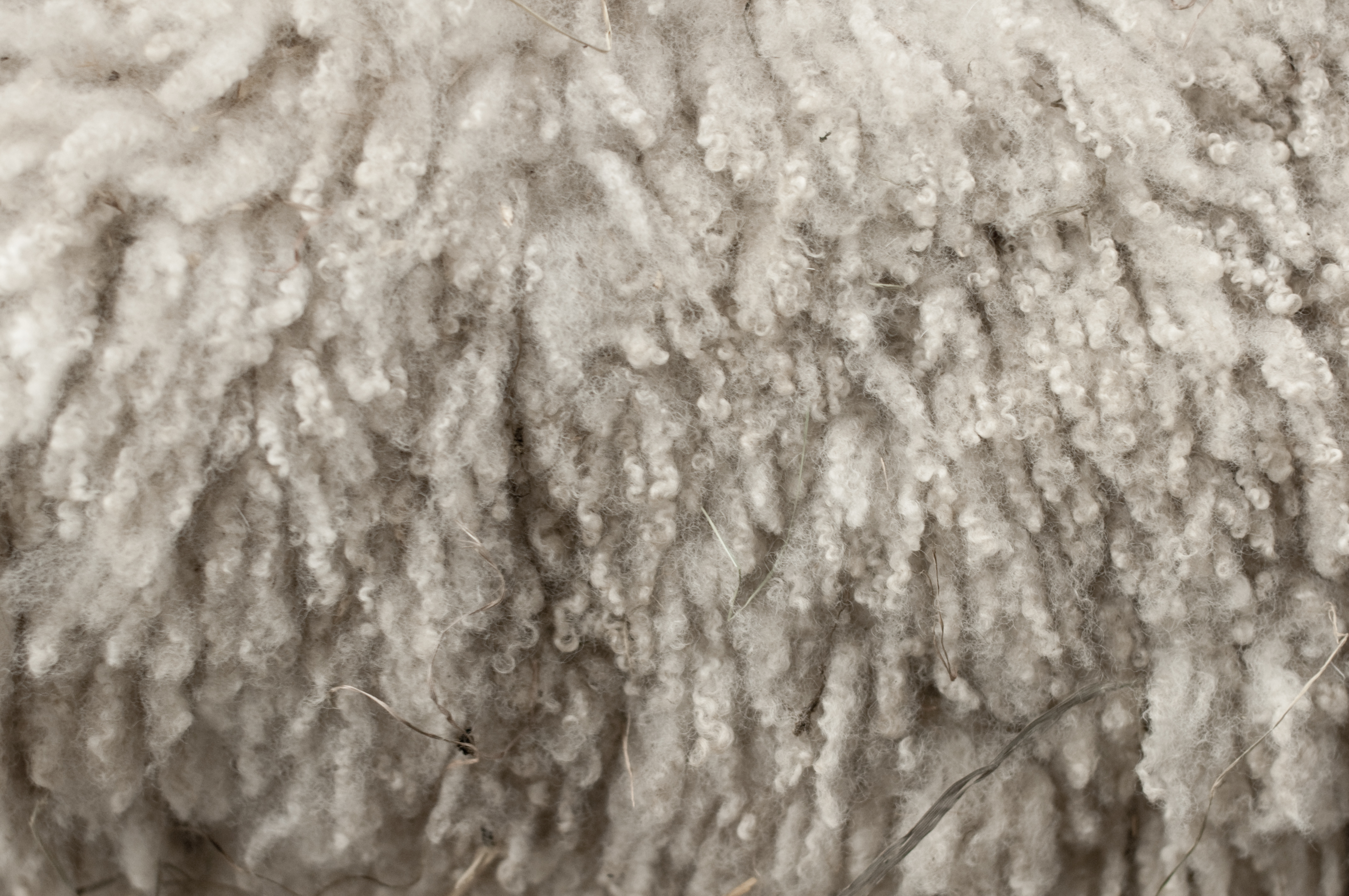
Wool
Wool is the textile fibre obtained from sheep and other mammals, especially goats, rabbits, and camelids. The term may also refer to inorganic materials, such as mineral wool and glass wool, that have properties similar to animal wool. As an animal fibre, wool consists of protein together with a small percentage of lipids. This makes it chemically quite distinct from cotton and other plant fibres, which are mainly cellulose. Characteristics Wool is produced by follicles which are small cells located in the skin. These follicles are located in the upper layer of the skin called the epidermis and push down into the second skin layer called the dermis as the wool fibers grow. Follicles can be classed as either primary or secondary follicles. Primary follicles produce three types of fiber: kemp, medullated fibers, and true wool fibers. Secondary follicles only produce true wool fibers. Medullated fibers share nearly identical characteristics to hair and are long but lack c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bristle
A bristle is a stiff hair or feather (natural or artificial), either on an animal, such as a pig, a plant, or on a tool such as a brush or broom. Synthetic types Synthetic materials such as nylon are also used to make bristles in items such as brooms and sweepers. Bristles are often used to make brushes for cleaning purposes, as they are strongly abrasive; common examples include the toothbrush and toilet brush. The bristle brush and the scrub brush are common household cleaning tools, often used to remove dirt or grease from pots and pans. Bristles are also used on brushes other than for cleaning, notably paintbrushes. Bristles are distinguished as ''flagged'' (split, bushy ends) or ''unflagged;'' these are also known as ''flocked'' or ''unflocked'' bristles. In cleaning applications, flagged bristles are suited for dry cleaning (due to picking up dust better than unflagged), and unflagged suited for wet cleaning (due to flagged ends becoming dirty and matted when wet). In painti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
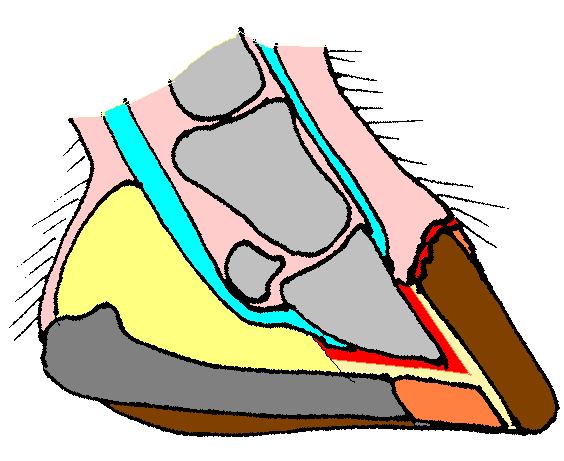
Hoof
The hoof (plural: hooves) is the tip of a toe of an ungulate mammal, which is covered and strengthened with a thick and horny keratin covering. Artiodactyls are even-toed ungulates, species whose feet have an even number of digits, yet the ruminants with two digits, are the most numerous, e.g. giraffe, deer, bison, cattle, goat, and sheep. The feet of perissodactyl mammals have an odd number of toes, e.g. the horse, the rhinoceros, and the tapir. Hooves are limb structures restricted to placental mammals, which have long pregnancies; however, the marsupial ''Chaeropus'' had hooves. Description The hoof surrounds the distal end of the second phalanx, the distal phalanx, and the navicular bone. The hoof consists of the hoof wall, the bars of the hoof, the sole and frog and soft tissue shock absorption structures. The weight of the animal is normally borne by both the sole and the edge of the hoof wall. Hooves perform many functions, including supporting the weight of the animal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tusk
Tusks are elongated, continuously growing front teeth that protrude well beyond the mouth of certain mammal species. They are most commonly canine teeth, as with pigs and walruses, or, in the case of elephants, elongated incisors. Tusks share common features such as extra-oral position, growth pattern, composition and structure, and lack of contribution to ingestion. Tusks are thought to have adapted to the extra-oral environments, like dry or aquatic or arctic. In most tusked species both the males and the females have tusks although the males' are larger. Most mammals with tusks have a pair of them growing out from either side of the mouth. Tusks are generally curved and have a smooth, continuous surface. The male narwhal's straight single helical tusk, which usually grows out from the left of the mouth, is an exception to the typical features of tusks described above. Continuous growth of tusks is enabled by formative tissues in the apical openings of the roots of the teeth. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tooth
A tooth ( : teeth) is a hard, calcified structure found in the jaws (or mouths) of many vertebrates and used to break down food. Some animals, particularly carnivores and omnivores, also use teeth to help with capturing or wounding prey, tearing food, for defensive purposes, to intimidate other animals often including their own, or to carry prey or their young. The roots of teeth are covered by gums. Teeth are not made of bone, but rather of multiple tissues of varying density and hardness that originate from the embryonic germ layer, the ectoderm. The general structure of teeth is similar across the vertebrates, although there is considerable variation in their form and position. The teeth of mammals have deep roots, and this pattern is also found in some fish, and in crocodilians. In most teleost fish, however, the teeth are attached to the outer surface of the bone, while in lizards they are attached to the inner surface of the jaw by one side. In cartilaginous fish, s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dental Formula
Dentition pertains to the development of teeth and their arrangement in the mouth. In particular, it is the characteristic arrangement, kind, and number of teeth in a given species at a given age. That is, the number, type, and morpho-physiology (that is, the relationship between the shape and form of the tooth in question and its inferred function) of the teeth of an animal. Animals whose teeth are all of the same type, such as most non-mammalian vertebrates, are said to have '' homodont'' dentition, whereas those whose teeth differ morphologically are said to have '' heterodont'' dentition. The dentition of animals with two successions of teeth (deciduous, permanent) is referred to as '' diphyodont'', while the dentition of animals with only one set of teeth throughout life is ''monophyodont''. The dentition of animals in which the teeth are continuously discarded and replaced throughout life is termed ''polyphyodont''. The dentition of animals in which the teeth are set in s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)