|
Pembroke, New Hampshire
Pembroke is a town in Merrimack County, New Hampshire, United States. The population was 7,207 at the 2020 census. Pembroke includes part of the village of Suncook. The center of population of New Hampshire is close to the Pembroke town center. History First granted in 1728, the town was known as "Lovewell's Town", in honor of Captain John Lovewell, who built the stockade at Ossipee. Shortly afterward, the town took the name of "Suncook", the Pennacook Abenaki name for the river flowing through the area. When the town was incorporated in 1759 by colonial Governor Benning Wentworth, it was given the name "Pembroke" in honor of Henry Herbert, ninth Earl of Pembroke in southern Wales. Pembroke's early history is reflected in the various mills of the downtown area, located to use water power from the Suncook River. The better-known mills were the Pembroke Mills, Webster Manufacturing, and China Manufacturing, all producing print cloth. Pembroke industries included brickmaking, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Merrimack County, New Hampshire
Merrimack County is a county in the U.S. state of New Hampshire. As of the 2020 Census, the population was 153,808, making it the third-most populous county in New Hampshire. Its county seat is Concord, the state capital. The county was organized in 1823 from parts of Hillsborough and Rockingham counties, and is named for the Merrimack River. Merrimack County comprises the Concord, NH Micropolitan Statistical Area, which in turn constitutes a portion of the Boston–Worcester–Providence, MA– RI–NH– CT Combined Statistical Area. In 2010, the center of population of New Hampshire was located in Merrimack County, in the town of Pembroke. Geography According to the U.S. Census Bureau, the county has a total area of , of which is land and (2.3%) is water. It is the third-largest county in New Hampshire by land area. The highest point in Merrimack county is Mount Kearsarge, on the border of Warner and Wilmot, at 2,937 feet (895 m). Adjacent counties * Belknap Count ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Lovewell
John Lovewell (October 14, 1691 – May 9, 1725) was a militia captain in the 18th century who fought during Father Rale's War (also known as Lovewell's War). He lived in present-day Nashua, New Hampshire. He led three expeditions against the Abenaki Indians. Lovewell became the most famous ranger ( scalp hunter) of the 18th century. Although the outcome was a draw, Lovewell's Fight in May 1725 marked the end of hostilities between the English and the Abenakis of Maine. This conflict was a turning point. So important was it to western Maine, New Hampshire and even Massachusetts colonists that the Fight was celebrated in song and story; more than 100 years later, Henry Wadsworth Longfellow, Nathaniel Hawthorne, and Henry David Thoreau all wrote about Lovewell's Fight. 1st and 2nd expeditions In early September 1724, Indians captured three men near Dunstable, Massachusetts, in the area now known as Nashua, New Hampshire. When the men did not return from work a party of ten or mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clay
Clay is a type of fine-grained natural soil material containing clay minerals (hydrous aluminium phyllosilicates, e.g. kaolin, Al2 Si2 O5( OH)4). Clays develop plasticity when wet, due to a molecular film of water surrounding the clay particles, but become hard, brittle and non–plastic upon drying or firing. Most pure clay minerals are white or light-coloured, but natural clays show a variety of colours from impurities, such as a reddish or brownish colour from small amounts of iron oxide. Clay is the oldest known ceramic material. Prehistoric humans discovered the useful properties of clay and used it for making pottery. Some of the earliest pottery shards have been dated to around 14,000 BC, and clay tablets were the first known writing medium. Clay is used in many modern industrial processes, such as paper making, cement production, and chemical filtering. Between one-half and two-thirds of the world's population live or work in buildings made with clay, often ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brickmaking
A brick is a type of block used to build walls, pavements and other elements in masonry construction. Properly, the term ''brick'' denotes a block composed of dried clay, but is now also used informally to denote other chemically cured construction blocks. Bricks can be joined using mortar, adhesives or by interlocking them. Bricks are usually produced at brickworks in numerous classes, types, materials, and sizes which vary with region and time period, and are produced in bulk quantities. ''Block'' is a similar term referring to a rectangular building unit composed of similar materials, but is usually larger than a brick. Lightweight bricks (also called lightweight blocks) are made from expanded clay aggregate. Fired bricks are one of the longest-lasting and strongest building materials, sometimes referred to as artificial stone, and have been used since circa 4000 BC. Air-dried bricks, also known as mud-bricks, have a history older than fired bricks, and have an additio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Suncook River
The Suncook River is a river located in central New Hampshire in the United States. It is a tributary of the Merrimack River, which flows to the Gulf of Maine. Course The Suncook River begins at the outlet of Crystal Lake in the town of Gilmanton, New Hampshire. The village of Gilmanton Ironworks is located at the lake's outlet. The Suncook flows south two miles to the Suncook Lakes (Upper and Lower) in Barnstead. Below the lakes, the river passes through the village of Center Barnstead and enters the town of Pittsfield, whose village is centered on a 19th century dam on the river. The river continues south through the towns of Chichester and Epsom, and then forms the town boundary between Pembroke and Allenstown. Shortly before reaching the Merrimack River, the Suncook drops in , a natural waterpower site that led to the growth of the village of Suncook. 2006 flood On May 16, 2006, the Suncook River, responding to the highest rainfall amounts in at least 70 years (more ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Water Power
Hydropower (from el, ὕδωρ, "water"), also known as water power, is the use of falling or fast-running water to produce electricity or to power machines. This is achieved by converting the gravitational potential or kinetic energy of a water source to produce power. Hydropower is a method of sustainable energy production. Hydropower is now used principally for hydroelectric power generation, and is also applied as one half of an energy storage system known as pumped-storage hydroelectricity. Hydropower is an attractive alternative to fossil fuels as it does not directly produce carbon dioxide or other atmospheric pollutants and it provides a relatively consistent source of power. Nonetheless, it has economic, sociological, and environmental downsides and requires a sufficiently energetic source of water, such as a river or elevated lake. International institutions such as the World Bank view hydropower as a low-carbon means for economic development. Since ancient times, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Watermill
A watermill or water mill is a mill that uses hydropower. It is a structure that uses a water wheel or water turbine to drive a mechanical process such as milling (grinding), rolling, or hammering. Such processes are needed in the production of many material goods, including flour, lumber, paper, textiles, and many metal products. These watermills may comprise gristmills, sawmills, paper mills, textile mills, hammermills, trip hammering mills, rolling mills, wire drawing mills. One major way to classify watermills is by wheel orientation (vertical or horizontal), one powered by a vertical waterwheel through a gear mechanism, and the other equipped with a horizontal waterwheel without such a mechanism. The former type can be further divided, depending on where the water hits the wheel paddles, into undershot, overshot, breastshot and pitchback (backshot or reverse shot) waterwheel mills. Another way to classify water mills is by an essential trait about their location: tide mills ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wales
Wales ( cy, Cymru ) is a Countries of the United Kingdom, country that is part of the United Kingdom. It is bordered by England to the Wales–England border, east, the Irish Sea to the north and west, the Celtic Sea to the south west and the Bristol Channel to the south. It had a population in 2021 of 3,107,500 and has a total area of . Wales has over of coastline and is largely mountainous with its higher peaks in the north and central areas, including Snowdon (), its highest summit. The country lies within the Temperateness, north temperate zone and has a changeable, maritime climate. The capital and largest city is Cardiff. Welsh national identity emerged among the Celtic Britons after the Roman withdrawal from Britain in the 5th century, and Wales was formed as a Kingdom of Wales, kingdom under Gruffydd ap Llywelyn in 1055. Wales is regarded as one of the Celtic nations. The Conquest of Wales by Edward I, conquest of Wales by Edward I of England was completed by 1283, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Earl Of Pembroke
Earl of Pembroke is a title in the Peerage of England that was first created in the 12th century by King Stephen of England. The title, which is associated with Pembroke, Pembrokeshire in West Wales, has been recreated ten times from its original inception. Due to the number of creations of the Earldom, the original seat of Pembroke Castle is no longer attached to the title. , the current holder of the earldom is William Herbert, 18th Earl of Pembroke, which is the 10th creation of the title. For the past 400 years, his family's seat has been Wilton House, Wiltshire. The Earls of Pembroke also hold the title Earl of Montgomery, created for the younger son of Henry Herbert, 2nd Earl of Pembroke before he succeeded as the 4th Earl in 1630. The current Earls of Pembroke also carry the subsidiary titles: Baron Herbert of Cardiff, of Cardiff in the County of Glamorgan (1551), Baron Herbert of Shurland, of Shurland in the Isle of Sheppey in the County of Kent (1605), and Baron Herbe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Benning Wentworth
Benning Wentworth (July 24, 1696 – October 14, 1770) was an American merchant and colonial administrator who served as the governor of New Hampshire from 1741 to 1766. While serving as governor, Wentworth is best known for issuing several land grants in territory claimed by the Province of New Hampshire west of the Connecticut River, which led to disputes with the neighboring colony of New York and the eventual founding of Vermont. Born in Portsmouth, New Hampshire into a prominent colonial family in 1692, Wentworth was groomed by his father John while growing up to assume control over the family business before misbehavior while studying at Harvard College led him to be sent to Boston instead in 1715. There, Wentworth was apprenticed at his uncle's business before becoming a merchant. In 1730, he returned to Portsmouth to assume control over his father's estate. After Wentworth returned to his family, he soon started becoming involved in politics, sitting on both the House ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British North America
British North America comprised the colonial territories of the British Empire in North America from 1783 onwards. English overseas possessions, English colonisation of North America began in the 16th century in Newfoundland (island), Newfoundland, then further south at Roanoke Colony, Roanoke and Jamestown, Virginia, and more substantially with the founding of the Thirteen Colonies along the Atlantic coast of North America. The British Empire's colonial territories in North America were greatly expanded in connection with the Treaty of Paris (1763), which formally concluded the Seven Years' War, referred to by the English colonies in North America as the French and Indian War, and by the French colonies as . With the ultimate acquisition of most of New France (), Territorial evolution of North America since 1763, British territory in North America was more than doubled in size, and the exclusion of France also dramatically altered the political landscape of the continent. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
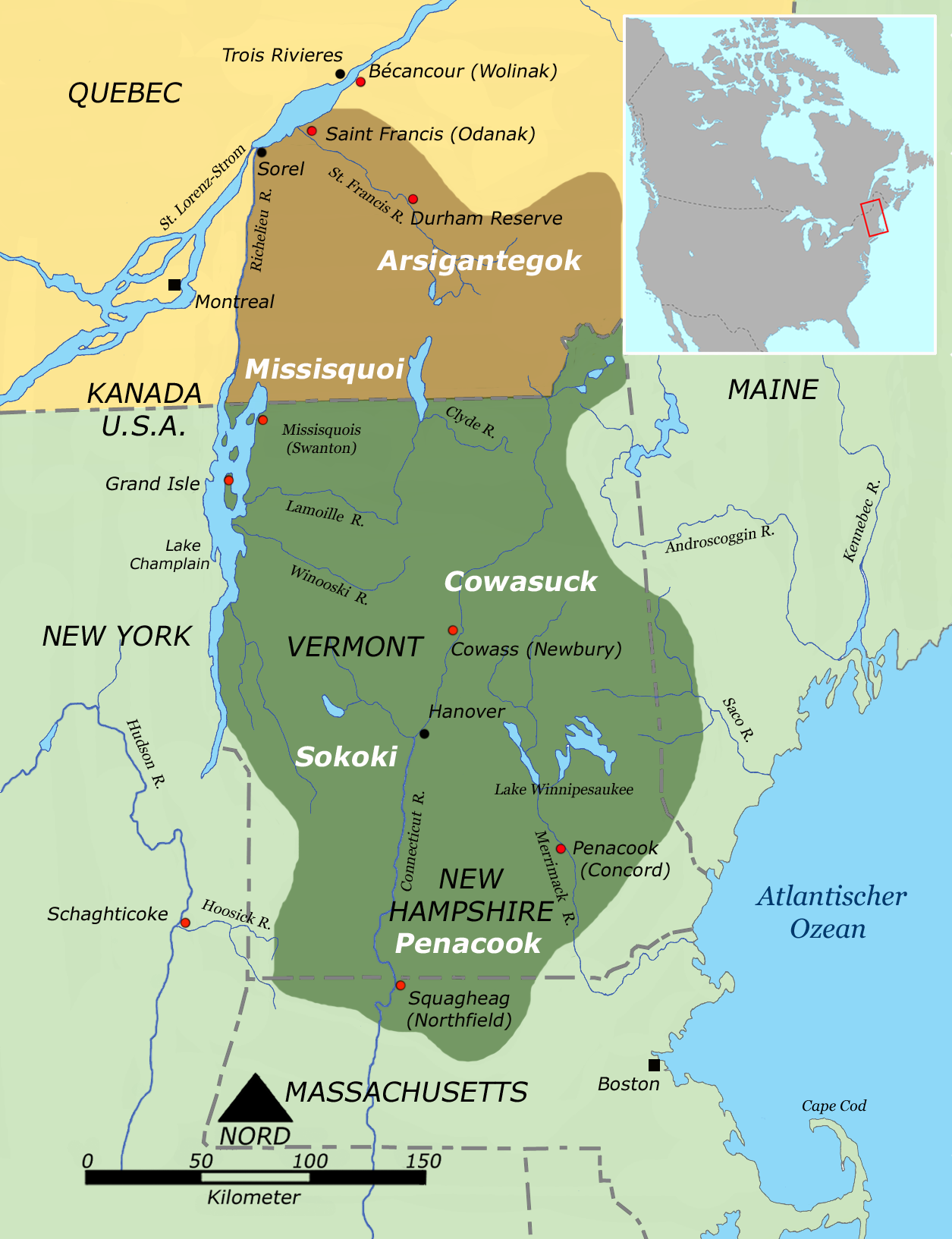
Abenaki
The Abenaki (Abenaki: ''Wαpánahki'') are an Indigenous peoples of the Northeastern Woodlands of Canada and the United States. They are an Algonquian-speaking people and part of the Wabanaki Confederacy. The Eastern Abenaki language was predominantly spoken in Maine, while the Western Abenaki language was spoken in Quebec, Vermont, and New Hampshire. While Abenaki peoples have shared cultural traits, they did not historically have a centralized government. They came together as a post-contact community after their original tribes were decimated by colonization, disease, and warfare. Names The word ''Abenaki'' and its syncope, ''Abnaki,'' are both derived from ''Wabanaki'', or ''Wôbanakiak,'' meaning "People of the Dawn Land" in the Abenaki language. While the two terms are often confused, the Abenaki are one of several tribes in the Wabanaki Confederacy. The name is spelled several ways including Abnaki, Abinaki, and Alnôbak. ''Wôbanakiak'' is derived from ''wôban'' ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)