|
Nepoviruses
''Nepovirus'' is a genus of viruses in the order ''Picornavirales'', in the family ''Secoviridae'', in the subfamily ''Comovirinae''. Plants serve as natural hosts. There are 40 species in this genus. Nepoviruses, unlike the other two genera (''Comovirus'' and ''Fabavirus'') in the subfamily ''Comovirinae'', are transmitted by nematodes. Taxonomy The genus contains the following species: *'' Aeonium ringspot virus'' *'' Apricot latent ringspot virus'' *'' Arabis mosaic virus'' *'' Arracacha virus A'' *'' Artichoke Aegean ringspot virus'' *'' Artichoke Italian latent virus'' *'' Artichoke yellow ringspot virus'' *'' Beet ringspot virus'' *'' Blackcurrant reversion virus'' *'' Blueberry latent spherical virus'' *'' Blueberry leaf mottle virus'' *'' Cassava American latent virus'' *'' Cassava green mottle virus'' *'' Cherry leaf roll virus'' *'' Chicory yellow mottle virus'' *'' Cocoa necrosis virus'' *'' Crimson clover latent virus'' *'' Cycas necrotic stunt virus'' *'' Grapevin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cocoa Necrosis Virus
''Cocoa necrosis virus'' (CoNV) is a plant pathogenic virus of the genus ''nepovirus'' that infects ''Theobroma cacao'' en natura causing cacao necrosis disease. CoNV is considered synonymous with Strain S of cacao swollen shoot virus. Unlike ''Cacao swollen shoot virus'', it is not transmitted by mealybugs nor vectored by aphids, beetles, or leafhoppers that also commonly infest cacao. It is serologically, distantly related to '' Tomato black ring virus'' and very distantly related to '' Grapevine chrome mosaic virus''. Hosts and symptoms Cacao necrosis virus is restricted to systemic infection of ''Theobroma cacao'' in nature. Symptoms on cacao include an acute stage showing translucent veinal necrosis of leaves, necrotic or chlorotic spots of leaves, defoliation, and dieback of shoots that rarely leads to seedling death if infected by the Ghanaian isolate."Cocoa""Pests of Cocoa" A following recovery phase of live plants shows limited leaf symptoms. The virus has been transmitt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arabis Mosaic Virus
''Arabis mosaic virus'' is a viral plant pathogen that is known to infect multiple hosts. The pathogen, commonly referred to as ArMV, is from the family ''Secoviridae'', and it causes yellow dwarf of raspberry and is one of the causes of mosaic of rhubarb. ''Arabis mosaic virus'' infects multiple hosts, including strawberries, hops, hemp, grape, geraniums, raspberries, sugar beets, celery, horseradish, lilac, peach, and lettuces. Symptoms While it is common for the hosts not to show any symptoms of the pathogens influence, there are some symptoms that can occur in the hosts. The most prevalent symptoms of the ArMV are stunting of the plant and leaf flecking/molting and leaf enations. The symptoms will vary based on the type of rootstock, environmental conditions and variety. Disease cycle This virus is transmitted mainly through the soil by nematodes, but it can also be transmitted by arthropods (such as insects), and through seed and pollen transmission. Nepoviruses are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grapevine Fanleaf Virus
Grapevine fanleaf virus (GFLV) is a plant pathogenic virus of the family ''Secoviridae''. It infects grapevines, causing chlorosis of the leaves and lowering the fruit quality.P. Andret-Link ''et al.'' Journal of Plant Pathology (2004), 86(3), 183–195 Because of its effect on grape yield, GFLV is a pathogen of commercial importance. It is transmitted via a nematode vector, ''Xiphinema index ''Xiphinema index'', the California dagger nematode, is a species of plant-parasitic nematodes. History A major pest of grapes, the California dagger nematode provided the first example of a nematode acting as a vector for a viral plant diseas ...''. This nematode acquires the virus through feeding on roots of an infected plant, and passes it on in the same manner. Host and Symptoms: The host for Grapevine fanleaf virus or GFLV is the vitis species. This includes V. vinifera, V. rupestris, and hybrids. The symptoms of GFLV are “distortion of leaves and may cause unusual chlorotic (yell ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grapevine Chrome Mosaic Virus
''Grapevine chrome mosaic virus'' (GCMV) is a plant pathogenic virus of the family ''Secoviridae ''Secoviridae'' is a family of viruses in the order ''Picornavirales''. Plants serve as natural hosts. There are 8 genera and 86 species in this family, one of which is unassigned to a genus. The family was created in 2009 with the grouping of f ...''. References External links ICTVdB—The Universal Virus Database: Grapevine chrome mosaic virus Nepoviruses Viral grape diseases {{Virus-plant-disease-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grapevine Bulgarian Latent Virus
Grapevine Bulgarian latent virus (GBLV) is a plant pathogenic virus of the family ''Secoviridae ''Secoviridae'' is a family of viruses in the order ''Picornavirales''. Plants serve as natural hosts. There are 8 genera and 86 species in this family, one of which is unassigned to a genus. The family was created in 2009 with the grouping of f ...''. External linksICTVdB—The Universal Virus Database: Grapevine Bulgarian latent virus Nepoviruses Viral grape diseases {{Virus-plant-disease-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cherry Leaf Roll Virus
''Cherry leaf roll virus'' (CLRV) is a plant pathogenic virus of the subfamily ''Comovirinae'', family ''Secoviridae'', order ''Picornavirales''. Hosts The ''Cherry leaf roll virus'' infects a wide variety of woody plants and produces different symptoms by host. Symptoms of infection were first identified in walnut and sweet cherry trees. The virus is known to infect at least 36 plant families and natural hosts include olive, elm, ash, elderberry, beech, rhubarb, dogwood, and lilac ''Syringa'' is a genus of 12 currently recognized species of flowering plant, flowering woody plants in the olive family or Oleaceae called lilacs. These lilacs are native to woodland and scrub from southeastern Europe to eastern Asia, and wid .... Symptoms Symptoms include leaf roll, leaf yellowing, early dropping of leaves, stunted growth, and plant dieback. Plants can also be infected without exhibiting symptoms. References External links ICTVdB—The Universal Virus Database: ''Cherry l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cassava Green Mottle Virus
Cassava green mottle virus (CGMV) is a plant pathogenic virus of the family ''Secoviridae ''Secoviridae'' is a family of viruses in the order ''Picornavirales''. Plants serve as natural hosts. There are 8 genera and 86 species in this family, one of which is unassigned to a genus. The family was created in 2009 with the grouping of f ...''. External linksICTVdB—The Universal Virus Database: Cassava green mottle virus Viral plant pathogens and diseases Nepoviruses {{Virus-plant-disease-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cassava American Latent Virus
Cassava American latent virus (CsAlV) is a plant pathogenic virus of the family ''Secoviridae ''Secoviridae'' is a family of viruses in the order ''Picornavirales''. Plants serve as natural hosts. There are 8 genera and 86 species in this family, one of which is unassigned to a genus. The family was created in 2009 with the grouping of f ...''. External linksICTVdB—The Universal Virus Database: Cassava American latent virus Viral plant pathogens and diseases Nepoviruses {{Virus-plant-disease-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Artichoke Italian Latent Virus
Artichoke Italian latent virus is a virus that infects plants. It consists of two segments of positive-sense, single-stranded RNA enclosed in an icosahedral capsid. ''Artichoke Italian latent virus'' can infect a variety of flowering plants, causing discoloration and growth stunting. See also * List of grape diseases This is a list of diseases of grapes (''Vitis'' spp.). Bacterial diseases Fungal diseases Miscellaneous diseases and disorders Nematodes, parasitic Phytoplasma, virus and viruslike diseases See also *'' Ampeloglypter ater'' *'' Am ... References External links Family Groups—The Baltimore Method Nepoviruses Viral grape diseases {{Virus-plant-disease-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blueberry Leaf Mottle Virus
The ''Blueberry leaf mottle virus'' (BLMV) is a ''Nepovirus'' that was first discovered in Michigan in 1977. It has also appeared in New York, eastern Canada, Bulgaria, Hungary, and Portugal. Structure The BLMV genome is bipartite containing two segmented regions of linear, positive-sense, single stranded RNA. The entire genome of the virus is 14600 nucleotides long, and the RNA-1 has a partially sequenced region that is 7600 nucleotides long. The virus consists of a naked, icosahedral capsid that is 28 nm in diameter. The genome of the virus codes for both structural and non-structural proteins, and the lipids of this virus are unknown. Strains of the virus There are currently three known strains of the ''Blueberry leaf mottle virus''. The original strain (BLMV) infects highbush and lowbush varieties in Michigan and eastern Canada. A second strain (BLMV-NY) has only been reported in one case in New York and infected an American grapevine. The third strain was discovere ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
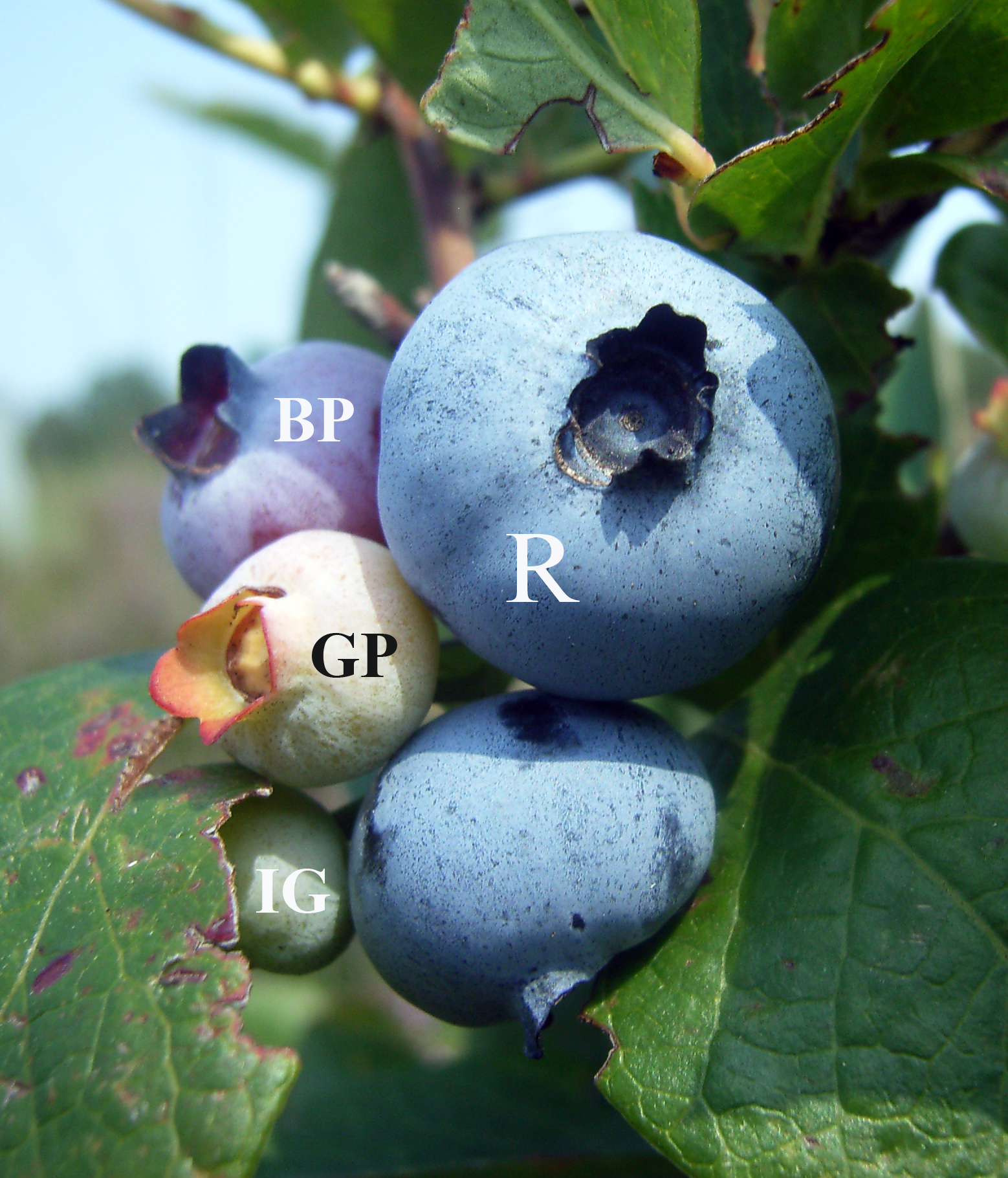
Blueberry Latent Spherical Virus
Blueberries are a widely distributed and widespread group of perennial flowering plants with blue or purple berries. They are classified in the section ''Cyanococcus'' within the genus ''Vaccinium''. ''Vaccinium'' also includes cranberries, bilberries, huckleberries and Madeira blueberries. Commercial blueberries—both wild (lowbush) and cultivated (highbush)—are all native to North America. The highbush varieties were introduced into Europe during the 1930s. Blueberries are usually prostrate shrubs that can vary in size from to in height. In commercial production of blueberries, the species with small, pea-size berries growing on low-level bushes are known as "lowbush blueberries" (synonymous with "wild"), while the species with larger berries growing on taller, cultivated bushes are known as "highbush blueberries". Canada is the leading producer of lowbush blueberries, while the United States produces some 40% of the world supply of highbush blueberries. Origin and hi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grapevine Deformation Virus
''Vitis'' (grapevine) is a genus of 79 accepted species of vining plants in the flowering plant family Vitaceae. The genus is made up of species predominantly from the Northern Hemisphere. It is economically important as the source of grapes, both for direct consumption of the fruit and for fermentation to produce wine. The study and cultivation of grapevines is called viticulture. Most cultivated ''Vitis'' varieties are wind-pollinated with hermaphroditic flowers containing both male and female reproductive structures, while wild species are dieceous. These flowers are grouped in bunches called inflorescences. In many species, such as ''Vitis vinifera'', each successfully pollinated flower becomes a grape berry with the inflorescence turning into a cluster of grapes. While the flowers of the grapevines are usually very small, the berries are often large and brightly colored with sweet flavors that attract birds and other animals to disperse the seeds contained within the berrie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |