|
Modica
Modica (; scn, Muòrica) is a city and ''comune'' of 54,456 inhabitants in the Province of Ragusa, Sicily, southern Italy. The city is situated in the Hyblaean Mountains. Modica has neolithic origins and it represents the historical capital of the area which today almost corresponds to the Province of Ragusa. Until the 19th century it was the capital of a County that exercised such a wide political, economical and cultural influence to be counted among the most powerful feuds of the Mezzogiorno. Rebuilt following the devastating earthquake of 1693, its architecture has been recognised as providing outstanding testimony to the exuberant genius and final flowering of Baroque art in Europe and, along with other towns in the Val di Noto, is part of UNESCO Heritage Sites in Italy. History According to Thucydides, the city was founded in 1360 BC or 1031 BC and was inhabited by the Sicels in the 7th century BC. It was probably a dependency of Syracuse. Modica was occupied by the R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Modica San Giorgio Front1
Modica (; scn, Muòrica) is a city and ''comune'' of 54,456 inhabitants in the Province of Ragusa, Sicily, southern Italy. The city is situated in the Hyblaean Mountains. Modica has neolithic origins and it represents the historical capital of the area which today almost corresponds to the Province of Ragusa. Until the 19th century it was the capital of a County that exercised such a wide political, economical and cultural influence to be counted among the most powerful feuds of the Mezzogiorno. Rebuilt following the devastating earthquake of 1693, its architecture has been recognised as providing outstanding testimony to the exuberant genius and final flowering of Baroque art in Europe and, along with other towns in the Val di Noto, is part of UNESCO Heritage Sites in Italy. History According to Thucydides, the city was founded in 1360 BC or 1031 BC and was inhabited by the Sicels in the 7th century BC. It was probably a dependency of Syracuse. Modica was occupied by the Ro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Modica Chiesa S Maria Del Soccorso
Modica (; scn, Muòrica) is a city and ''comune'' of 54,456 inhabitants in the Province of Ragusa, Sicily, southern Italy. The city is situated in the Hyblaean Mountains. Modica has neolithic origins and it represents the historical capital of the area which today almost corresponds to the Province of Ragusa. Until the 19th century it was the capital of a County that exercised such a wide political, economical and cultural influence to be counted among the most powerful feuds of the Mezzogiorno. Rebuilt following the devastating earthquake of 1693, its architecture has been recognised as providing outstanding testimony to the exuberant genius and final flowering of Baroque art in Europe and, along with other towns in the Val di Noto, is part of UNESCO Heritage Sites in Italy. History According to Thucydides, the city was founded in 1360 BC or 1031 BC and was inhabited by the Sicels in the 7th century BC. It was probably a dependency of Syracuse. Modica was occupied by the Ro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
County Of Modica
The County of Modica was a feudal territory within the Kingdom of Sicily from 1296 to 1812. Its capital was Modica, on the southern tip of the island, although the cities of Ragusa and Scicli housed some government offices for a period. Today it perpetuates as a title only held by the head of the House of Alba, Carlos Fitz-James Stuart, 19th Duke of Alba. History The Chiaramontes On 25 March 1296, the Aragonese King Frederick III of Sicily conceded the great County of Modica to Manfredi I Chiaramonte, who fought the Angevin and their king, Charles, and married Isabella Mosca, daughter of the rebel count Federico Mosca. The king gave the first dynasty of counts many fiefdoms in Agrigento, Caccamo, Licata and Palermo, where they built the Palazzo Chiaramonte, also known as Palazzo Steri; once the residence of the Aragonese-Spanish viceroys of Sicily and later the tribunal of the Inquisition, it now belongs to the University of Palermo. On its ceilings is one of the most importan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
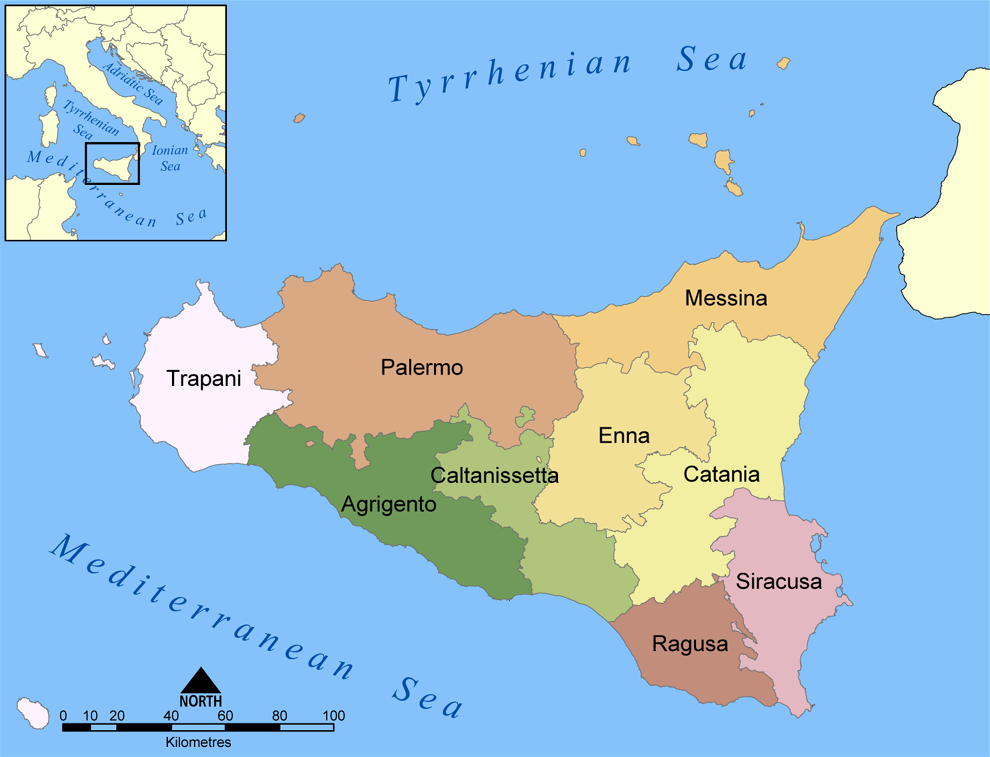
Province Of Ragusa
The Province of Ragusa ( it, Provincia di Ragusa; Sicilian: ''Pruvincia 'i Rausa'') was a province in the autonomous region of Sicily in southern Italy, located in the south-east of the island. Following the abolition of the Sicilian provinces, it was replaced in 2015 by the Free municipal consortium of Ragusa. Its capital is the city of Ragusa, which is the most southerly provincial capital in Italy. Geography From Scoglitti to Pozzallo, the Ragusan coastline is approximately long. Along the Ragusan coast are many fishing villages such as Kaukana, Punta Secca, Marina di Ragusa and Marina di Modica. The Hyblaean Mountains are dominating the north of the province and its highest peaks are Monte Lauro, Monte Casale and Monte Arcibessi. The rivers of the province are the Irminio, Dirillo and Ippari and the only lake in the province is the Lago di Santa Rosalia along the course of the Irminio river. The skyline of Ragusa is punctuated by the towers, domes and cupolas of the many ch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sicily
(man) it, Siciliana (woman) , population_note = , population_blank1_title = , population_blank1 = , demographics_type1 = Ethnicity , demographics1_footnotes = , demographics1_title1 = Sicilian , demographics1_info1 = 98% , demographics1_title2 = , demographics1_info2 = , demographics1_title3 = , demographics1_info3 = , timezone1 = CET , utc_offset1 = +1 , timezone1_DST = CEST , utc_offset1_DST = +2 , postal_code_type = , postal_code = , area_code_type = ISO 3166 code , area_code = IT-82 , blank_name_sec1 = GDP (nominal) , blank_info_sec1 = €89.2 billion (2018) , blank1_name_sec1 = GDP per capita , blank1_info_sec1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
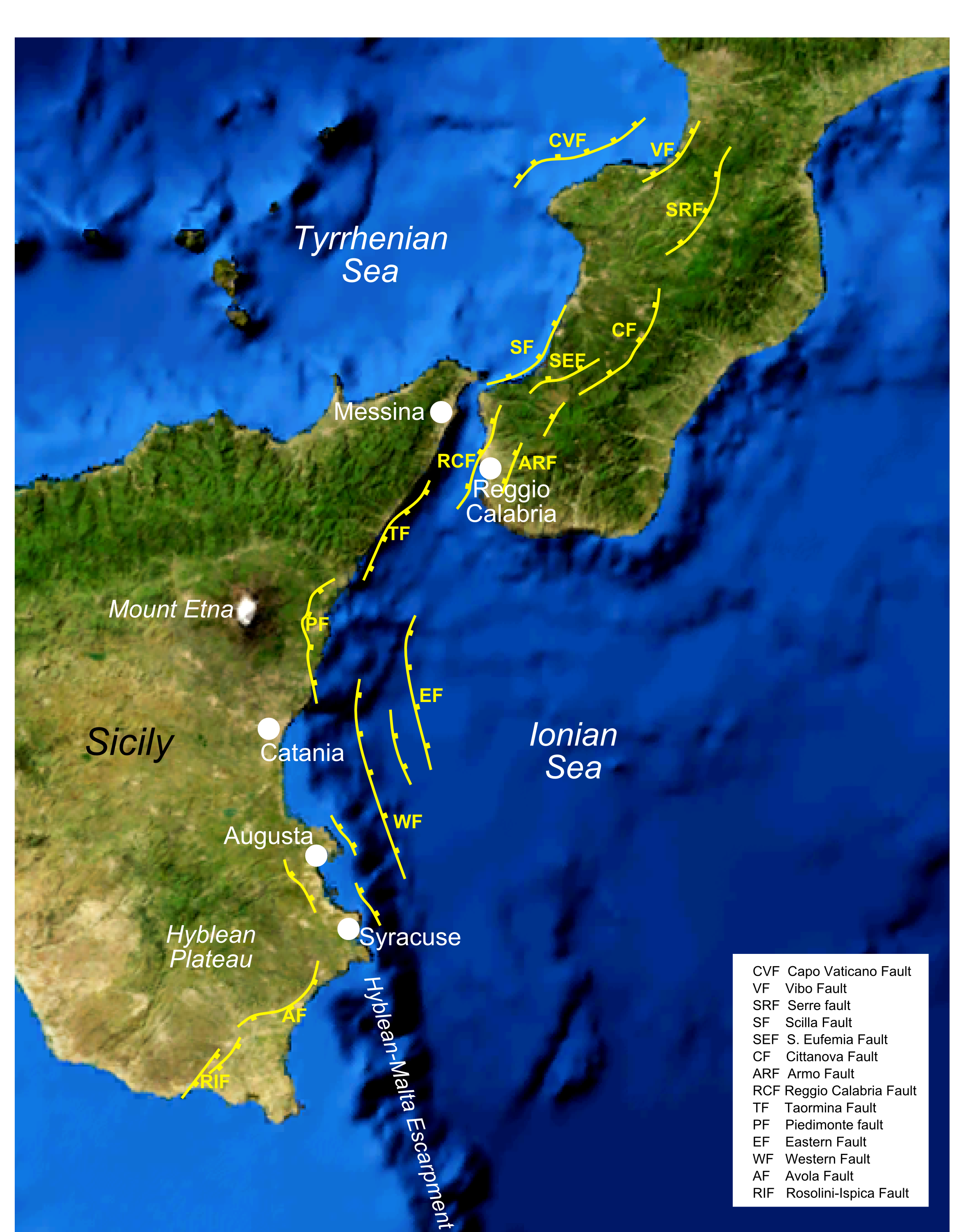
Hyblaean Mountains
The Hyblaean Mountains ( scn, Munt'Ibblei; it, Monti Iblei; la, Hyblaei montes) is a mountain range in south-eastern Sicily, Italy. It straddles the provinces of Ragusa, Syracuse and Catania. The highest peak of the range is Monte Lauro, at 986 m. History The name derives from the Siculi king Hyblon, who gave a portion of his territory to Greek colonists to build the town of Megara Hyblaea. Geology The range is composed of white limestone rocks, characterized by Karst topography. Originally a plateau, rivers have eroded the landscape, forming numerous deep canyons. In the coastal area sandstone is also present. In some areas, such as that of Monte Lauro (once part of a submerged volcanic complex), volcanic rocks are also present. The hyblaean area is characterized by a high seismic risk. Landscape The Hyblaean Mountains are characterized by gentle slopes, interrupted by sharp valleys. In the central area are numerous woods which are intermingled with dry stone walls of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Val Di Noto
Val di Noto (English: ''Province of Noto'') is a historical and geographical area encompassing the south-eastern third of Sicily; it is dominated by the limestone Hyblaean plateau. Historically, it was one of the three valli of Sicily. History The oldest recorded settlement in the Val di Noto was the ancient town of ''Akrai'', near Palazzolo Acreide, which was founded in 664 BC. It was the first colony of the Corinthian settlement at Syracuse. The settlements of the Val di Noto were completely destroyed by the enormous 1693 Sicily earthquake. Following the earthquake, many towns were rebuilt on entirely new sites, such as Noto and Grammichele. The rulers of the time, the kings of Spain, granted the nobleman Giuseppe Lanza special authority to redesign the damaged towns, which he achieved by sympathetically designing the new towns in a baroque and renaissance style. The new settlements were redesigned to have a town square in the centre and to spread out in a radial pattern fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1693 Sicily Earthquake
The 1693 Sicily earthquake struck parts of southern Italy near Sicily, Calabria, and Malta on January 11 at around 21:00 local time. This earthquake was preceded by a damaging foreshock on January 9. The main quake had an estimated magnitude of 7.4 on the moment magnitude scale, the most powerful in Italian recorded history, and a maximum intensity of XI (''Extreme'') on the Mercalli intensity scale, destroying at least 70 towns and cities, seriously affecting an area of and causing the death of about 60,000 people. The earthquake was followed by tsunamis that devastated the coastal villages on the Ionian Sea and in the Straits of Messina. Almost two-thirds of the entire population of Catania were killed. The epicentre of the disaster was probably close to the coast, possibly offshore, although the exact position remains unknown. The extent and degree of destruction caused by the earthquake resulted in the extensive rebuilding of the towns and cities of southeastern Sicily, partic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Syracuse, Italy
Syracuse ( ; it, Siracusa ; scn, Sarausa ), ; grc-att, wikt:Συράκουσαι, Συράκουσαι, Syrákousai, ; grc-dor, wikt:Συράκοσαι, Συράκοσαι, Syrā́kosai, ; grc-x-medieval, Συρακοῦσαι, Syrakoûsai, ; el, label=Modern Greek language, Modern Greek, Συρακούσες, Syrakoúses, . is a historic city on the Italy, Italian island of Sicily, the capital of the Italian province of Syracuse. The city is notable for its rich Greek and Roman history, Greek culture, culture, amphitheatres, architecture, and as the birthplace of the pre-eminent mathematician and engineer Archimedes. This 2,700-year-old city played a key role in ancient times, when it was one of the major powers of the Mediterranean world. Syracuse is located in the southeast corner of the island of Sicily, next to the Gulf of Syracuse beside the Ionian Sea. It is situated in a drastic rise of land with depths being close to the city offshore although the city itself is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geographer Of Ravenna
The ''Ravenna Cosmography'' ( la, Ravennatis Anonymi Cosmographia, "The Cosmography of the Unknown Ravennese") is a list of place-names covering the world from India to Ireland, compiled by an anonymous cleric in Ravenna around 700 AD. Textual evidence indicates that the author frequently used maps as his source. The text There are three known copies of the Cosmography in existence. The Vatican Library holds a 14th-century copy, there is a 13th-century copy in Paris at the Bibliothèque Nationale, and the library at Basle University has another 14th-century copy. The Vatican copy was used as the source for the first publication of the manuscript in 1688 by Porcheron. The German scholar Joseph Schnetz published the text in 1940, basing it on the Vatican and Paris editions, which he believed to be more reliable than the Basle edition. Parts of the text, notably that covering Britain, have been published by others, including Richmond and Crawford in 1949, but their document sh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pliny The Elder
Gaius Plinius Secundus (AD 23/2479), called Pliny the Elder (), was a Roman author, naturalist and natural philosopher, and naval and army commander of the early Roman Empire, and a friend of the emperor Vespasian. He wrote the encyclopedic ''Naturalis Historia'' (''Natural History''), which became an editorial model for encyclopedias. He spent most of his spare time studying, writing, and investigating natural and geographic phenomena in the field. His nephew, Pliny the Younger, wrote of him in a letter to the historian Tacitus: Among Pliny's greatest works was the twenty-volume work ''Bella Germaniae'' ("The History of the German Wars"), which is no longer extant. ''Bella Germaniae'', which began where Aufidius Bassus' ''Libri Belli Germanici'' ("The War with the Germans") left off, was used as a source by other prominent Roman historians, including Plutarch, Tacitus and Suetonius. Tacitus—who many scholars agree had never travelled in Germania—used ''Bella Germani ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ptolemy
Claudius Ptolemy (; grc-gre, Πτολεμαῖος, ; la, Claudius Ptolemaeus; AD) was a mathematician, astronomer, astrologer, geographer, and music theorist, who wrote about a dozen scientific treatises, three of which were of importance to later Byzantine, Islamic, and Western European science. The first is the astronomical treatise now known as the '' Almagest'', although it was originally entitled the ''Mathēmatikē Syntaxis'' or ''Mathematical Treatise'', and later known as ''The Greatest Treatise''. The second is the ''Geography'', which is a thorough discussion on maps and the geographic knowledge of the Greco-Roman world. The third is the astrological treatise in which he attempted to adapt horoscopic astrology to the Aristotelian natural philosophy of his day. This is sometimes known as the ''Apotelesmatika'' (lit. "On the Effects") but more commonly known as the '' Tetrábiblos'', from the Koine Greek meaning "Four Books", or by its Latin equivalent ''Quadrip ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |