|
History Of Mogadishu
Mogadishu ( so, Muqdisho, popularly ''Xamar''; ar, مقديشو) is the largest city in Somalia and the nation's capital. Located in the coastal Benadir region on the Indian Ocean, the city has served as an important port for centuries. Antiquity Tradition and old records assert that southern Somalia, including the Mogadishu area, was inhabited very early by hunter-gatherers of Khoisan descent. Although most of these early inhabitants are believed to have been either overwhelmed, driven away or, in some cases, assimilated by later migrants to the area, physical traces of their occupation survive in certain ethnic minority groups inhabiting modern-day Jubaland and other parts of the south. The latter descendants include relict populations such as the Eile, Aweer, the Wa-Ribi, and especially the Wa-Boni. By the time of the arrival of peoples from the Cushitic Rahanweyn (Digil and Mirifle) clan confederacy, who would go on to establish a local aristocracy, other Cushitic g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mogadishu
Mogadishu (, also ; so, Muqdisho or ; ar, مقديشو ; it, Mogadiscio ), locally known as Xamar or Hamar, is the capital and List of cities in Somalia by population, most populous city of Somalia. The city has served as an important port connecting traders across the Indian Ocean for millennia, and has an estimated population of 2,388,000 (2021). Mogadishu is located in the coastal Banadir region on the Indian Ocean, which unlike other Somali regions, is considered a municipality rather than a (federal state). Mogadishu has a long history, which ranges from the Ancient history, ancient period up until the present, serving as the capital of the Sultanate of Mogadishu in the 9th-13th century, which for many centuries controlled the Indian Ocean gold trade, and eventually came under the Ajuran Empire in the 13th century which was an important player in the medieval Silk Road maritime trade. Mogadishu enjoyed the height of its prosperity during the 14th and 15th centuries a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Somali People
The Somalis ( so, Soomaalida 𐒈𐒝𐒑𐒛𐒐𐒘𐒆𐒖, ar, صوماليون) are an ethnic group native to the Horn of Africa who share a common ancestry, culture and history. The Lowland East Cushitic Somali language is the shared mother tongue of ethnic Somalis, which is part of the Cushitic branch of the Afroasiatic language family, and are predominantly Sunni Muslim.Mohamed Diriye Abdullahi, ''Culture and Customs of Somalia'', (Greenwood Press: 2001), p.1 They form one of the largest ethnic groups on the African continent, and cover one of the most expansive landmasses by a single ethnic group in Africa. According to most scholars, the ancient Land of Punt and its native inhabitants formed part of the ethnogenesis of the Somali people. An ancient historical kingdom where a great portion of their cultural traditions and ancestry has been said to derive from.Egypt: 3000 Years of Civilization Brought to Life By Christine El MahdyAncient perspectives on Egypt By Ro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Book Of The Zanj
The ''Book of the Zanj'' (or ''Kitāb al-Zunūj'') is an Arabic history of the Zanj (Zenj, Zengi) who live in East Africa from their origins down to the turn of the 20th century. There are two manuscripts of the ''Book'', the more recent one offering an expanded text. The older one, labelled K or C, was produced shortly after 1888. In 1923, it was in the possession of the ''qāḍī'' of Kismayo, when a copy was procured by Enrico Cerulli. The younger one, labelled L or W, was made after 1902 in Witu for Alice Werner. It was acquired by Cerulli in 1926. Both manuscripts have been translated into English.In . The authors of both versions of the ''Book'' are unknown. The text is written in Arabic of low quality and the authors' first language was certainly Swahili. There are numerous Swahilisms in the text and one quatrain in Swahili. Both authors wrote in Bājūn and were sympathetic to the rulers of Pate and of Siyu, but opposed to the Mazrūʿī ''liwali''s of Mombasa. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Fage
John Donnelly Fage (3 June 1921–6 August 2002) was a British historian who was among the earliest academic historians specialising in African history, especially of the pre-colonial period, in the United Kingdom and West Africa. He published a number of influential studies on West African history including ''Introduction to the History of West Africa'' (1955). He subsequently co-founded the ''Journal of African History'', the first specialist academic journal in the field, with Roland Oliver in 1960. Career Early life John Fage was born in Teddington in Middlesex, England on 3 June 1921. He was educated at Tonbridge School and Magdalene College, Cambridge from 1939 where he studied history but his studies were interrupted by World War II. Fage was conscripted into the Royal Air Force (RAF) in 1942 and was posted to Southern Rhodesia (modern-day Zimbabwe) as part of the Commonwealth Air Training Plan and was subsequently given several postings in Africa, including in Ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enrico Cerulli
Enrico Cerulli (15 February 1898 - 19 September 1988) was an Italian scholar of Somali and Ethiopian studies, a governor and a diplomat. Biography Cerulli was born in Naples, Italy in 1898. He wrote his doctoral thesis at the University of Naples Federico II on the traditional law of the Somali. At the same time, he studied Ethio-Semitic languages under Francesco Gallina, and Arabic and Islamic studies under Carlo Alfonso Nallino and Giorgio Levi Della Vida at the Regio Istituto Orientale (later Istituto Universitario Orientale, today Università di Napoli "L'Orientale").Ricci 2003, p. 708b. Cerulli is also renowned for his studies on the Latin and Old French translation of the Arabic ''Kitab al-Miraj'', a famous Muslim book concerned with Muhammad's ascension into Heaven (known as the ''Mi'raj''), following his miraculous one-night journey from Mecca to Jerusalem (the ''Isra''). The book's Islamic depictions of Hell are believed by some scholars, including Cerulli, to hav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ioan Lewis
Ioan Myrddin Lewis FBA (January 30, 1930 – March 14, 2014), popularly known as I. M. Lewis, was a professor emeritus of anthropology at the London School of Economics. Early life and education Born in Scotland to a Welsh father and a Scottish mother, Lewis lived in Glasgow after the death of his father during his childhood. He was educated at Glasgow High School before receiving a Bachelor of Science in Chemistry from the University of Glasgow in 1951. He proceeded to St Catherine's College, Oxford, where he obtained a diploma in Anthropology in 1952 with the aid of a grant from the Nuffield Foundation, and a Bachelor of Letters in 1953. He studied under Franz Steiner and social anthropologist Sir Edward Evan Evans-Pritchard, who was himself an authority on the Nuer and Azande people of South Sudan, as a graduate student – finishing with a doctorate in 1957. Steiner was working on a multi-language bibliography on the Somali, Afar (Danakil), and Saho peoples, a project ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beden
The Beden, badan, or alternate type names Beden-seyed and Beden-safar, is a fast, ancient Somali single or double-masted maritime vessel and ship, typified by its towering stern-post and powerful rudder. It is also the longest surviving sewn boat in the Horn of Africa and the Arabian Peninsula. Its shipyards predominantly lie in the northeastern Hafun region of Somalia (notably Bayla), as well as Muscat. There are 2 types of Beden ships, with one type geared towards fishing (the Beden-seyed) and the other, trading (Beden-safar). The average trading Beden-safar ship measure more than in length, and are significantly larger than the fishing Beden-seyed ships, which measure on average, but both are dwarfed by a much larger trading variant called the 'uwassiye'. This ship is the most common trading and voyaging vessel, with some measuring up to . The ship is noticeable and unique in its strengthened and substantial gunwale, which is attached by treenail. Originally, all Beden ships ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ( la, Imperium Romanum ; grc-gre, Βασιλεία τῶν Ῥωμαίων, Basileía tôn Rhōmaíōn) was the post-Republican period of ancient Rome. As a polity, it included large territorial holdings around the Mediterranean Sea in Europe, North Africa, and Western Asia, and was ruled by emperors. From the accession of Caesar Augustus as the first Roman emperor to the military anarchy of the 3rd century, it was a Principate with Italia as the metropole of its provinces and the city of Rome as its sole capital. The Empire was later ruled by multiple emperors who shared control over the Western Roman Empire and the Eastern Roman Empire. The city of Rome remained the nominal capital of both parts until AD 476 when the imperial insignia were sent to Constantinople following the capture of the Western capital of Ravenna by the Germanic barbarians. The adoption of Christianity as the state church of the Roman Empire in AD 380 and the fall of the Western ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
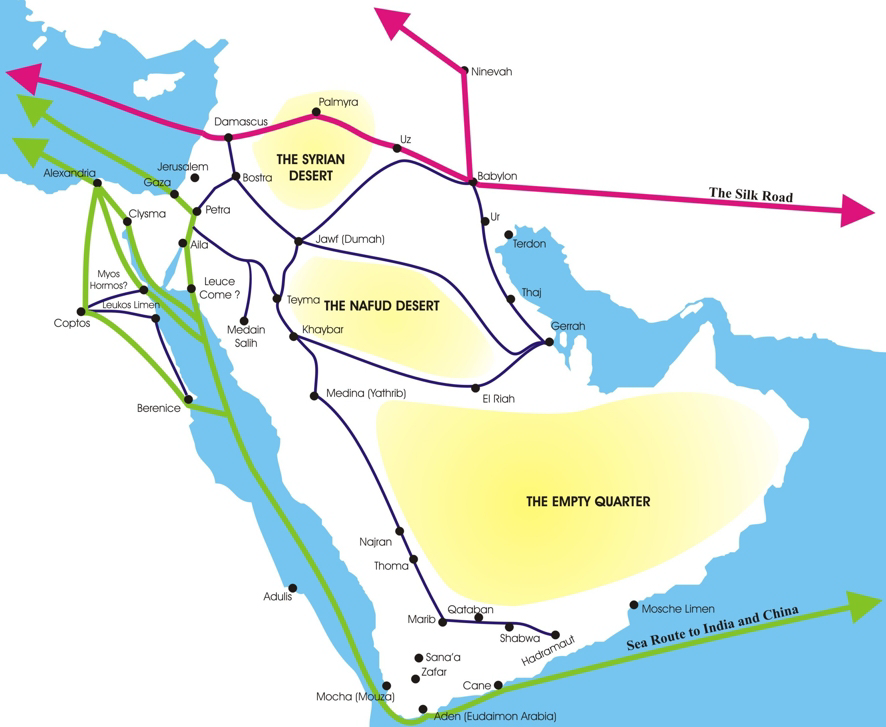
Nabataea
The Nabataean Kingdom (Nabataean Aramaic: 𐢕𐢃𐢋𐢈 ''Nabāṭū''), also named Nabatea (), was a political state of the Arab Nabataeans during classical antiquity. The Nabataean Kingdom controlled many of the trade routes of the region, amassing large wealth and drawing the envy of its neighbors. It stretched south along the Red Sea coast into the Hejaz, up as far north as Damascus, which it controlled for a short period (85–71 BC). Nabataea remained an independent political entity from the mid-3rd century BC until it was annexed in AD 106 by the Roman Empire, which renamed it Arabia Petraea. History Nabataeans The Nabataeans were one among several nomadic Bedouin tribes that roamed the Arabian Desert and moved with their herds to wherever they could find pasture and water. They became familiar with their area as seasons passed, and they struggled to survive during bad years when seasonal rainfall diminished. Although the Nabataeans were initially embedded in Aramaic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sabaeans
The Sabaeans or Sabeans (Sabaean language, Sabaean:, ; ar, ٱلسَّبَئِيُّوْن, ''as-Sabaʾiyyūn''; he, סְבָאִים, Səḇāʾīm) were an ancient group of South Arabians. They spoke the Sabaean language, one of the Old South Arabian languages.Stuart Munro-Hay, ''Aksum: An African Civilization of Late Antiquity'', 1991. They founded the kingdom of Sabaʾ ( ar, سَبَأ, links=no) in modern-day Yemen,Quran 27:6-93 Quran 34:15-18 which was believed to be the biblical land of Sheba and "the oldest and most important of the South Arabian kingdoms". The exact date of the foundation of Sabaʾ is a point of disagreement among scholars. Kenneth Kitchen dates the kingdom to between 1200 BCE and 275 CE, with its capital at Marib, Maʾrib, in what is now Yemen.Kenneth A. Kitchen ''The World of "Ancient Arabia" Series''. Documentation for Ancient Arabia. Part I. Chronological Framework and Historical Sources p.110 On the other hand, Israel Finkelstein and Neil Asher S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parthia
Parthia ( peo, 𐎱𐎼𐎰𐎺 ''Parθava''; xpr, 𐭐𐭓𐭕𐭅 ''Parθaw''; pal, 𐭯𐭫𐭮𐭥𐭡𐭥 ''Pahlaw'') is a historical region located in northeastern Greater Iran. It was conquered and subjugated by the empire of the Medes during the 7th century BC, was incorporated into the subsequent Achaemenid Empire under Cyrus the Great in the 6th century BC, and formed part of the Hellenistic Seleucid Empire following the 4th-century-BC conquests of Alexander the Great. The region later served as the political and cultural base of the Eastern Iranian Parni people and Arsacid dynasty, rulers of the Parthian Empire (247 BC – 224 AD). The Sasanian Empire, the last state of pre-Islamic Iran, also held the region and maintained the seven Parthian clans as part of their feudal aristocracy. Name The name "Parthia" is a continuation from Latin ', from Old Persian ', which was the Parthian language self-designator signifying "of the Parthians" who were an Iranian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |