|
High-speed Rail In Switzerland
High-speed rail in Switzerland consists of two new lines and three new base tunnels, including the world's longest railway and deepest traffic tunnel: the Gotthard Base Tunnel whose length is . Each of these tunnels have a technical maximum speed of , which is reduced, at least in the Gotthard Base Tunnel and the Ceneri Base Tunnel to a maximal authorized speed of for ecological and economical reasons, while the normal operational speed of passenger trains is restricted to in order to accommodate the freight traffic, with the possibility to accelerate up to 230 km/h in case of delay.Axe nord-sud du Saint-Gothard ( website). [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GBT North
GBT may refer to: Transport * Gambat railway station, in Pakistan * Gorgan Airport, in Iran * Gotthard Base Tunnel, in Switzerland * Greater Bridgeport Transit Authority, in Connecticut Other uses * Gelora Bung Tomo Stadium, in Surabaya, Indonesia * Generalised beam theory * Global Bio-Chem, a Hong Kong biotechnology company * Government and binding theory, in linguistics * Great Baikal Trail, a Russian environmental organisation * Green Bank Telescope The Robert C. Byrd Green Bank Telescope (GBT) in Green Bank, West Virginia, US is the world's largest fully steerable radio telescope, surpassing the Effelsberg 100-m Radio Telescope in Germany. The Green Bank site was part of the National Radio ..., in West Virginia * G-TELP Business Test, English language test * Gwinnett Ballet Theatre, in Lawrenceville, Georgia, United States {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lötschberg Base Tunnel
, line = Lötschberg Line , location = Traversing the Bernese Alps in Switzerland , coordinates = – , system = BLS, SBB CFF FFS , status = , start = Frutigen, canton of Bern, , end = Raron, canton of Valais, , stations = , startwork = 5 July 1999 , opened = 14 June 2007 , closed = , owner = BLS NETZ AG , operator = BLS , traffic = Railway , character = Passenger, Freight , length = , linelength = , tracklength = , notrack = One single-track tube for 20km, two single-track tubes for 14km , gauge = (standard gauge) , el = 15 kV 16.7 Hz , speed = , hielevation = , lowelevation = (south portal) , height = , grade = 3–13 ‰ , map = The Lötschberg Base Tunnel (LBT) is a railway base tunnel on the BLS AG's Lötschberg line cutting through the Bernese Alps of Switzerland some below the existing Lötschb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
High-speed Rail In Austria
The West railway between the capital Vienna and Salzburg is being upgraded. Most new sections have a continuous maximum design speed of 250 km/h. German and Austrian ICE trains operate at a maximum speed of 230 km/h, as do Austrian locomotive-hauled trains (called railjet) which were launched in 2008. The section between Attnang-Puchheim and Salzburg has not been part of the massive investments during the past decades. Therefore a new high-speed rail line between Köstendorf and Salzburg is being planned by ÖBB. Long distance and freight trains are planned to run through a 21,3 km long new track that is designed for a maximum speed of 250 km/h. This new infrastructure should enable to substantially increase the number of regional trains on the existing tracks and cut travel times for long distance connections by using the new tunnels. Construction works are expected to begin in 2025/2026. The Brenner Base Tunnel under construction will allow speeds of up to 250 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
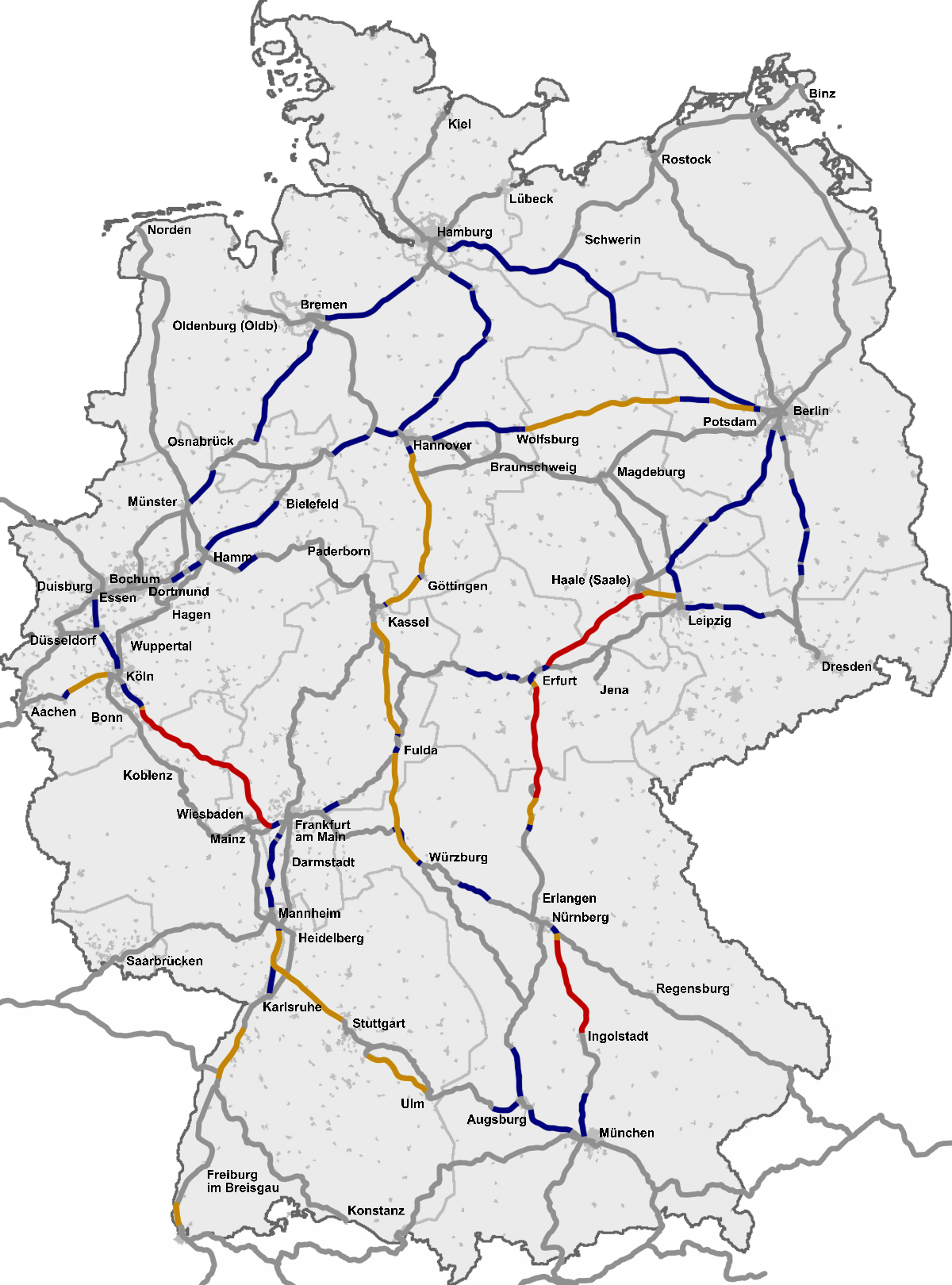
High-speed Rail In Germany
Construction of the first high-speed rail in Germany began shortly after that of the French LGVs (''lignes à grande vitesse'', high-speed lines). However, legal battles caused significant delays, so that the German Intercity-Express (ICE) trains were deployed ten years after the TGV network was established. InterCityExpress The first regularly scheduled ICE trains ran on 2 June 1991 from Hamburg-Altona via Hamburg Hbf – Hannover Hbf – Kassel-Wilhelmshöhe – Fulda – Frankfurt Hbf – Mannheim Hbf and Stuttgart Hbf toward München Hbf on the new ICE line 6. The ICE network is more tightly integrated with pre-existing lines and trains as a result of the different settlement structure in Germany, which has almost twice the population density of France. ICE trains reached destinations in Austria and Switzerland soon after they entered service, taking advantage of the same voltage used in these countries. Starting in 2000, multisystem third-generation ICE trains entered the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
High-speed Rail In Europe
High-speed rail (HSR) has developed in Europe as an increasingly popular and efficient means of transport. The first high-speed rail lines on the continent, built in the 1970s, 1980s, and 1990s, improved travel times on intra-national corridors. Since then, several countries have built extensive high-speed networks, and there are now several cross-border high-speed rail links. Railway operators frequently run international services, and tracks are continuously being built and upgraded to international standards on the emerging European high-speed rail network. In 2007, a consortium of European Railway operators, Railteam, emerged to co-ordinate and boost cross-border high-speed rail travel. Developing a Trans-European high-speed rail network is a stated goal of the European Union, and most cross-border railway lines receive EU funding. Several countries — France, Spain, Italy, Germany, Austria, Sweden, Belgium, the Netherlands, Poland, Portugal, Russia and the United Kingdom � ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solothurn–Wanzwil Railway
The Solothurn–Wanzwil railway was opened on 12 December 2004 to connect with the Mattstetten–Rothrist new line (high-speed line) as part of a package of railways forming Rail 2000. The built route mostly uses the route of the Solothurn–Herzogenbuchsee railway, which was closed in 1992. The Solothurn–Wanzwil section is single-track and, together with the Mattstetten–Rothrist line, was the first line in Switzerland to use the European Train Control System in regular operation. The maximum speed from Solothurn to Subingen is 140 km/h and from there it is 200 km/h. The turnout at the transition to double-track can also be run at 200 km/h. The line is mainly used by the ICN services on the St. Gallen–Lausanne/Geneva Geneva ( ; french: Genève ) frp, Genèva ; german: link=no, Genf ; it, Ginevra ; rm, Genevra is the List of cities in Switzerland, second-most populous city in Switzerland (after Zürich) and the most populous city of Romandy, the Fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pendolino
Pendolino (from Italian ''pendolo'' "pendulum", and ''-ino,'' a diminutive suffix) is an Italian family of tilting trains used in Italy, Spain, Germany, Poland, Portugal, Slovenia, Finland, Russia, the Czech Republic, Slovakia, the UK, the US, Switzerland, China and Greece. Based on the design of the Italian ETR 401 (itself being based on British Rail innovations), it was further developed and manufactured by Fiat Ferroviaria, which was taken over by Alstom in 2000. The idea of a tilting train became popular in the 1960s and 1970s when various rail operators, impressed by the high-speed rail services being introduced in France and Japan, wondered how they could similarly speed up travel without building a dedicated parallel rail network (as those two countries were doing). By tilting, the train could go around curves designed for slower trains at higher speeds without causing undue discomfort to passengers. Current use Italy In Italy, various possibilities were explor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trenitalia
Trenitalia is the primary train operator in Italy. A subsidiary of Ferrovie dello Stato Italiane, itself owned by the Italian government, the company was established in 2000 following a European Union directive on the deregulation of rail transport. History The Italian government formed Trenitalia to comply with Regulation (European Union), European regulations. The European Commission's First Railway Directive from 1991 (91/440/EC) required separation of accounting between entities which manage the rail infrastructure and entities which provide the actual rail transportation. On 1 June 2000, therefore, Italy created Trenitalia as the primary rail transportation company and on 1 July 2001 established Rete Ferroviaria Italiana (RFI) as the company overseeing the rail network. However, the separation was only formal, since both are subsidiaries of the Ferrovie dello Stato Italiane holding and are owned wholly by the government. Trenitalia operated freight rail services under the Tr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cisalpino
Cisalpino AG () was a railway company, referred to as CIS in timetables, operating international trains between Switzerland and Italy connecting Basel, Schaffhausen, Zürich, Geneva, Milan, Venice, Trieste, Livorno, and Florence. The company has its legal headquarters in Muri bei Bern, Switzerland, and is jointly owned by the Swiss Federal Railways and Trenitalia. It was founded in 1993 to operate fast trains across the Alps using tilting trains. In 2005, however, it also took over all daytime long-distance passenger trains between Switzerland and Italy run with conventional, non-tilting trains. In the fall of 2009, the project was abandoned because of mounting bad press over the quality of service and the fiasco surrounding orders placed for new trains. The remaining trains were split nearly evenly between the two owners. Until December 2012 the company owned the ETR 610 trainsets and leased them to Trenitalia and the Swiss Federal Railways (SBB CFF FFS). The company still e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
InterCityExpress
The Intercity Express (commonly known as ICE ()) is a system of high-speed trains predominantly running in Germany. It also serves some destinations in Austria, Denmark (ceased in 2017 but planned to resume in 2022), France, Belgium, Switzerland and the Netherlands, mostly as part of cross border services. It is the highest service category of rail and the flagship train of the German state railway, Deutsche Bahn. There are currently 315 trainsets in use. ICE trains are the highest category (Class A) trains in the fare system of the Deutsche Bahn. Their fares are not calculated on a fixed per-kilometre table as with other trains, but instead have fixed prices for station-to-station connections, levied on the grounds that the ICE trains have a higher level of comfort. Travelling at speeds up to , they are tailored for business travellers or long-distance commuters and are marketed by Deutsche Bahn as an alternative to flights. Apart from domestic use, the trains can also be seen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TGV Lyria
TGV Lyria is the brand name used for TGV railway lines connecting France and Switzerland. Lyria is also a corporation that runs the service using the staff of the SNCF in France and Swiss Federal Railways (SBB CFF FFS) in Switzerland – the staff consists of one French and one Swiss train manager on the whole journey. Corporate status Initially, the corporation was a ''groupement d'intérêt économique'' (GIE: "group of (shared) economic interest") between SNCF and SBB CFF FFS whose goal was the creation of a TGV service between Gare de Lyon (Paris) and Lausanne/Bern. Today, the corporation is officially a limited company according to French law (''Société par actions simplifiée'' / SAS). SNCF owns 74% of the capital and SBB CFF FFS the remaining 26%. History Starting in mid-1961, the route between Paris and Lausanne was operated by the Trans Europ Express ''Cisalpin'' trains, which continued on to Milan. On 22 January 1984 this service was r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SBB RABe 501
The RABe 501, nicknamed ''Giruno'', is a high-speed electric multiple unit train built by Stadler Rail of Switzerland for the Swiss Federal Railways (SBB). According to Stadler Rail, it is the world's first single-decker low-floor high-speed train. The trains are intended to replace the ETR610 trains on the trans-Alpine route between Milan (Italy) and Basel / Zürich, with eventually further connections with Germany and Austria. The main route goes through the 57 kilometre-long Gotthard Base Tunnel. As a consequence, the Giruno is also referred to as the "Gotthard train". The 11-car units operate with a top speed of and can accommodate up to 403 passengers (117 in first class, 286 in second class). Two train sets can be coupled together to accommodate over 800 passengers. Names Stadler originally named the train the EC250. This was changed in 2017 to SMILE, [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.jpg)