|
Hematopoietic Stem Cells
Hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) are the stem cells that give rise to other blood cells. This process is called haematopoiesis. In vertebrates, the very first definitive HSCs arise from the ventral endothelial wall of the embryonic aorta within the (midgestational) aorta-gonad-mesonephros region, through a process known as endothelial-to-hematopoietic transition. In adults, haematopoiesis occurs in the red bone marrow, in the core of most bones. The red bone marrow is derived from the layer of the embryo called the mesoderm. Haematopoiesis is the process by which all mature blood cells are produced. It must balance enormous production needs (the average person produces more than 500 billion blood cells every day) with the need to regulate the number of each blood cell type in the circulation. In vertebrates, the vast majority of hematopoiesis occurs in the bone marrow and is derived from a limited number of hematopoietic stem cells that are multipotent and capable of extensive se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hemangioblast
Hemangioblasts are the multipotent precursor cells that can differentiate into both hematopoietic stem cells, hematopoietic and endothelial cells. In the mouse embryo, the emergence of blood islands in the yolk sac at embryonic day 7 marks the onset of hematopoiesis. From these blood islands, the hematopoietic cells and vasculature are formed shortly after. Hemangioblasts are the progenitors that form the blood islands. To date, the hemangioblast has been identified in human, mouse and zebrafish embryos. Hemangioblasts have been first extracted from embryonic cultures and manipulated by cytokines to differentiate along either hematopoietic or endothelial route. It has been shown that these pre-endothelial/pre-hematopoietic cells in the embryo arise out of a phenotype CD34 population. It was then found that hemangioblasts are also present in the tissue of post-natal individuals, such as in newborn infants and adults. Adult hemangioblast There is now emerging evidence of hemangiobla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Macrophage
Macrophages (abbreviated as M φ, MΦ or MP) ( el, large eaters, from Greek ''μακρός'' (') = large, ''φαγεῖν'' (') = to eat) are a type of white blood cell of the immune system that engulfs and digests pathogens, such as cancer cells, microbes, cellular debris, and foreign substances, which do not have proteins that are specific to healthy body cells on their surface. The process is called phagocytosis, which acts to defend the host against infection and injury. These large phagocytes are found in essentially all tissues, where they patrol for potential pathogens by amoeboid movement. They take various forms (with various names) throughout the body (e.g., histiocytes, Kupffer cells, alveolar macrophages, microglia, and others), but all are part of the mononuclear phagocyte system. Besides phagocytosis, they play a critical role in nonspecific defense (innate immunity) and also help initiate specific defense mechanisms (adaptive immunity) by recruiting other immune ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Unipotency
Pluripotency: These are the cells that can generate into any of the three Germ layers which imply Endodermal, Mesodermal, and Ectodermal cells except tissues like the placenta. According to Latin terms, Pluripotentia means the ability for many things. We can generate Induced Pluripotent cells by using the Induced pluripotency technique by triggering or expressing the genes or the transcription factors of the normal somatic cells. They are abbreviated as iPSC or IPS. We can forcefully express the transcription factors like Oct4, Sox2, Klf4, and c-Myc of a non-pluripotent cell and convert them into a stem cell. This procedure is first studied in a Mouse fibroblast cell in 2006 and followed the same instructions in developing a Human pluripotent cell from a Human epidermal fibroblast cell. The technique is called Regeneration. Though the iPSC has similar properties to embryonic stem cells they were never approved for clinical stage research because they are highly Tumerogenic, hav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oligopotency
Pluripotency: These are the cells that can generate into any of the three Germ layers which imply Endodermal, Mesodermal, and Ectodermal cells except tissues like the placenta. According to Latin terms, Pluripotentia means the ability for many things. We can generate Induced Pluripotent cells by using the Induced pluripotency technique by triggering or expressing the genes or the transcription factors of the normal somatic cells. They are abbreviated as iPSC or IPS. We can forcefully express the transcription factors like Oct4, Sox2, Klf4, and c-Myc of a non-pluripotent cell and convert them into a stem cell. This procedure is first studied in a Mouse fibroblast cell in 2006 and followed the same instructions in developing a Human pluripotent cell from a Human epidermal fibroblast cell. The technique is called Regeneration. Though the iPSC has similar properties to embryonic stem cells they were never approved for clinical stage research because they are highly Tumerogenic, hav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multipotent
Pluripotency: These are the cells that can generate into any of the three Germ layers which imply Endodermal, Mesodermal, and Ectodermal cells except tissues like the placenta. According to Latin terms, Pluripotentia means the ability for many things. We can generate Induced Pluripotent cells by using the Induced pluripotency technique by triggering or expressing the genes or the transcription factors of the normal somatic cells. They are abbreviated as iPSC or IPS. We can forcefully express the transcription factors like Oct4, Sox2, Klf4, and c-Myc of a non-pluripotent cell and convert them into a stem cell. This procedure is first studied in a Mouse fibroblast cell in 2006 and followed the same instructions in developing a Human pluripotent cell from a Human epidermal fibroblast cell. The technique is called Regeneration. Though the iPSC has similar properties to embryonic stem cells they were never approved for clinical stage research because they are highly Tumerogenic, hav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Innate Lymphoid Cell
Innate lymphoid cells (ILCs) are the most recently discovered family of innate immune cells, derived from common lymphoid progenitors (CLPs). In response to pathogenic tissue damage, ILCs contribute to immunity via the secretion of signalling molecules, and the regulation of both innate and adaptive immune cells. ILCs are primarily tissue resident cells, found in both lymphoid (immune associated), and non- lymphoid tissues, and rarely in the blood. They are particularly abundant at mucosal surfaces, playing a key role in mucosal immunity and homeostasis. Characteristics allowing their differentiation from other immune cells include the regular lymphoid morphology, absence of rearranged antigen receptors found on T cells and B cells (due to the lack of the RAG gene), and phenotypic markers usually present on myeloid or dendritic cells. Based on the difference in developmental pathways, phenotype, and signalling molecules produced, in 2013, ILCs were divided into three groups: ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Natural Killer Cell
Natural killer cells, also known as NK cells or large granular lymphocytes (LGL), are a type of cytotoxic lymphocyte critical to the innate immune system that belong to the rapidly expanding family of known innate lymphoid cells (ILC) and represent 5–20% of all circulating lymphocytes in humans. The role of NK cells is analogous to that of cytotoxic T cells in the vertebrate adaptive immune response. NK cells provide rapid responses to virus-infected cell and other intracellular pathogens acting at around 3 days after infection, and respond to tumor formation. Typically, immune cells detect the major histocompatibility complex (MHC) presented on infected cell surfaces, triggering cytokine release, causing the death of the infected cell by lysis or apoptosis. NK cells are unique, however, as they have the ability to recognize and kill stressed cells in the absence of antibodies and MHC, allowing for a much faster immune reaction. They were named "natural killers" because ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
B Cell
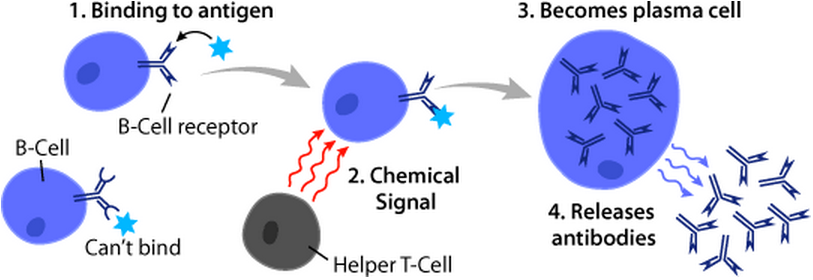
B cells, also known as B lymphocytes, are a type of white blood cell of the lymphocyte subtype. They function in the humoral immunity component of the adaptive immune system. B cells produce antibody molecules which may be either secreted or inserted into the plasma membrane where they serve as a part of B-cell receptors. When a naïve or memory B cell is activated by an antigen, it proliferates and differentiates into an antibody-secreting effector cell, known as a plasmablast or plasma cell. Additionally, B cells present antigens (they are also classified as professional antigen-presenting cells (APCs)) and secrete cytokines. In mammals, B cells mature in the bone marrow, which is at the core of most bones. In birds, B cells mature in the bursa of Fabricius, a lymphoid organ where they were first discovered by Chang and Glick, which is why the 'B' stands for bursa and not bone marrow as commonly believed. B cells, unlike the other two classes of lymphocytes, T cells and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
T Cell
A T cell is a type of lymphocyte. T cells are one of the important white blood cells of the immune system and play a central role in the adaptive immune response. T cells can be distinguished from other lymphocytes by the presence of a T-cell receptor (TCR) on their cell surface. T cells are born from hematopoietic stem cells, found in the bone marrow. Developing T cells then migrate to the thymus gland to develop (or mature). T cells derive their name from the thymus. After migration to the thymus, the precursor cells mature into several distinct types of T cells. T cell differentiation also continues after they have left the thymus. Groups of specific, differentiated T cell subtypes have a variety of important functions in controlling and shaping the immune response. One of these functions is immune-mediated cell death, and it is carried out by two major subtypes: CD8+ "killer" and CD4+ "helper" T cells. (These are named for the presence of the cell surface proteins CD8 or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Platelet
Platelets, also called thrombocytes (from Greek θρόμβος, "clot" and κύτος, "cell"), are a component of blood whose function (along with the coagulation factors) is to react to bleeding from blood vessel injury by clumping, thereby initiating a blood clot. Platelets have no cell nucleus; they are fragments of cytoplasm that are derived from the megakaryocytes of the bone marrow or lung, which then enter the circulation. Platelets are found only in mammals, whereas in other vertebrates (e.g. birds, amphibians), thrombocytes circulate as intact mononuclear cells. One major function of platelets is to contribute to hemostasis: the process of stopping bleeding at the site of interrupted endothelium. They gather at the site and, unless the interruption is physically too large, they plug the hole. First, platelets attach to substances outside the interrupted endothelium: ''adhesion''. Second, they change shape, turn on receptors and secrete chemical messengers: ''activatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Megakaryocyte
A megakaryocyte (''mega-'' + '' karyo-'' + '' -cyte'', "large-nucleus cell") is a large bone marrow cell with a lobated nucleus responsible for the production of blood thrombocytes (platelets), which are necessary for normal blood clotting. In humans, megakaryocytes usually account for 1 out of 10,000 bone marrow cells, but can increase in number nearly 10-fold during the course of certain diseases. Owing to variations in combining forms and spelling, synonyms include megalokaryocyte and megacaryocyte. Structure In general, megakaryocytes are 10 to 15 times larger than a typical red blood cell, averaging 50–100 μm in diameter. During its maturation, the megakaryocyte grows in size and replicates its DNA without cytokinesis in a process called endomitosis. As a result, the nucleus of the megakaryocyte can become very large and lobulated, which, under a light microscope, can give the false impression that there are several nuclei. In some cases, the nucleus may contain up to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Erythrocyte
Red blood cells (RBCs), also referred to as red cells, red blood corpuscles (in humans or other animals not having nucleus in red blood cells), haematids, erythroid cells or erythrocytes (from Greek ''erythros'' for "red" and ''kytos'' for "hollow vessel", with ''-cyte'' translated as "cell" in modern usage), are the most common type of blood cell and the vertebrate's principal means of delivering oxygen (O2) to the body tissues—via blood flow through the circulatory system. RBCs take up oxygen in the lungs, or in fish the gills, and release it into tissues while squeezing through the body's capillaries. The cytoplasm of a red blood cell is rich in hemoglobin, an iron-containing biomolecule that can bind oxygen and is responsible for the red color of the cells and the blood. Each human red blood cell contains approximately 270 million hemoglobin molecules. The cell membrane is composed of proteins and lipids, and this structure provides properties essential for physiologi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |