|
Finnveden
Finnveden or Finnheden is one of the ancient ''small lands'' of Småland. It corresponded to the hundreds of Sunnerbo Hundred, Östbo Hundred and Västbo Hundred. Finnveden had its own judicial system and laws, as did the other ''small lands''. Finnveden is situated around lake Bolmen and the river Lagan River (Sweden), Lagan. Most runestones in Finnveden describe men who died in England. Finnveden is today divided and is a part of the counties of Hallands län, Halland, Kronobergs län, Kronoberg and Jönköpings län, Jönköping. It was first mentioned by Jordanes when he referred to its population as the ''Finnaithae'' (derived from an old form of ''Finnheden'', ''Finn(h)aith-'') when describing the nations of Scandza in ''Getica''. Etymology The Scandinavian languages, Scandinavian placenames Finnveden, Finnmark and the province of Finland (which gave name to Finland) are all thought to be derived from ''finnic peoples, finn'', an ancient Germanic word for nomadic hunter-gat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Finnveden
Finnveden or Finnheden is one of the ancient ''small lands'' of Småland. It corresponded to the hundreds of Sunnerbo Hundred, Östbo Hundred and Västbo Hundred. Finnveden had its own judicial system and laws, as did the other ''small lands''. Finnveden is situated around lake Bolmen and the river Lagan River (Sweden), Lagan. Most runestones in Finnveden describe men who died in England. Finnveden is today divided and is a part of the counties of Hallands län, Halland, Kronobergs län, Kronoberg and Jönköpings län, Jönköping. It was first mentioned by Jordanes when he referred to its population as the ''Finnaithae'' (derived from an old form of ''Finnheden'', ''Finn(h)aith-'') when describing the nations of Scandza in ''Getica''. Etymology The Scandinavian languages, Scandinavian placenames Finnveden, Finnmark and the province of Finland (which gave name to Finland) are all thought to be derived from ''finnic peoples, finn'', an ancient Germanic word for nomadic hunter-gat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Småland
Småland () is a historical province () in southern Sweden. Småland borders Blekinge, Scania, Halland, Västergötland, Östergötland and the island Öland in the Baltic Sea. The name Småland literally means ''Small Lands''. The Latinized form has been used in other languages. The highest point in Småland is Tomtabacken, at 377 metres (1,237 ft). In terms of total area, Småland is of a similar size as Belgium. Administration The traditional provinces of Sweden no longer serve any governmental purpose, but they do remain important historically and culturally. The province of Småland today is divided almost entirely into the three administrative counties of Jönköping, Kalmar, and Kronoberg. Some few small portions of historic Småland are situated in Halland and Östergötland Counties. Heraldry The current coat of arms, granted in 1569, displays a rampant red lion carrying a crossbow, all on a golden background. The arms may be surmounted by a ducal coronet. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fenni
The Fenni were an ancient people of northeastern Europe, first described by Cornelius Tacitus in ''Germania'' in AD 98. Ancient accounts The Fenni are first mentioned by Cornelius Tacitus in ''Germania'' in 98 A.D. Their location is uncertain, due to the vagueness of Tacitus' account: ''"they (Venedi) overrun in their predatory excursions all the woody and mountainous tracts between the Peucini and the Fenni"''.Tacitus G.46 The Greco-Roman geographer Ptolemy, who produced his ''Geographia'' in ca. 150 AD, mentions a people called the ''Phinnoi'' (Φιννοι), generally believed to be synonymous with the Fenni. He locates them in two different areas: a northern group in northern ''Scandia'' (Scandinavia), then believed to be an island; and a southern group, apparently dwelling to the East of the upper Vistula river (SE Poland). It remains unclear what was the relationship between the two groups. The next ancient mention of the Fenni/Finni is in the ''Getica'' of 6th-century ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
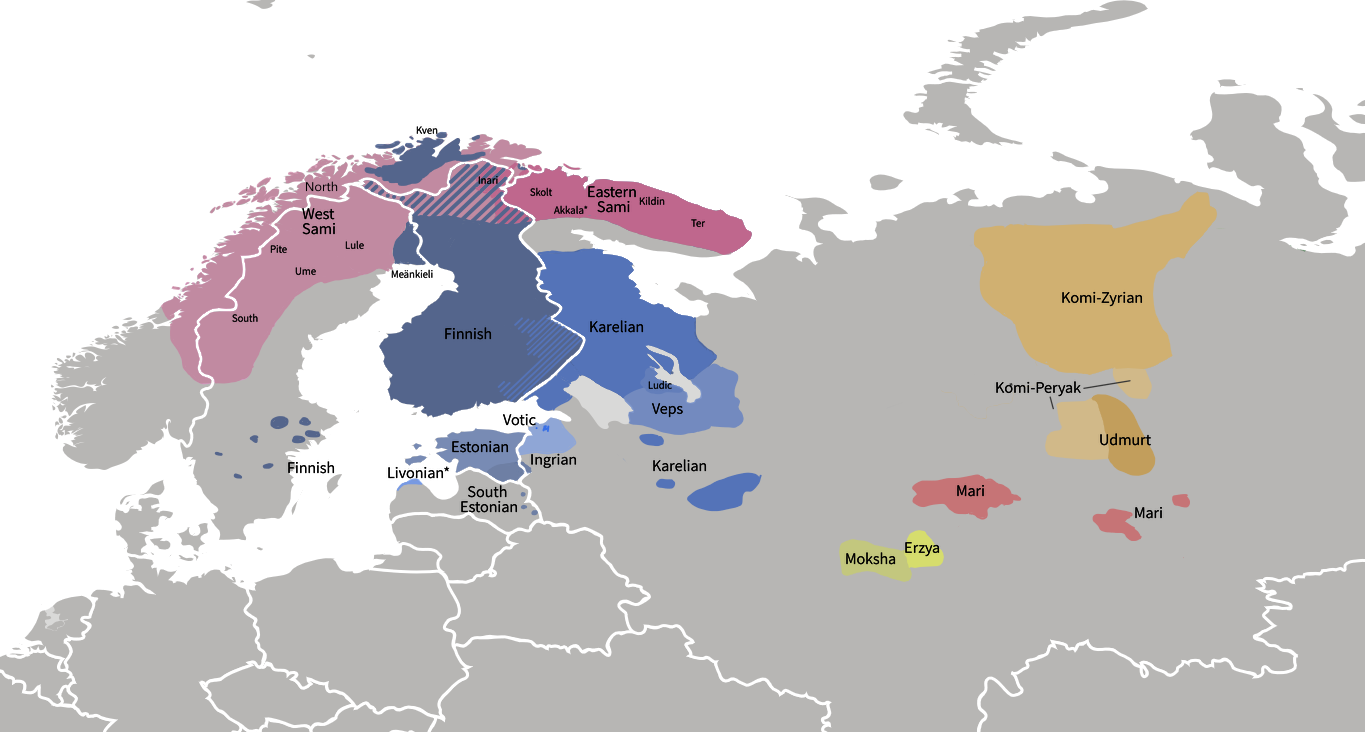
Finnic Peoples
The Finnic or Fennic peoples, sometimes simply called Finns, are the nations who speak languages traditionally classified in the Finnic (now commonly '' Finno-Permic'') language family, and which are thought to have originated in the region of the Volga River. The largest Finnic peoples by population are the Finns (or more precisely the Suomi, 6 million), the Estonians (1 million), the Mordvins (800,000), the Mari (570,000), the Udmurts (550,000), the Komis (330,000) and the Sami (100,000). The scope of the name "Finn" and "Finnic" varies by country. Today, Finnish and Estonian scholars restrict the term "Finnic" to the Baltic Finns, who include the Western Finns of Finland and their closest relatives but not the Sami. In Russia, however, where the Eastern Finns live, the word continues to be used in the broad sense, and sometimes implies the Volga Finns who have their own national republics. Three groups of people are covered by the names "Finn" and "Finnic" in the broad se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scandza
Scandza was described as a "great island" by Gothic-Byzantine historian Jordanes in his work ''Getica''. The island was located in the Arctic regions of the sea that surrounded the world. The location is usually identified with Scandinavia. Jordanes was a Roman citizen living in Constantinople but described himself as being of Gothic descent. His ''Getica'', written in 551 AD, gives a history of the Goths, beginning in Scandza from where they later migrated to Gothiscandza, near the mouth of the Vistula River. The Swedish archaeologist Göran Burenhult describes this account as a unique glimpse into the tribes of Scandinavia in the 6th century. Geographical description through history Early Greek and Roman geographers used the name ''Scandia'' for various uncharted islands in Northern Europe. The name originated in Greek sources, which used it for a long time for different islands in the Mediterranean region. In the Iliad the name denotes an ancient city in Kythira, Greece. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bolmen
Bolmen () is a lake in Småland, Sweden. Covering 184 km², and with a maximum depth of 37 m, it supplies a considerable part of Skåne with fresh water by means of an 82-km long tunnel, the Bolmen Water Tunnel, built during the 1970s and 80s. Bolmen is situated at the heart of Finnveden, one of the ''small lands'' of today's Småland. It is the tenth largest lake in Sweden. It contains 365 islands, of which the largest is Bolmsö, which was historically the meeting-place of the local assembly Assembly may refer to: Organisations and meetings * Deliberative assembly, a gathering of members who use parliamentary procedure for making decisions * General assembly, an official meeting of the members of an organization or of their representa .... References Småland Lakes of Kronoberg County {{Kronoberg-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Placename
Toponymy, toponymics, or toponomastics is the study of ''toponyms'' (proper names of places, also known as place names and geographic names), including their origins, meanings, usage and types. Toponym is the general term for a proper name of any geographical feature, and full scope of the term also includes proper names of all cosmographical features. In a more specific sense, the term ''toponymy'' refers to an inventory of toponyms, while the discipline researching such names is referred to as ''toponymics'' or ''toponomastics''. Toponymy is a branch of onomastics, the study of proper names of all kinds. A person who studies toponymy is called ''toponymist''. Etymology The term toponymy come from grc, τόπος / , 'place', and / , 'name'. The ''Oxford English Dictionary'' records ''toponymy'' (meaning "place name") first appearing in English in 1876. Since then, ''toponym'' has come to replace the term ''place-name'' in professional discourse among geographers. Toponym ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sunnerbo Hundred
A hundred is a geographic division formerly used in northern Germanic countries and related colonies, which historically was used to divide a larger region into smaller administrative divisions. The equivalent term in Swedish is (in Uppland also known as during the early Middle Ages); in Danish and Norwegian, ; in Finnish, ; and in Estonian, . The Scanian hundreds were Danish until the Treaty of Roskilde The Treaty of Roskilde (concluded on 26 February ( OS), or 8 March 1658) ( NS) during the Second Northern War between Frederick III of Denmark–Norway and Karl X Gustav of Sweden in the Danish city of Roskilde. After a devastating defeat, ... of 1658. List {{DEFAULTSORT:Hundreds Of Sweden, List Of Subdivisions of Sweden Hundreds of Sweden Hundreds ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
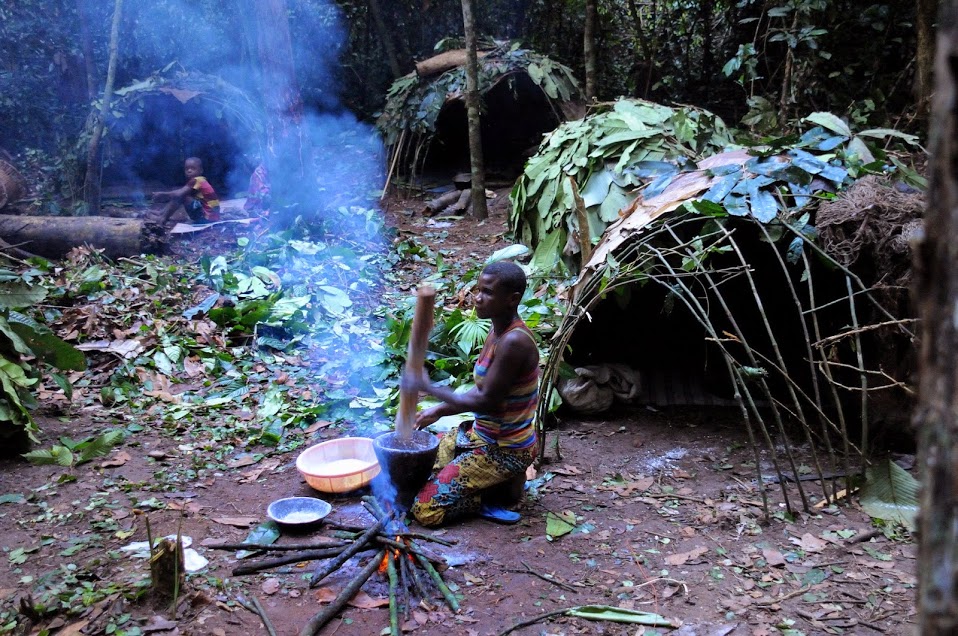
Hunter-gatherer
A traditional hunter-gatherer or forager is a human living an ancestrally derived lifestyle in which most or all food is obtained by foraging, that is, by gathering food from local sources, especially edible wild plants but also insects, fungi, honey, or anything safe to eat, and/or by hunting game (pursuing and/or trapping and killing wild animals, including catching fish), roughly as most animal omnivores do. Hunter-gatherer societies stand in contrast to the more sedentary agricultural societies, which rely mainly on cultivating crops and raising domesticated animals for food production, although the boundaries between the two ways of living are not completely distinct. Hunting and gathering was humanity's original and most enduring successful competitive adaptation in the natural world, occupying at least 90 percent of human history. Following the invention of agriculture, hunter-gatherers who did not change were displaced or conquered by farming or pastoralist groups in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nomadic
A nomad is a member of a community without fixed habitation who regularly moves to and from the same areas. Such groups include hunter-gatherers, pastoral nomads (owning livestock), tinkers and trader nomads. In the twentieth century, the population of nomadic pastoral tribes slowly decreased, reaching an estimated 30–40 million nomads in the world . Nomadic hunting and gathering—following seasonally available wild plants and game—is by far the oldest human subsistence method. Pastoralists raise herds of domesticated livestock, driving or accompanying them in patterns that normally avoid depleting pastures beyond their ability to recover. Nomadism is also a lifestyle adapted to infertile regions such as steppe, tundra, or ice and sand, where mobility is the most efficient strategy for exploiting scarce resources. For example, many groups living in the tundra are reindeer herders and are semi-nomadic, following forage for their animals. Sometimes also described as "nomad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Östbo Hundred
A hundred is a geographic division formerly used in northern Germanic countries and related colonies, which historically was used to divide a larger region into smaller administrative divisions. The equivalent term in Swedish is (in Uppland also known as during the early Middle Ages); in Danish and Norwegian, ; in Finnish, ; and in Estonian, . The Scanian hundreds were Danish until the Treaty of Roskilde The Treaty of Roskilde (concluded on 26 February ( OS), or 8 March 1658) ( NS) during the Second Northern War between Frederick III of Denmark–Norway and Karl X Gustav of Sweden in the Danish city of Roskilde. After a devastating defeat, ... of 1658. List {{DEFAULTSORT:Hundreds Of Sweden, List Of Subdivisions of Sweden Hundreds of Sweden Hundreds ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Finland
Finland ( fi, Suomi ; sv, Finland ), officially the Republic of Finland (; ), is a Nordic country in Northern Europe. It shares land borders with Sweden to the northwest, Norway to the north, and Russia to the east, with the Gulf of Bothnia to the west and the Gulf of Finland across Estonia to the south. Finland covers an area of with a population of 5.6 million. Helsinki is the capital and largest city, forming a larger metropolitan area with the neighbouring cities of Espoo, Kauniainen, and Vantaa. The vast majority of the population are ethnic Finns. Finnish, alongside Swedish, are the official languages. Swedish is the native language of 5.2% of the population. Finland's climate varies from humid continental in the south to the boreal in the north. The land cover is primarily a boreal forest biome, with more than 180,000 recorded lakes. Finland was first inhabited around 9000 BC after the Last Glacial Period. The Stone Age introduced several differ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |