|
Dinocaridida
DinocarididaGreek, "Terrible crabs" – sometimes informally spelt Dinocarida, but the second 'id' is linguistically correct – see is a proposed fossil taxon of basal arthropods that flourished in the Cambrian period with occasional OrdovicianVan Roy, P.; Briggs, D. E. G. (2011). "A giant Ordovician anomalocaridid". Nature 473 (7348): 510–513. doi:10.1038/nature09920. edit and Devonian records. Characterized by a pair of frontal appendages and series of body flaps, the name of Dinocaridids comes from Greek language, Greek, "deinos" and "caris" ("terrible crab"), referring to the suggested role of some of these members as the largest Marine life, marine Predation, predators of their time. Dinocaridids are occasionally referred to as the 'AOPK group' by some literatures, as the group compose of Radiodonta (''Anomalocaris'' and relatives), Opabiniidae (''Opabinia'' and relatives), ''Pambdelurion'' and ''Kerygmachela.'' It is most likely paraphyletic, with ''Kerygmachela'' and ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
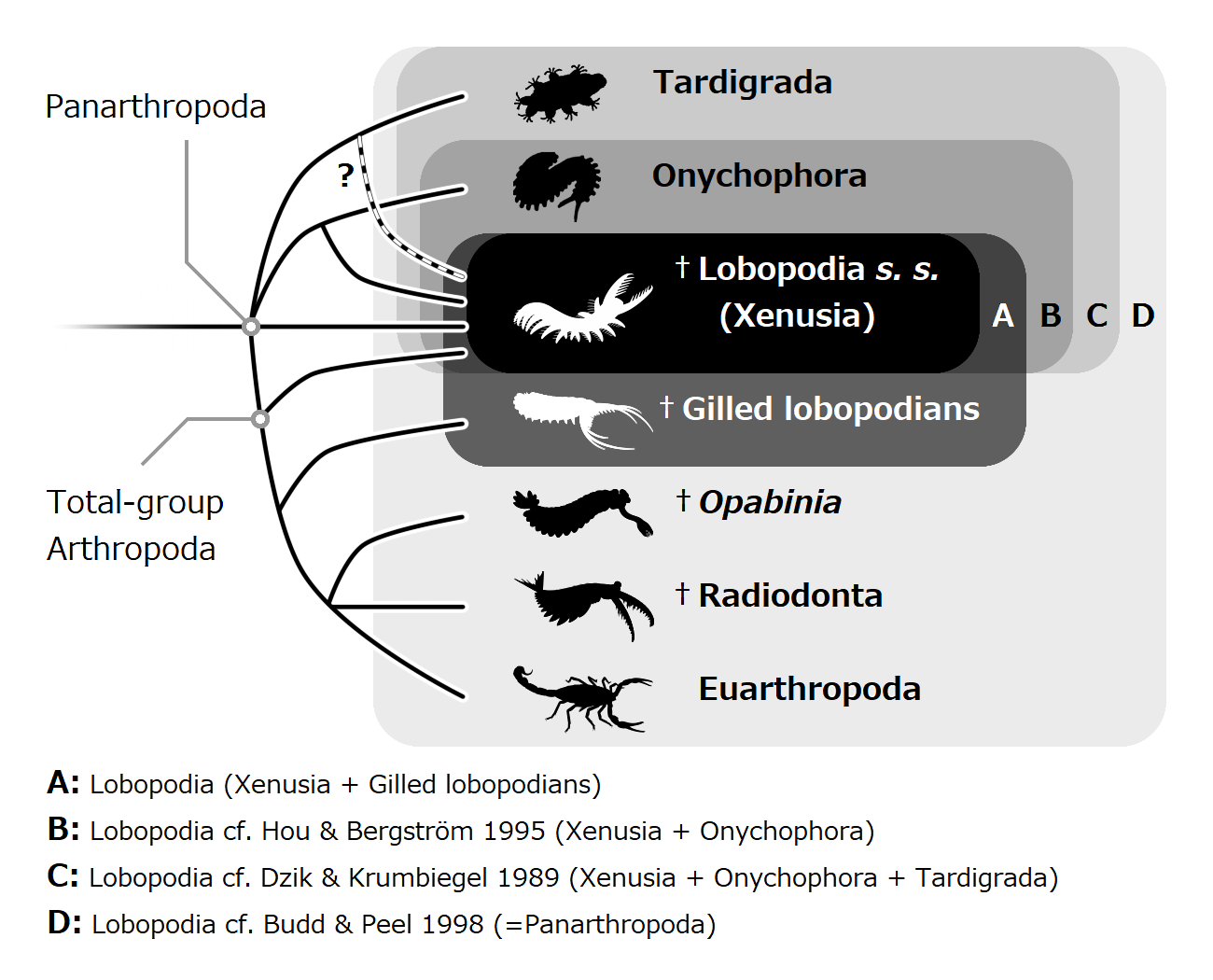
Lobopodia
The lobopodians, members of the informal group Lobopodia (from the Greek language, Greek, meaning "blunt feet"), or the formally erected phylum Lobopoda Cavalier-Smith (1998), are panarthropods with stubby legs called lobopods, a term which may also be used as a common name of this group as well. While the definition of lobopodians may differ between literatures, it usually refers to a group of soft-bodied, worm-like fossil panarthropods such as ''Aysheaia'' and ''Hallucigenia''. The oldest near-complete fossil lobopodians date to the Lower Cambrian; some are also known from Ordovician, Silurian and Carboniferous Lagerstätten. Some bear toughened claws, plates or spines, which are commonly preserved as small carbonaceous fossil, carbonaceous or Small Shelly Fossils, mineralized microfossils in Cambrian strata. The grouping is considered to be paraphyletic, as the three living panarthropod groups (Arthropoda, Tardigrada and Onychophora) are thought to have evolved from lobopodian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anomalocaris
''Anomalocaris'' ("unlike other shrimp", or "abnormal shrimp") is an extinct genus of Radiodonta, radiodont, an Order (biology), order of early-diverging stem-group arthropods. The first fossils of ''Anomalocaris'' were discovered in the ''Ogygopsis'' Shale of the Stephen Formation in British Columbia, Canada by Joseph Frederick Whiteaves, with more examples found by Charles Doolittle Walcott in the Burgess Shale unit of the Stephen Formation. Other closely related fossils have been found in the older Emu Bay Shale of Australia, as well as possibly elsewhere. Originally several fossilized parts discovered separately (the mouth, frontal appendages and trunk) were thought to be three separate creatures, a misapprehension corrected by Harry B. Whittington and Derek Briggs in a 1985 journal article. With a body length close to 40 centimetres, ''A. canadensis'' is thought to be one of the earliest examples of an apex predator, though others have been found in older Cambrian lagerstätte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bilateral Symmetry
Symmetry in biology refers to the symmetry observed in organisms, including plants, animals, fungi, and bacteria. External symmetry can be easily seen by just looking at an organism. For example, take the face of a human being which has a plane of symmetry down its centre, or a pine cone with a clear symmetrical spiral pattern. Internal features can also show symmetry, for example the tubes in the human body (responsible for transporting gases, nutrients, and waste products) which are cylindrical and have several planes of symmetry. Biological symmetry can be thought of as a balanced distribution of duplicate body parts or shapes within the body of an organism. Importantly, unlike in mathematics, symmetry in biology is always approximate. For example, plant leaves – while considered symmetrical – rarely match up exactly when folded in half. Symmetry is one class of patterns in nature whereby there is near-repetition of the pattern element, either by reflection or rotation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ganglion
A ganglion is a group of neuron cell bodies in the peripheral nervous system. In the somatic nervous system this includes dorsal root ganglia and trigeminal ganglia among a few others. In the autonomic nervous system there are both sympathetic and parasympathetic ganglia which contain the cell bodies of postganglionic sympathetic and parasympathetic neurons respectively. A pseudoganglion looks like a ganglion, but only has nerve fibers and has no nerve cell bodies. Structure Ganglia are primarily made up of somata and dendritic structures which are bundled or connected. Ganglia often interconnect with other ganglia to form a complex system of ganglia known as a plexus. Ganglia provide relay points and intermediary connections between different neurological structures in the body, such as the peripheral and central nervous systems. Among vertebrates there are three major groups of ganglia: *Dorsal root ganglia (also known as the spinal ganglia) contain the cell bodies of se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brain
A brain is an organ that serves as the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate and most invertebrate animals. It is located in the head, usually close to the sensory organs for senses such as vision. It is the most complex organ in a vertebrate's body. In a human, the cerebral cortex contains approximately 14–16 billion neurons, and the estimated number of neurons in the cerebellum is 55–70 billion. Each neuron is connected by synapses to several thousand other neurons. These neurons typically communicate with one another by means of long fibers called axons, which carry trains of signal pulses called action potentials to distant parts of the brain or body targeting specific recipient cells. Physiologically, brains exert centralized control over a body's other organs. They act on the rest of the body both by generating patterns of muscle activity and by driving the secretion of chemicals called hormones. This centralized control allows rapid and coordinated respon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cuttlefish
Cuttlefish or cuttles are marine molluscs of the order Sepiida. They belong to the class Cephalopoda which also includes squid, octopuses, and nautiluses. Cuttlefish have a unique internal shell, the cuttlebone, which is used for control of buoyancy. Cuttlefish have large, W-shaped pupils, eight arms, and two tentacles furnished with denticulated suckers, with which they secure their prey. They generally range in size from , with the largest species, the giant cuttlefish (''Sepia apama''), reaching in mantle length and over in mass. Cuttlefish eat small molluscs, crabs, shrimp, fish, octopus, worms, and other cuttlefish. Their predators include dolphins, sharks, fish, seals, seabirds, and other cuttlefish. The typical life expectancy of a cuttlefish is about 1–2 years. Studies are said to indicate cuttlefish to be among the most intelligent invertebrates. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chelicerae
The chelicerae () are the mouthparts of the subphylum Chelicerata, an arthropod group that includes arachnids, horseshoe crabs, and sea spiders. Commonly referred to as "jaws", chelicerae may be shaped as either articulated fangs, or similarly to pincers. Some chelicerae, such as those found on nearly all spiders, are hollow and contain (or are connected to) venom glands, and are used to inject venom into prey or a perceived threat. In ''Pisaurina mira'', also known as the nursery web spider, the chelicerae are utilized to snatch the prey once it becomes within reach, facilitating the "sit-and-wait ambush predator" behavior. Both pseudoscorpions and harvestmen have structures on their chelicerae that are used for grooming (papillae in pseudoscorpions, cheliceral teeth in Opiliones). Types Chelicerae can be divided into three kinds: jackknife chelicerae, scissor chelicerae, and 3-segmented chelate chelicerae. Jackknife chelicerae The jackknife chelicera is subchelate (with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antenna (anatomy)
Antennae ( antenna), sometimes referred to as "feelers", are paired appendages used for sensing in arthropods. Antennae are connected to the first one or two segments of the arthropod head. They vary widely in form but are always made of one or more jointed segments. While they are typically sensory organs, the exact nature of what they sense and how they sense it is not the same in all groups. Functions may variously include sensing touch, air motion, heat, vibration (sound), and especially smell or taste. Antennae are sometimes modified for other purposes, such as mating, brooding, swimming, and even anchoring the arthropod to a substrate. Larval arthropods have antennae that differ from those of the adult. Many crustaceans, for example, have free-swimming larvae that use their antennae for swimming. Antennae can also locate other group members if the insect lives in a group, like the ant. The common ancestor of all arthropods likely had one pair of uniramous (unbranched) a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Appendage
Great appendages are claw-like appendages which attach to the heads of the "great appendage arthropods", a name usually refers to Megacheira, a class of extinct arthropod characterized by a pair of "short-great appendages" bearing in front of the animal's head. In general, megacheiran's great appendage have 6 segments, with the two proximal segments forming a peduncle and the four finger-like distal segments forming a claw, both connected by an elbow joint. Great appendages have been interpreted as raptorial limbs involved in predation, with those of some genera such as ''Yohoia'' being structurally comparable to the raptorial maxillipeds of mantis shrimp. The great appendages of leanchoilid megacheirans such as ''Leanchoilia'' and ''Yawunik'' have elongated flagella, suggesting a sensory role alongside predatory function. Radiodonta, Radiodont's frontal appendages have controversial relationships to those of the megacheirans. They have been suggested to be Homology (biology), ho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Onychophoran
Onychophora (from grc, ονυχής, , "claws"; and , , "to carry"), commonly known as velvet worms (due to their velvety texture and somewhat wormlike appearance) or more ambiguously as peripatus (after the first described genus, '' Peripatus''), is a phylum of elongate, soft-bodied, many-legged panarthropods. In appearance they have variously been compared to worms with legs, caterpillars, and slugs. They prey upon other invertebrates, which they catch by ejecting an adhesive slime. Approximately 200 species of velvet worms have been described, although the true number of species is likely greater. The two extant families of velvet worms are Peripatidae and Peripatopsidae. They show a peculiar distribution, with the peripatids being predominantly equatorial and tropical, while the peripatopsids are all found south of the equator. It is the only phylum within Animalia that is wholly endemic to terrestrial environments, at least among extant members. Velvet worms are generally ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antenna (biology)
Antennae ( antenna), sometimes referred to as "feelers", are paired appendages used for sensing in arthropods. Antennae are connected to the first one or two segments of the arthropod head. They vary widely in form but are always made of one or more jointed segments. While they are typically sensory organs, the exact nature of what they sense and how they sense it is not the same in all groups. Functions may variously include sensing touch, air motion, heat, vibration (sound), and especially smell or taste. Antennae are sometimes modified for other purposes, such as mating, brooding, swimming, and even anchoring the arthropod to a substrate. Larval arthropods have antennae that differ from those of the adult. Many crustaceans, for example, have free-swimming larvae that use their antennae for swimming. Antennae can also locate other group members if the insect lives in a group, like the ant. The common ancestor of all arthropods likely had one pair of uniramous (unbranched ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Euarthropod
Arthropods (, (gen. ποδός)) are invertebrate animals with an exoskeleton, a segmented body, and paired jointed appendages. Arthropods form the phylum Arthropoda. They are distinguished by their jointed limbs and cuticle made of chitin, often mineralised with calcium carbonate. The arthropod body plan consists of segments, each with a pair of appendages. Arthropods are bilaterally symmetrical and their body possesses an external skeleton. In order to keep growing, they must go through stages of moulting, a process by which they shed their exoskeleton to reveal a new one. Some species have wings. They are an extremely diverse group, with up to 10 million species. The haemocoel, an arthropod's internal cavity, through which its haemolymph – analogue of blood – circulates, accommodates its interior organs; it has an open circulatory system. Like their exteriors, the internal organs of arthropods are generally built of repeated segments. Their nervous system is "ladder-lik ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)



