|
Den (pharaoh)
Den, also known as Hor-Den, Dewen, and Udimu, was the Horus name of a pharaoh of the Early Dynastic Period who ruled during the First Dynasty of Egypt. He is the best archaeologically-attested ruler of this period, credited with bringing prosperity to his realm. Den was attributed the title "King of Upper and Lower Egypt" and wore the double crown (red and white). Notably, the floor of his tomb at Umm El Qa'ab, near Abydos, was constructed using red and black granite, making it the earliest known use of this hard stone as a building material in Egypt with a flight of stairs leading to it. During his long reign, he established many of the customs of court ritual and royalty drawn on by later rulers and was held in high regard by his immediate successors. Length of reign The Ancient Egyptian historian Manetho called him “Oúsaphaîdos” and credited him with a reign of 20 years, William Gillan Waddell: ''Manetho (The Loeb Classical Library, Volume 350)''. Harvard Univers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MacGregor Plaque
The MacGregor Plaque (or MacGregor Tablet, also King Den's sandal label) is an artefact that was probably found in the tomb of King Den at Abydos, and dated circa 2985 BCE. According to its inscriptions, the plaque was originally attached to the king's sandal. The plaque is displayed in the British Museum. It is, with the depictions of Narmer, among the oldest images of a ruler. Origin and description The MacGregor Plaque is a tablet is made of carved ivory that measures 4.5 cm x 5.4 cm; it is about 0.2 cm thick. Images are engraved and fired into it. The artefact was probably found in the mastaba tomb of the ancient Egyptian king Den ( First Dynasty), and dated circa 2985 BCE. It derives from the excavations of French archaeologist, Coptologist, and Egyptologist Émile Amélineau. The artefact is also known as ''MacGregor Tablet'', also ''King Den's sandal label''. The plaque was acquired by the British Museum in 1922; before that it, was part of the MacGre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
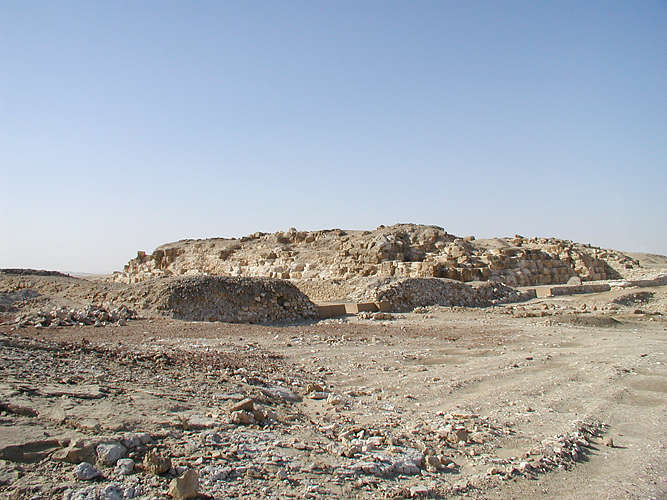
Abydos, Egypt
Abydos ( or ; Sahidic ') is one of the oldest cities of ancient Egypt, and also of the Ta-wer, eighth Nome (Egypt), nome in Upper Egypt. It is located about west of the Nile at latitude 26° 10' N, near the modern Egyptian towns of El Araba El Madfuna and El Balyana. In the ancient Egyptian language, the city was called Abedju (''ꜣbḏw'' or ''AbDw'')(Arabic Abdu عبد-و). The English name ''Abydos'' comes from the Greek language, Greek , a name borrowed by Greek geographers from the unrelated city of Abydos, Hellespont, Abydos on the Hellespont. Considered one of the most important archaeological sites in Egypt, the sacred city of Abydos was the site of many ancient Egyptian temple, temples, including Umm el-Qa'ab, a royal necropolis where early pharaohs were entombed. These tombs began to be seen as extremely significant burials and in later times it became desirable to be buried in the area, leading to the growth of the town's importance as a cult site. Today, Abydos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schist
Schist ( ) is a medium-grained metamorphic rock generally derived from fine-grained sedimentary rock, like shale. It shows pronounced ''schistosity'' (named for the rock). This means that the rock is composed of mineral grains easily seen with a low-power hand lens, oriented in such a way that the rock is easily split into thin flakes or plates. This texture (geology), texture reflects a high content of platy minerals, such as mica, talc, chlorite group, chlorite, or graphite. These are often interleaved with more granular minerals, such as feldspar or quartz. Schist typically forms during regional metamorphism accompanying the process of mountain building (orogeny) and usually reflects a medium Metamorphism#Metamorphic grades, grade of metamorphism. Schist can form from many different kinds of rocks, including sedimentary rocks such as mudstones and igneous rocks such as tuffs. Schist metamorphosed from mudstone is particularly common and is often very rich in mica (a ''mica schis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serekh
In Egyptian hieroglyphs, a serekh is a rectangular enclosure representing the niched or gated façade of a palace surmounted by (usually) the Horus falcon, indicating that the text enclosed is a royal name. The serekh was the earliest convention used to set apart the royal name in ancient Egyptian iconography, predating the later and better known cartouche by four dynasties and five to seven hundred years. Appearance A serekh was an ornamental vignette combining a view of a palace façade and a plan (top view) of the royal courtyard. The term ''serekh'' derives from the Egyptian word for "façade". Different serekhs on different types of object display countless variations of the façade decor in its complexity and detail. It seems that no strict artistic rules for the design of the serekh itself existed.Jürgen von Beckerath: ''Handbuch der ägyptischen Königsnamen''. Münchner Ägyptologische Studien. Bd. 49. Philipp von Zabern, Mainz 1999, , p. 7-9.Rolf Gundlach: ''Horus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abydos KL 01-05 N05
Abydos may refer to: *Abydos, a progressive metal side project of German singer Andy Kuntz *Abydos (Hellespont), an ancient city in Mysia, Asia Minor * Abydos (''Stargate''), name of a fictional planet in the ''Stargate'' science fiction universe *Abydos, Egypt Abydos ( or ; Sahidic ') is one of the oldest cities of ancient Egypt, and also of the Ta-wer, eighth Nome (Egypt), nome in Upper Egypt. It is located about west of the Nile at latitude 26° 10' N, near the modern Egyptian towns of El Araba ..., a city in ancient Egypt * Abydos Station, a pastoral lease and cattle station in Western Australia See also * Abidu, a village in Iran * Abidos, Pyrénées-Atlantiques, in southwestern France {{disambiguation, geo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abu Rawash
Abu Rawash (also spelled ''Abu Roach'', Abu Roash; , , , "flesh of sensual pleasures"), north of Giza, is the site of Egypt's most northerly pyramid, also known as the lost pyramid – the mostly ruined Pyramid of Djedefre, the son and successor of Khufu. Originally, it was thought that this pyramid had never been completed, but the current archaeological consensus is that not only was it completed, but that it was built about the same size as the Pyramid of Menkaure – the third largest of the Giza pyramids. It's believed that the destruction of the pyramid started at the end of the New Kingdom of Egypt, New Kingdom at the latest, and was particularly intense during the Roman and early Christian eras when Wadi El Natrun#Invasion of Scetis, a Coptic monastery was built in nearby Wadi El Natrun, Wadi Karin. It has been proven, moreover, that at the end of the nineteenth century, stone was still being hauled away at the rate of three hundred camel loads a day. I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palermo Stone
The Palermo Stone is one of seven surviving fragments of a stele known as the Royal Annals of the Old Kingdom of Ancient Egypt. The stele contained a list of the kings of Egypt from the First Dynasty (c.3150–2890 BCE) through to the early part of the Fifth Dynasty (c.2498–2345 BCE) and noted significant events in each year of their reigns. It was probably made during the Fifth Dynasty.Dodson, Aidan (2004) ''The Complete Royal Families of Ancient Egypt'', p.62. Thames & Hudson, . The Palermo Stone is held in the Regional Archeological Museum Antonio Salinas in the city of Palermo, Italy, from which it derives its name. The Palermo Stone and other fragments of the Royal Annals preserve what is probably the oldest historical text that has survived from Ancient Egypt and form a key source for Egyptian history in the Old Kingdom.Hsu, Hsu, Shih-Wei (2010) ''The Palermo Stone: the Earliest Royal Inscription from Ancient Egypt'', Altoriental. Forsch., Akademie Verlag, 37 (2010) 1, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epigraphy
Epigraphy () is the study of inscriptions, or epigraphs, as writing; it is the science of identifying graphemes, clarifying their meanings, classifying their uses according to dates and cultural contexts, and drawing conclusions about the writing and the writers. Specifically excluded from epigraphy are the historical significance of an epigraph as a document and the artistic value of a literature, literary composition. A person using the methods of epigraphy is called an ''epigrapher'' or ''epigraphist''. For example, the Behistun inscription is an official document of the Achaemenid Empire engraved on native rock at a location in Iran. Epigraphists are responsible for reconstructing, translating, and dating the trilingual inscription and finding any relevant circumstances. It is the work of historians, however, to determine and interpret the events recorded by the inscription as document. Often, epigraphy and history are competences practised by the same person. Epigraphy is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Egyptologist
Egyptology (from ''Egypt'' and Greek , ''-logia''; ) is the scientific study of ancient Egypt. The topics studied include ancient Egyptian history, language, literature, religion, architecture and art from the 5th millennium BC until the end of its native religious practices in the 4th century AD. History First explorers The earliest explorers of ancient Egypt were the ancient Egyptians themselves. Inspired by a dream he had, Thutmose IV led an excavation of the Great Sphinx of Giza and inscribed a description of the dream on the Dream Stele. Less than two centuries later, Prince Khaemweset, fourth son of Ramesses II, would gain fame for identifying and restoring historic buildings, tombs and temples, including pyramids; and has subsequently been described as the first Egyptologist. Classical Antiquity Some of the first historical accounts of Egypt were given by Herodotus, Strabo, Diodorus Siculus and the largely lost work of Manetho, an Egyptian priest, during the reign ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alan Gardiner
Sir Alan Henderson Gardiner, (29 March 1879 – 19 December 1963) was an English Egyptologist, linguist, philologist, and independent scholar. He is regarded as one of the premier Egyptologists of the early and mid-20th century. Personal life Gardiner was born on 29 March 1879 in Eltham, which was then in the English county of Kent. His father was Henry John Gardiner, a highly successful entrepreneur and businessman who made a considerable fortune in the drapery and wholesale linen trade in Bristol and London.{{cite book , last=Lloyd , first=Stephen , title= H. Balfour Gardiner , publisher=Cambridge University Press , date=2005 , isbn=9780521619226 , pages=2–3 , url=https://books.google.com/books?id=NHdVK2-3ITkC His mother, Clara Elizabeth ''née'' Honey, died in his infancy and he and his elder brother, the composer H. Balfour Gardiner, were brought up by their father's housekeeper. Gardiner was educated at Temple Grove School and Charterhouse. At school ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Gillan Waddell
William Gillan Waddell (21 April 1884 – 25 January 1945) was a Scottish Professor of Classics at what is now Cairo University. Life Waddell was born in Neilston, Scotland. In 1906 he obtained his M.A. from the University of Glasgow. He was Professor of Classics at Fuad el Awal University in Cairo, Egypt (in 1940). Waddell was a translator of ancient Greek and Latin Latin ( or ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally spoken by the Latins (Italic tribe), Latins in Latium (now known as Lazio), the lower Tiber area aroun ... into English. Selected works * * * * References {{DEFAULTSORT:Waddell, William Gillan 1884 births 1945 deaths Academic staff of Cairo University Scottish translators 20th-century British translators British expatriates in Egypt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manetho
Manetho (; ''Manéthōn'', ''gen''.: Μανέθωνος, ''fl''. 290–260 BCE) was an Egyptian priest of the Ptolemaic Kingdom who lived in the early third century BCE, at the very beginning of the Hellenistic period. Little is certain about his life. He is known today as the author of a history of Egypt in Greek called the '' Aegyptiaca'' (''History of Egypt''), written during the reign of Ptolemy I Soter or Ptolemy II Philadelphus (285–246 BCE). None of Manetho’s original texts have survived; they are lost literary works, known only from fragments transmitted by later authors of classical and late antiquity. The remaining fragments of the ''Aegyptiaca'' continue to be a singular resource for delineating Egyptian chronology, more than two millennia since its composition. Until the decipherment of Ancient Egyptian scripts in the early 19th century CE, Manetho's fragments were an essential source for understanding Egyptian history. His work remains of unique importan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |