|
Decision-making Software
Decision-making software (DM software) is software for computer applications that help individuals and organisations make choices and take decisions, typically by ranking, prioritizing or choosing from a number of options. An early example of DM software was described in 1973.Dyer, JS (1973), "A time-sharing computer program for the solution of the multiple criteria problem", ''Management Science'', 19: 1379-83.Wallenius, J, Dyer, JS, Fishburn, PC, Steuer, RE, Zionts, S and Deb, K (1992), "Multiple criteria decision making, multiattribute utility theory: The next ten years", ''Management Science'', 38: 645-54. Before the advent of the World Wide Web, most DM software was spreadsheet-based, with the first web-based DM software appearing in the mid-1990s.Koksalan, M, Wallenius, J, and Zionts, S, ''Multiple Criteria Decision Making: From Early History to the 21st Century'', World Scientific Publishing: Singapore, 2011. Nowadays, many DM software products (mostly web-based) are availabl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Software
Software consists of computer programs that instruct the Execution (computing), execution of a computer. Software also includes design documents and specifications. The history of software is closely tied to the development of digital computers in the mid-20th century. Early programs were written in the machine language specific to the hardware. The introduction of high-level programming languages in 1958 allowed for more human-readable instructions, making software development easier and more portable across different computer architectures. Software in a programming language is run through a compiler or Interpreter (computing), interpreter to execution (computing), execute on the architecture's hardware. Over time, software has become complex, owing to developments in Computer network, networking, operating systems, and databases. Software can generally be categorized into two main types: # operating systems, which manage hardware resources and provide services for applicat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pairwise Comparisons
Pairwise comparison generally is any process of comparing entities in pairs to judge which of each entity is preferred, or has a greater amount of some quantitative property, or whether or not the two entities are identical. The method of pairwise comparison is used in the scientific study of preferences, attitudes, voting systems, social choice, public choice, requirements engineering and multiagent AI systems. In psychology literature, it is often referred to as paired comparison. Prominent psychometrician L. L. Thurstone first introduced a scientific approach to using pairwise comparisons for measurement in 1927, which he referred to as the law of comparative judgment. Thurstone linked this approach to psychophysical theory developed by Ernst Heinrich Weber and Gustav Fechner. Thurstone demonstrated that the method can be used to order items along a dimension such as preference or importance using an interval-type scale. Mathematician Ernst Zermelo (1929) first descr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Criterium DecisionPlus
Criterium DecisionPlus is decision-making software that is based on multi-criteria decision making. The software implements the Analytic Hierarchy Process In the theory of decision making, the analytic hierarchy process (AHP), also analytical hierarchy process, is a structured technique for organizing and analyzing MCDA, complex decisions, based on mathematics and psychology. It was developed by ... (AHP) and the Simple Multi-Attribute Rating Technique (SMART) and has been used in fields such as materials science and environmental management. Criterium DecisionPlus is supplied by InfoHarvest Inc. References Decision-making software {{business-software-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Analytica (software)
Analytica is a visual software developed by Lumina Decision Systems for creating, analyzing and communicating quantitative decision models. It combines hierarchical influence diagrams for visual creation and view of models, intelligent arrays for working with multidimensional data, Monte Carlo simulation for analyzing risk and uncertainty, and optimization, including linear and nonlinear programming. Its design is based on ideas from the field of decision analysis. As a computer language, it combines a declarative (non-procedural) structure for referential transparency, array abstraction, and automatic dependency maintenance for efficient sequencing of computation. Hierarchical influence diagrams Analytica models are organized as influence diagrams. Variables (and other objects) appear as nodes of various shapes on a diagram, connected by arrows that provide a visual representation of dependencies. Analytica influence diagrams may be hierarchical, in which a single ''module'' n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MetaTeam
Altova is a commercial software development company with headquarters in Beverly, MA, United States and Vienna, Austria, that produces integrated XML, JSON, database, UML, and data management software development tools. Company Altova was founded in 1992 as an XML development software company. Its software is used by more than 4 million users and more than 100,000 companies globally. The first product was XMLSpy, and around the year 2000, Altova began to develop new tools to augment XMLSpy and expand into new areas of software development. The CEO and president of Altova is Alexander Falk, who has explained that the development of Altova software has occurred through the inclusion of features most requested by the users of previous program incarnations. Falk is also the inventor behind Altova's patents. Altova software attempts to increase the efficiency of program use in order to reduce the amount of time needed for users to learn database software and other tasks such as que ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Utility
In economics, utility is a measure of a certain person's satisfaction from a certain state of the world. Over time, the term has been used with at least two meanings. * In a normative context, utility refers to a goal or objective that we wish to maximize, i.e., an objective function. This kind of utility bears a closer resemblance to the original utilitarian concept, developed by moral philosophers such as Jeremy Bentham and John Stuart Mill. * In a descriptive context, the term refers to an ''apparent'' objective function; such a function is revealed by a person's behavior, and specifically by their preferences over lotteries, which can be any quantified choice. The relationship between these two kinds of utility functions has been a source of controversy among both economists and ethicists, with most maintaining that the two are distinct but generally related. Utility function Consider a set of alternatives among which a person has a preference ordering. A utility fu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Weighted Sum Model
In decision theory, the weighted sum model (WSM), also called weighted linear combination (WLC) or simple additive weighting (SAW), is the best known and simplest multi-criteria decision analysis (MCDA) / multi-criteria decision making method for evaluating a number of alternatives in terms of a number of decision criteria. Description In general, suppose that a given MCDA problem is defined on ''m'' alternatives and ''n'' decision criteria. Furthermore, let us assume that all the criteria are benefit criteria, that is, the higher the values are, the better it is. Next suppose that ''wj'' denotes the relative weight of importance of the criterion ''Cj'' and ''aij'' is the performance value of alternative ''Ai'' when it is evaluated in terms of criterion ''Cj''. Then, the total (i.e., when all the criteria are considered simultaneously) importance of alternative ''Ai'', denoted as ''A''''i''WSM-score, is defined as follows: ::A^\text_i = \sum_^n w_j a_,\texti = 1, 2, 3, \dots , m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
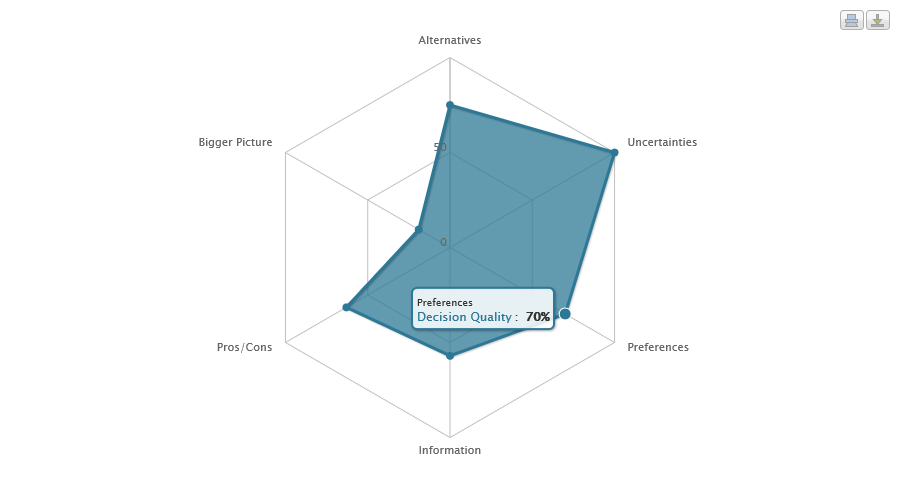
Ahoona
Ahoona is a free online social network that is focused on crowd-sourcing six elements of decision quality to help people make better decisions in their daily lives. The project started through a National Science Foundation initiative known as I-Corps. It has resulted in numerous media publications, TEDx talks, TV coverage, and distribution lists of professional decision making societies. This web-based decision making project first crowd-sources the inputs to a decision and then makes a decision recommendation. The crowd-sourced elements include the bigger picture, the alternatives, the preferences, the uncertainties, the information and the pros and cons. A decision recommendation is made after the elements of decision quality are crowd-sourced using decision tree analysis, pros cons analysis or weight and rate analysis. Motivation While the field of decision analysis has advanced significantly in the last few decades, it has not penetrated the daily lives of the general public ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
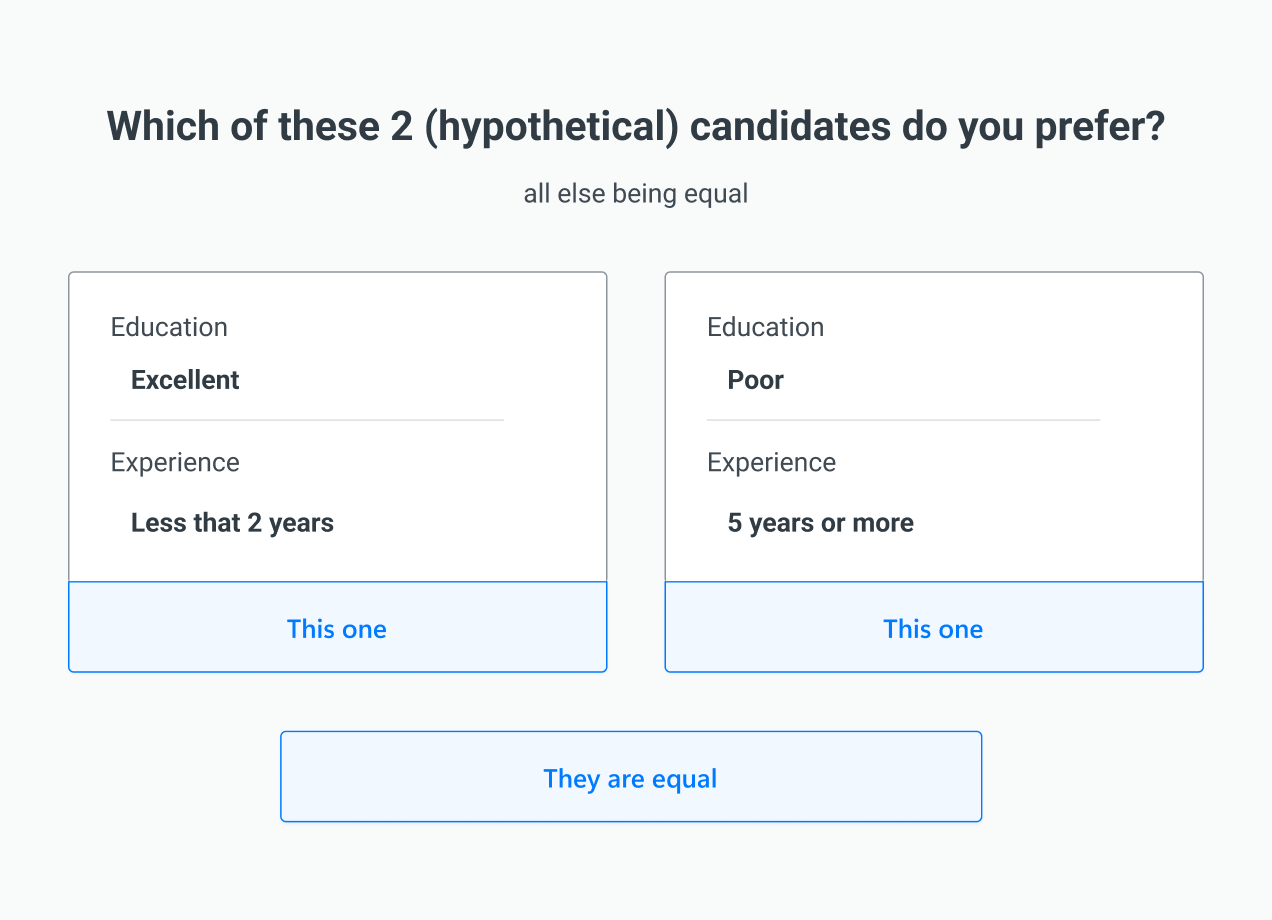
1000minds
1000minds is a web application for decision-making and conjoint analysis supplied by 1000minds Ltd since 2003. 1000minds implements the PAPRIKA method to help organizations, individuals and groups to make decisions based on considering multiple objectives or criteria (i.e. multiple-criteria decision analysis). 1000minds conjoint analysis involves surveying people about their preferences with respect to the relative importance of features or attributes characterizing products or other objects of interest. In addition, a free consumer-oriented web application based on 1000minds technology to help with 'everyday' decision-making, known as MeenyMo, was released in 2016. Overview 1000minds helps with decisions that involve ranking, prioritizing or choosing between alternatives when multiple objectives or criteria need to be considered simultaneously (i.e. multi-criteria decision making). Depending on the application, budgets or other scarce resources can also be allocated across compe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MCDA
Multiple-criteria decision-making (MCDM) or multiple-criteria decision analysis (MCDA) is a sub-discipline of operations research that explicitly evaluates multiple conflicting criteria in decision making (both in daily life and in settings such as business, government and medicine). It is also known as known as multi-attribute decision making (MADM), multiple attribute utility theory, multiple attribute value theory, multiple attribute preference theory, and multi-objective decision analysis. Conflicting criteria are typical in evaluating options: cost or price is usually one of the main criteria, and some measure of quality is typically another criterion, easily in conflict with the cost. In purchasing a car, cost, comfort, safety, and fuel economy may be some of the main criteria we consider – it is unusual that the cheapest car is the most comfortable and the safest one. In portfolio management, managers are interested in getting high returns while simultaneously reduc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sensitivity Analysis
Sensitivity analysis is the study of how the uncertainty in the output of a mathematical model or system (numerical or otherwise) can be divided and allocated to different sources of uncertainty in its inputs. This involves estimating sensitivity indices that quantify the influence of an input or group of inputs on the output. A related practice is uncertainty analysis, which has a greater focus on uncertainty quantification and propagation of uncertainty; ideally, uncertainty and sensitivity analysis should be run in tandem. Motivation A mathematical model (for example in biology, climate change, economics, renewable energy, agronomy...) can be highly complex, and as a result, its relationships between inputs and outputs may be faultily understood. In such cases, the model can be viewed as a black box, i.e. the output is an "opaque" function of its inputs. Quite often, some or all of the model inputs are subject to sources of uncertainty, including errors of measurement, er ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |