|
Cytoskeletal Drugs
Cytoskeletal drugs are small molecules that interact with actin or tubulin. These drugs can act on the cytoskeletal components within a cell in three main ways. Some cytoskeletal drugs stabilize a component of the cytoskeleton, such as taxol, which stabilizes microtubules, or Phalloidin, which stabilizes actin filaments. Others, such as Cytochalasin D, bind to actin monomers and prevent them from polymerizing into filaments. Drugs such as demecolcine act by enhancing the depolymerisation of already formed microtubules. Some of these drugs have multiple effects on the cytoskeleton: for example, Latrunculin both prevents actin polymerization as well as enhancing its rate of depolymerization. Typically the microtubule targeting drugs can be found in the clinic where they are used therapeutically in the treatment of some forms of cancer. As a result of the lack of specificity for specific type of actin (i.e. cannot distinguish between cardiac, smooth muscle, muscle and cytoskeletal for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Actin
Actin is a family of globular multi-functional proteins that form microfilaments in the cytoskeleton, and the thin filaments in muscle fibrils. It is found in essentially all eukaryotic cells, where it may be present at a concentration of over 100 μM; its mass is roughly 42 kDa, with a diameter of 4 to 7 nm. An actin protein is the monomeric subunit of two types of filaments in cells: microfilaments, one of the three major components of the cytoskeleton, and thin filaments, part of the contractile apparatus in muscle cells. It can be present as either a free monomer called G-actin (globular) or as part of a linear polymer microfilament called F-actin (filamentous), both of which are essential for such important cellular functions as the mobility and contraction of cells during cell division. Actin participates in many important cellular processes, including muscle contraction, cell motility, cell division and cytokinesis, vesicle and organelle movement, cell sign ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tubulin
Tubulin in molecular biology can refer either to the tubulin protein superfamily of globular proteins, or one of the member proteins of that superfamily. α- and β-tubulins polymerize into microtubules, a major component of the eukaryotic cytoskeleton. Microtubules function in many essential cellular processes, including mitosis. Tubulin-binding drugs kill cancerous cells by inhibiting microtubule dynamics, which are required for DNA segregation and therefore cell division. In eukaryotes, there are six members of the tubulin superfamily, although not all are present in all species.Turk E, Wills AA, Kwon T, Sedzinski J, Wallingford JB, Stearns "Zeta-Tubulin Is a Member of a Conserved Tubulin Module and Is a Component of the Centriolar Basal Foot in Multiciliated Cells"Current Biology (2015) 25:2177-2183. Both α and β tubulins have a mass of around 50 kDa and are thus in a similar range compared to actin (with a mass of ~42 kDa). In contrast, tubulin polymers (microtubules) te ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
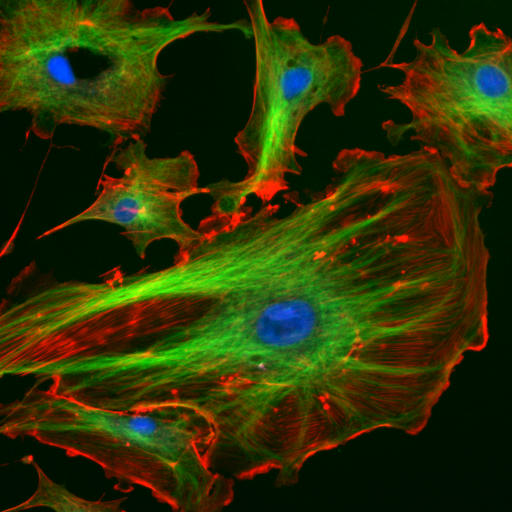
Phalloidin
Phalloidin belongs to a class of toxins called phallotoxins, which are found in the death cap mushroom ''(Amanita phalloides)''. It is a rigid bicyclic heptapeptide that is lethal after a few days when injected into the bloodstream. The major symptom of phalloidin poisoning is acute hunger due to the destruction of liver cells. It functions by binding and stabilizing filamentous actin (F-actin) and effectively prevents the depolymerization of actin fibers. Due to its tight and selective binding to F-actin, derivatives of phalloidin containing fluorescent tags are used widely in microscopy to visualize F-actin in biomedical research. Discovery and background Phalloidin was one of the first cyclic peptides to be discovered. It was isolated from the death cap mushroom and crystallized by Feodor Lynen and Ulrich WielandG. Semenza, E.C. Slater, R. JaenickeSelected Topics in the History of Biochemistry. Personal Recollections- Google books in 1937. Its structure is unusual in that it co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cytochalasin D
Cytochalasin D is a member of the class of mycotoxins known as cytochalasins. Cytochalasin D is an alkaloid produced by Helminthosporium and other molds. Cytochalasin D is a cell-permeable and potent inhibitor of actin polymerization. It disrupts actin microfilaments and activates the p53-dependent pathways causing arrest of the cell cycle at the G1-S transition. It is believed to bind to F-actin Actin is a family of globular multi-functional proteins that form microfilaments in the cytoskeleton, and the thin filaments in muscle fibrils. It is found in essentially all eukaryotic cells, where it may be present at a concentration of ov ... polymer and prevent polymerization of actin monomers. References External links * {{organic-compound-stub Mycotoxins Actin inhibitors Acetate esters Vinylidene compounds ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phalloidin Staining Of Actin Filaments
Phalloidin belongs to a class of toxins called phallotoxins, which are found in the death cap mushroom ''(Amanita phalloides)''. It is a rigid bicyclic heptapeptide that is lethal after a few days when injected into the bloodstream. The major symptom of phalloidin poisoning is acute hunger due to the destruction of liver cells. It functions by binding and stabilizing filamentous actin (F-actin) and effectively prevents the depolymerization of actin fibers. Due to its tight and selective binding to F-actin, derivatives of phalloidin containing fluorescent tags are used widely in microscopy to visualize F-actin in biomedical research. Discovery and background Phalloidin was one of the first cyclic peptides to be discovered. It was isolated from the death cap mushroom and crystallized by Feodor Lynen and Ulrich WielandG. Semenza, E.C. Slater, R. JaenickeSelected Topics in the History of Biochemistry. Personal Recollections- Google books in 1937. Its structure is unusual in that it co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Colchicine
Colchicine is a medication used to treat gout and Behçet's disease. In gout, it is less preferred to NSAIDs or steroids. Other uses for colchicine include the management of pericarditis and familial Mediterranean fever. Colchicine is taken by mouth. Colchicine has a narrow therapeutic index, so overdosing is a significant risk. Common side effects of colchicine include gastrointestinal upset, particularly at high doses. Severe side effects may include low blood cells and rhabdomyolysis, and the medication can be deadly in overdose. Whether colchicine is safe for use during pregnancy is unclear, but its use during breastfeeding appears to be safe. Colchicine works by decreasing inflammation via multiple mechanisms. Colchicine, in the form of the autumn crocus (''Colchicum autumnale''), has been used as early as 1500 BC to treat joint swelling. It was approved for medical use in the United States in 1961. It is available as a generic medication. In 2020, it was the 241st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cytochalasins
Cytochalasins are fungal metabolites that have the ability to bind to actin filaments and block polymerization and the elongation of actin. As a result of the inhibition of actin polymerization, cytochalasins can change cellular morphology, inhibit cellular processes such as cell division, and even cause cells to undergo apoptosis. Cytochalasins have the ability to permeate cell membranes, prevent cellular translocation and cause cells to enucleate. Cytochalasins can also have an effect on other aspects of biological processes unrelated to actin polymerization. For example, cytochalasin A and cytochalasin B can also inhibit the transport of monosaccharides across the cell membrane, cytochalasin H has been found to regulate plant growth, cytochalasin D inhibits protein synthesis and cytochalasin E prevents angiogenesis. Binding to actin filaments Cytochalasins are known to bind to the barbed, fast growing plus ends of microfilaments, which then blocks both the assembly and disasse ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Demecolcine
Demecolcine (INN; also known as colcemid) is a drug used in chemotherapy. It is closely related to the natural alkaloid colchicine with the replacement of the acetyl group on the amino moiety with methyl, but it is less toxic. It depolymerises microtubules and limits microtubule formation (inactivates spindle fibre formation), thus arresting cells in metaphase and allowing cell harvest and karyotyping to be performed. During cell division, demecolcine inhibits mitosis at metaphase by inhibiting spindle formation. Medically, demecolcine has been used to improve the results of cancer radiotherapy by synchronising tumour cells at metaphase, the radiosensitive stage of the cell cycle. In animal cloning procedures, demecolcine makes an ovum eject its nucleus, creating space for insertion of a new nucleus. Mechanism of action Demecolcine is a microtubule-depolymerizing drug like vinblastine. It acts by two distinct mechanisms. At very low concentration it binds to microtubule plus e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latrunculin
The latrunculins are a family of natural products and toxins produced by certain sponges, including genus '' Latrunculia'' and '' Negombata'', whence the name is derived. It binds actin monomers near the nucleotide binding cleft with 1:1 stoichiometry and prevents them from polymerizing. Administered ''in vivo'', this effect results in disruption of the actin filaments of the cytoskeleton, and allows visualization of the corresponding changes made to the cellular processes. This property is similar to that of cytochalasin, but has a narrow effective concentration range. Latrunculin has been used to great effect in the discovery of cadherin distribution regulation and has potential medical applications. Latrunculin A, a type of the toxin, was found to be able to make reversible morphological changes to mammalian cells by disrupting the actin network. Latrunculin A: Target and functions Gelsolin - Latrunculin A causes end- blocking; this protein binds to the barbed sides of the act ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nocodazole
Nocodazole is an antineoplastic agent which exerts its effect in cells by interfering with the polymerization of microtubules. Microtubules are one type of fibre which constitutes the cytoskeleton, and the dynamic microtubule network has several important roles in the cell, including vesicular transport, forming the mitotic spindle and in cytokinesis. Several drugs including vincristine and colcemid are similar to nocodazole in that they interfere with microtubule polymerization. Nocodazole has been shown to decrease the oncogenic potential of cancer cells via another microtubules-independent mechanisms. Nocodazole stimulates the expression of LATS2 which potently inhibits the Wnt signaling pathway by abrogating the interaction between the Wnt-dependent transcriptional co-factors beta-catenin and BCL9. It is related to mebendazole by replacement of the left most benzene ring by thiophene. Use in cell biology research As nocodazole affects the cytoskeleton, it is often used in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paclitaxel
Paclitaxel (PTX), sold under the brand name Taxol among others, is a chemotherapy medication used to treat a number of types of cancer. This includes ovarian cancer, esophageal cancer, breast cancer, lung cancer, Kaposi's sarcoma, cervical cancer, and pancreatic cancer. It is administered by intravenous injection. There is also an albumin-bound formulation. Common side effects include hair loss, bone marrow suppression, numbness, allergic reactions, muscle pains, and diarrhea. Other serious side effects include heart problems, increased risk of infection, and lung inflammation. There are concerns that use during pregnancy may cause birth defects. Paclitaxel is in the taxane family of medications. It works by interference with the normal function of microtubules during cell division. Paclitaxel was first isolated in 1971 from the Pacific yew and approved for medical use in 1993. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. It has been made from precu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vinblastine
Vinblastine (VBL), sold under the brand name Velban among others, is a chemotherapy medication, typically used with other medications, to treat a number of types of cancer. This includes Hodgkin's lymphoma, non-small cell lung cancer, bladder cancer, brain cancer, melanoma, and testicular cancer. It is given by injection into a vein. Most people experience some side effects. Commonly it causes a change in sensation, constipation, weakness, loss of appetite, and headaches. Severe side effects include low blood cell counts and shortness of breath. It should not be given to people who have a current bacterial infection. Use during pregnancy will likely harm the baby. Vinblastine works by blocking cell division. Vinblastine was isolated in 1958. An example of a natural herbal remedy that has since been developed into a conventional medicine, vinblastine was originally obtained from the Madagascar periwinkle. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |